
If I were a gambling man, I would bet on the notion that our global energy future must be multifaceted. Through a gradual transition toward renewable energies, several technologies have gained significant momentum in recent years including solar, wind, and geothermal. While solar and wind are familiar to most, a point of confusion regarding geothermal technology is that there are actually two different types - 'deep' and 'shallow' geothermal. This is discussed in more detail in an introductory post on the topic.
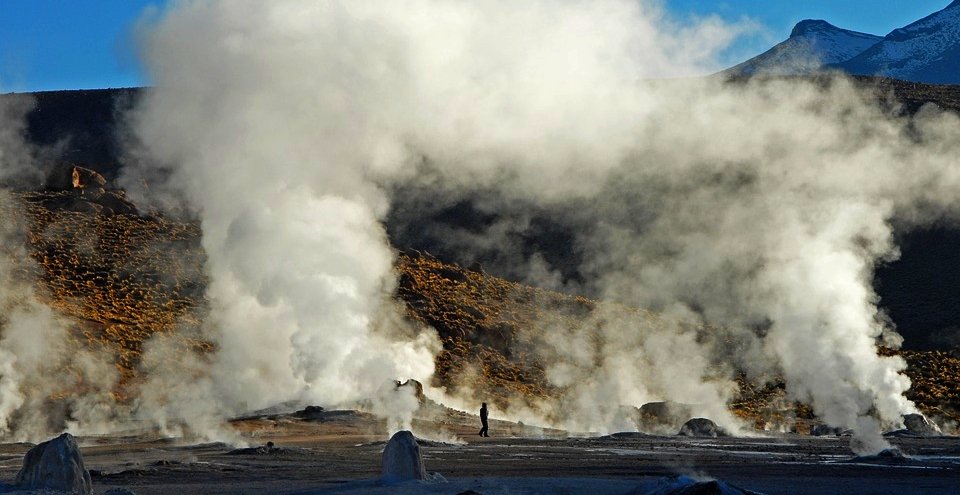

