This is the most type of bearberry, known as Arctostaphylos uva-ursi or just uva ursi, and also kinnikinick (for smoking) and sandberry (easily grows in sand). Like the constellations ursa minor and major, the name ursa refers to a bear in Latin. Uva-ursi means "grape of the bear", and the generic reference of Arctostaphylos means "bear-grape" in Greek.
The name comes from bears liking the edible but rather tasteless red fruits.

Photo by @krnel
Key Points
- bears like the red fruits, safe for humans to eat as well
- leaves used in folk medicine to treat urinary infections
- common to upper North America
- smoked by some Amerindian tribes

wikimedia
History
It's long been used in Norther American Native as part of a smoking herb mix called kinnikinnick ("smoking mixture") in Algonquin used for religious ceremonies. The Western First Nation use it most along with other herbs such as tobacco. The Blackfeet Nation used it as food.
Other names are Arberry, Arbousier, Arbousier Traînant, Arbutus uva-ursi, Arctostaphylos uva-ursi, Bearberry, Beargrape, Bearsgrape, Bussserole, Common Bearberry, Faux Buis, Hogberry, Kinnikinnik, Manzanita, Mountain Box, Mountain Cranberry, Petit Buis, Ptarmigan Berry, Raisin de Renard, Raisin d'Ours, Raisin d'Ours Commun, Red Bearberry, Redberry, Rockberry, Sagackhomi, Sandberry, Uva del Oso, Uva Ursi Extract, Uvae Ursi Folium.
Where is it found?
The common bearberry grows in the norther parts of the northern hemisphere, and some high latitudes further south. It grows in Europe from Iceland to Norway and down to Greece. In Asia it's from the Siberian arctic to Turkey and the Levant. In North America from Alaska to Greenland and down to California across to the Appalachian Mountains.
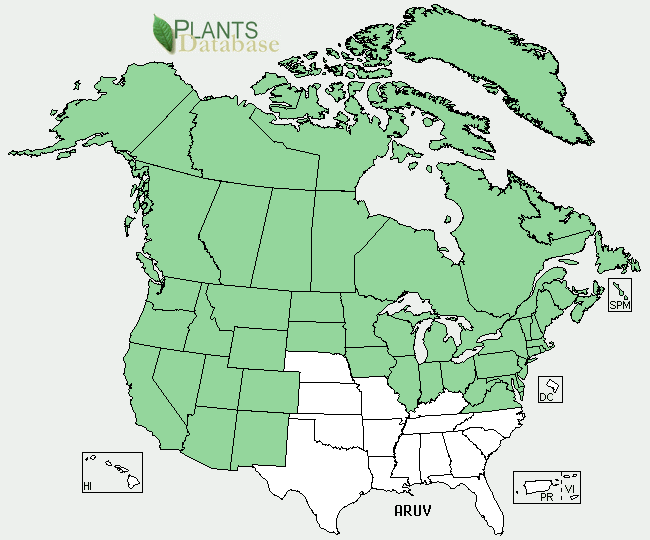
USDA public domain
What's it used for?
It's a useful ground cover that helps to control erosion.
No clinical trials exist to prove the effectiveness of using it as a medicine. But traditional and folk medicine use the leaves and stems to make teas, extract and tablets.
The stem has been used by some Native American tribes to prevent miscarriages and aid in recovery after childbirth. The leaves have an antibacterial chemical called hydroquinones. A dehydrated salve can be made to treat canker sores, sore gums, burns, and minor cuts.
A common use has been to reduce bacteria in the urine, such as for urinary tract disorders:
including infections of the kidney, bladder, and urethra; swelling (inflammation) of the urinary tract; increased urination; painful urination; and urine that contains excess uric acid or other acids. Uva ursi is also used for constipation and a lung condition called bronchitis.
Are there any risks?
The leave contains contain glycoside arbutin that becomes a liver toxin when metabolized. It's considered safe to take orally for up to a month, but in large doses or long-term use may cause nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, back pain, tinnitus, liver damage, eye problems, breathing problems, convulsions, and death.
Pregnant women should avoid it as it can induce start labor. Avoid for breast feeding and for children.
References:
Thank you for your time and attention. Peace.
If you appreciate and value the content, please consider: Upvoting, Sharing or Reblogging below.
 me for more content to come!
me for more content to come!
My goal is to share knowledge, truth and moral understanding in order to help change the world for the better. If you appreciate and value what I do, please consider supporting me as a Steem Witness by voting for me at the bottom of the Witness page.