Boiling hot springs like these in the Chilean Andes are a good indicator of deep geothermal energy! Modified from Source under CC0
Deep geothermal is likely what most people associate with the word concept of geothermal energy. It refers to the practice of drilling deep vertical wells in areas where molten rock is relatively close to the surface such as Iceland or Hawaii. The wells exploit this heat to boil water into steam which is used for the generation of electricity.
Shallow geothermal (the focus of this article) is quite different, working on the principle of heat transfer and storage to cool buildings in the summer and warm them in the winter. An initial look at shallow geothermal heat exchange is provided in the first part of this series, but here is the concept summarized in a couple of simple animations animation:
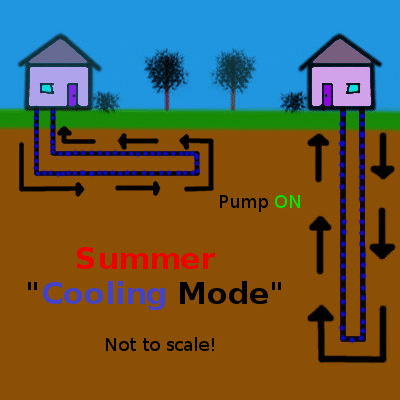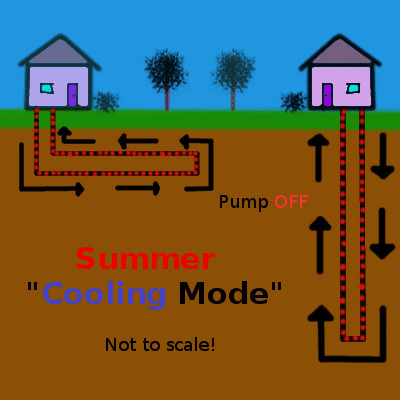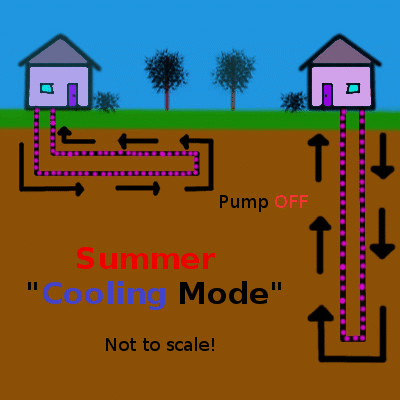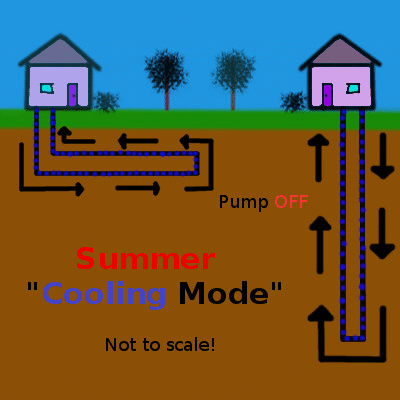
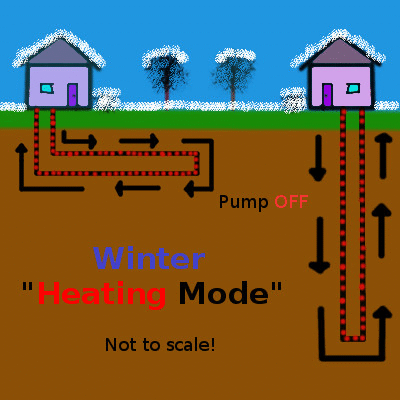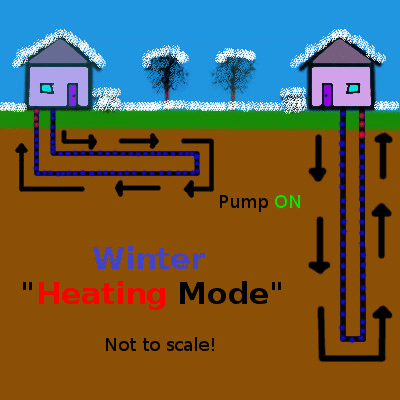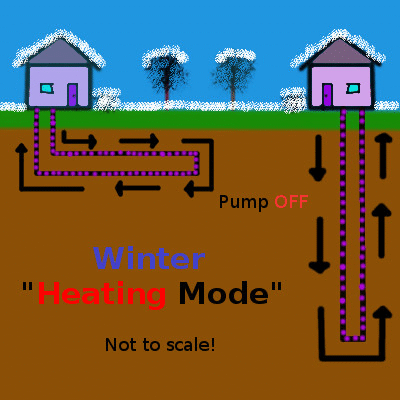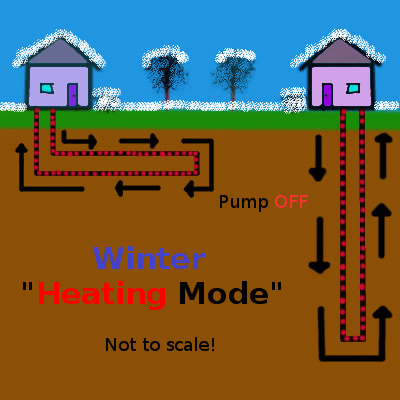
Heat, shown in red, is pumped into the earth during the summer and extracted during the winter. Animation by the author.
Significant Variables
One of the biggest hurdles preventing the widespread adoption of shallow geothermal is improper system sizing and design. A dizzying complex of of variables and unknowns converge and conspire to produce one of two stereotypical extremes - a system that is vastly larger than necessary for the space being conditioned and therefore slow to recoup the installation expense, or a system that is so undersized or inefficient that it hardly even works. In this article we will touch on some of the major design considerations that can greatly impact the overall success of a system and then brainstorm on how to optimize system design!House Size

No two houses are the same in Copenhagen. I doubt they have much lot space for a horizontal system, but perhaps a vertical one? Modified from Source under CC0
The total conditioned space in a house is perhaps the single most important factor in determining the appropriate shallow geothermal system arrangement. For extremely small spaces, the expense of installing a system might take up to a decade to recoup in utility savings. For large buildings, the size of the system must also be proportionally scaled up at increasing initial expense and greater overall risk. One of the lowest risk highest reward cases for shallow geothermal is the large suburban sprawl homes with oversized lots.
House Efficiency

This one is definitely a fixer-upper! Modified from Source under CC0
It should go without saying that before a geothermal system is installed, money should first be invested in improving the thermal efficiency of a house. After all, it is heat (or lack thereof) that we are trying to control with shallow geothermal or any other type of HVAC system. The more insulated and air-tight a house or building is, the less work the system will need to do. This decreases overall system size and cost, improving efficiency and payback time.
Today there are more options for insulating houses than ever before, with greatly varying levels of efficiency. Some of the most trusted technologies include fiberglass batting, extruded or expanded rigid foam board, structural insulated panels (SIPs), vacuum insulated panels (VIPs), open and closed cell spray foam, aerogel, bails of straw, and many others! In general, the more efficient the more costly, but this is always improving with technology!
Usage Requirements

Little apartments made of ticky-tacky. Modified from Source under CC0
Another consideration in determining the size requirements of a system is user demand. How many people will be occupying the building? Are the occupants of the structure willing to wear a jacket in the winter or open the windows and use fans during cool summer evenings? Is the building a restaurant where hot ovens will be producing excess heat? Is it an apartment building where each unit has their own notion of what is the ideal temperature? Each situation offers unique challenges that can make it difficult to accurately predict future usage levels.
Local Climate

If you live in a climate like this, you probably do not need a geothermal system. Nor would one work very well. Modified from Source under CC0
It is important to keep in mind that geothermal heat exchange systems exploit differences in temperature between the earth and the ambient air to make a space more comfortable. These systems will therefore work best in regions with larger temperature differentials. The temperature of the ground approximates the average air temperature over the course of an entire year. If it is a comfortable 72 degrees all year at your beach house in Hawaii, then geothermal heat pumps are pretty much pointless. However, if the winters are cold and the summers are hot where you live, you should really think about storing that summer heat for future use!
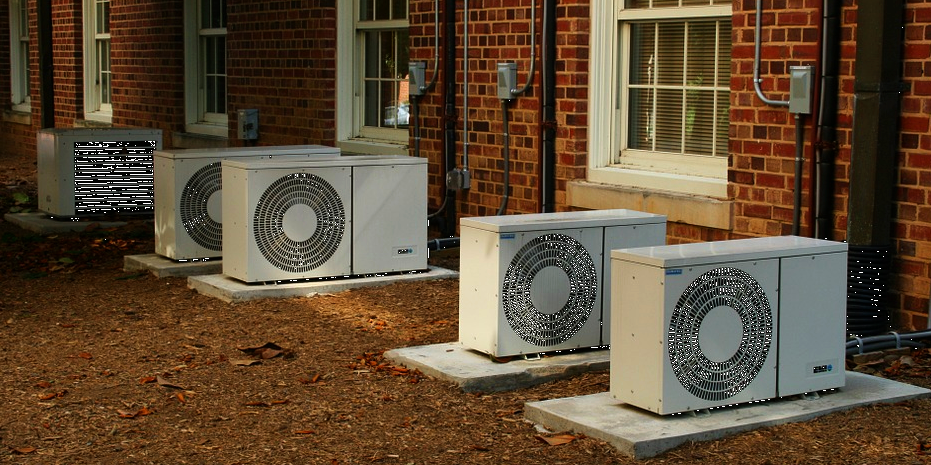
Heat Pumps

There are a healthy number of heat pumps to choose from! Modified from Source under CC0
Heat pumps come in all shapes and sizes, literally! Above are just a few examples of heat pumps from a single brand. A variety of options and types make it easier to fit a house with a heat pump system regardless of the available space. Most pumps require electricity for operation, so it may be desirable to pair a geothermal system with a solar array or wind turbines to power the heat pump. The best size and type of pump for a given situation depends on several factors, including the overall volume of air space to be conditioned, the space where the heat pump will be installed, and the local temperature extremes.
Heat Exchanger
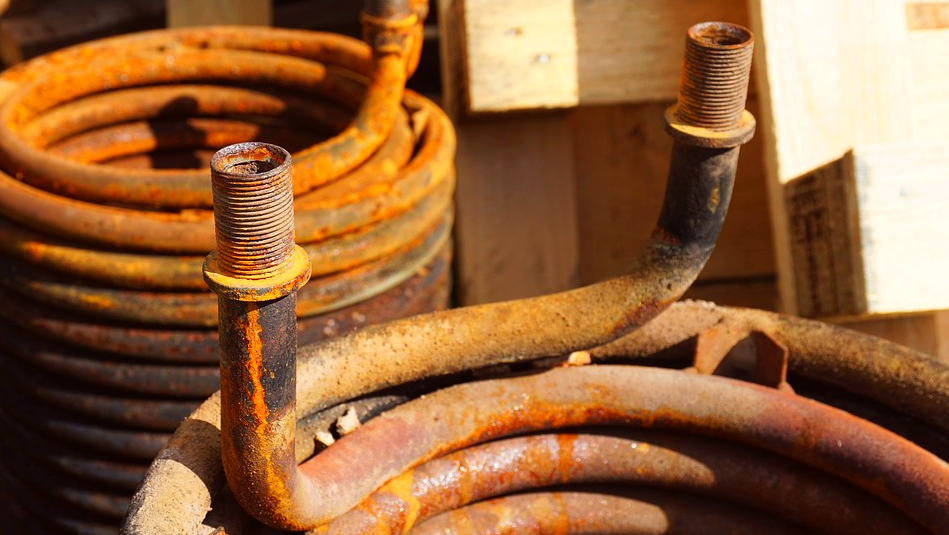

Striking the balance between conductivity and corrosivity. Modified from Source under CC0
The material through which heat is transferred to the earth is known as the heat exchanger. Because the heat exchangers in a geothermal system are covered in soil, bedrock, and/or groundwater, they are subject to both physical and chemical abrasion and erosion with time. For this reason, most geothermal systems are designed using high-density polyethylene tubing because it is relatively strong and stable while still having a moderate thermal conductivity (0.45 W·m−1·K−1 {or W/mK}) that is comparable to water (0.59 W/mK).
There are many more thermally conductive materials such as copper (400 W/mK) that are used in some heat exchange systems, but the applicability to geothermal heat exchange loops is so far limited. Copper is relatively expensive and can easily be corroded by sulphur and other chemical compounds found in groundwater, leading to reduced efficiency and the eventual need for a costly replacement. Perhaps the solution is improving upon a stable and conductive material such as graphene that can coat and protect the copper, or embedding more conductive material into the polyethylene tubing?
Loop Size

The slinky method: a common method of making shallow geothermal systems spatially 'dense'. Modified from Source under Public Domain
When installing geothermal systems, one of the most difficult questions to correctly answer is how long to make the 'loop', or the part of the geothermal system where heat is exchanged with the earth. The factors discussed above combine to determine the possible heating and cooling demands of a structure, and this is used as a rough basis for the system size in a number of software packages. Ultimately, the appropriate system size depends on much more than the demands of the structure. To more accurately predict the required length of a geothermal trench, we need to think about the soil...
Mineral Content

It turns out that not all dirt is created equal. Modified from Source under CC0
The soils and rocks that make up the surface of Earth are not all created thermodynamically equal. The composition of a given soil has a profound influence on how well that material will transfer heat. Some of the most common components of rocks and soils include quartz, plagioclase, iron, clay minerals, calcium, carbon, etc. While clay-rich soils tend to retain water better than well-drained soils in drought conditions, clay minerals and organic matter are less thermally conductive than quartz and most metals. In some circumstances, it may be worthwhile to replace or supplement a soil with more desirable minerals for improved performance.
Grain Size
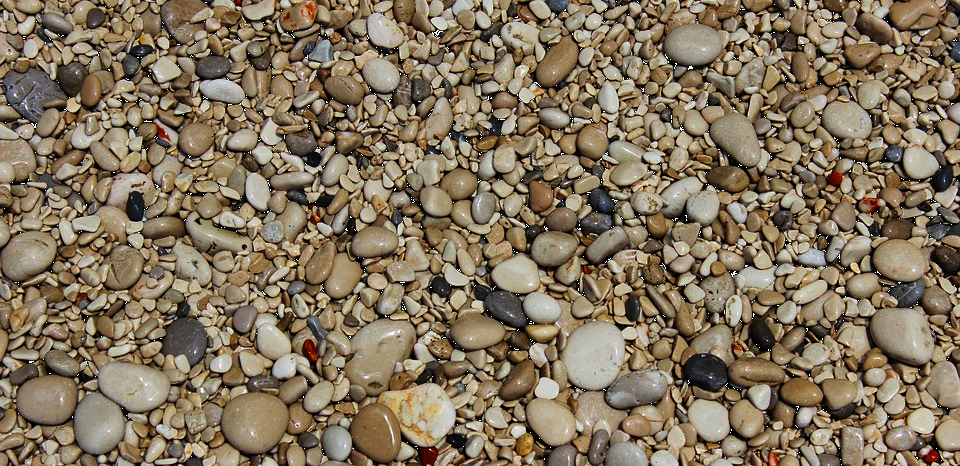

In soil science, it seems that size does matter. Modified from Source under CC0
A fundamental property of soil that can easily be determined is that of grain size. While coarse grained sediment like gravel tends to increase the hydraulic conductivity of a sediment (the ease with which water can flow through), the increased void space associated with larger clasts leads to a lower overall thermal conductivity for the soil.
One of the best examples of a sediment with a high thermal conductivity is Ottawa Sand, which has a very regular and fine size, a rounded shape, and boasts an extremely pure silica/quartz content. You might recall this lovely sand from a previous article on the St. Peter Sandstone. Packed Ottawa sand has a very low void space and high grain-to-grain connectivity, yielding a thermal conductivity up to 4 W/mK versus gravel at 0.7 W/mK. Clay-rich soils have an extremely fine grain size, but they often swell and shrink depending on moisture content and this can hinder the connection between the heat exchange loop and the soil.
Bulk Density

Dirt devoid of voids will move heat best! Modified from Source under CC0
As alluded to in the previous section, the presence of void space in soil tends to lower the thermal conductivity and accordingly decrease overall efficiency. For this reason, soils with a higher bulk density (less void space) are more ideal for geothermal installations. No matter how compacted a soil is, there will always be some voids; when sediment has spaces that are not filled by mineral grains, these spaces are typically filled with one of two substances - water or air. Air has an extremely low thermal conductivity (0.0262 W/mK) and a high thermal diffusivity (the ease with which heat is dissipated). Water is the opposite. Can you guess which one is better for geothermal systems?
Moisture Content

Water, along with air, are the two universal unconsolidated matrix ingredients. Modified from Source under CC0
The moisture content of a soil (the degree of saturation) has a profound influence on thermal conductivity. Because water is better at conducting heat than air, a saturated soil will be much more effective at moving heat toward or away from a ground source heat exchanger loop. Keep in mind that minerals like quartz are more ideal than water for transferring heat and thus increasing bulk density is a logical first step. Once the amount of void space is reduced as much as possible, keeping those voids filled with water will help to ensure that the geothermal system performs optimally.
Parting Thoughts
The Idealized System
In a perfect world, every geothermal heat exchange system would be installed to maximize efficiency and minimize cost. The world is far from perfect, but this does not mean that there is no merit in visualizing perfection and striving towards perpetual improvement.So what does this mean?
- Geothermal heat pump systems are not ideal for all locations. Ensure that you live in the appropriate climate and have the necessary space and hydrology / geology before investing in a system.
- Make improvements to the insulation of the structure before investing in HVAC to avoid designing a system that is not powerful enough.
- Choose a heat pump that is the appropriate size for the space that needs to be conditioned.
- For the exchange loop, consider a more conductive material like coated copper.
- When installing a horizontal trench system, pay close attention to the soil type. Consider adding quartz, iron, or other thermally conductive minerals if they are not already present.
- When possible, install the system in a low-lying area that is beneath the water table to ensure that the soil remains saturated for maximum thermal conductivity. In cases where this is not possible, consider installing an impermeable liner around the edges of the trench and add water from the surface during droughts.
- Ensure a good connection between the heat exchanger loop and the earth by packing the soil while backfilling to increase bulk density. This will improve the overall efficiency of the system through enhanced thermal conductivity.
External References
For many years I contemplated and experimented with the optimization of shallow geothermal heat exchange by way of both published and unpublished grant-funded research projects. Much of the information that I draw upon in these articles is based on the knowledge and understanding that I acquired during this time and cannot always be directly referenced. See the external references and links embedded within the text for more information on the subjects being discussed. All photos are credited to their original sources except the cover photo of (deep) geothermal geysers in Yellowstone National Park modified from Source under CC0
