Yesterday, October 2nd, 2017, a great scientific breakthrough was well awarded a Nobel Prize in the field of "physiology or medicine", and particularly to three chronobiology researchers: Jeffrey Hall, Michael Young, and Michael Rosbash.
What is Chronobiology?
A bit of a background at first.
Chronobiology is quite a young science that has been gaining popularity for the last 30 years. While it roots back to the 18th century, with astronomer Jean Jacques d’Ortous de Mairan and his work on the circadian rhythm of mimosa leaves, as well as following work by several other scientists including Charles Darwin reporting similar rhythmic findings, yet research took a bigger turn on the 20th century and on words, till yesterday's Nobel Prize!
As defined on the official site (reference 2 below):
Chronobiology is a field of biology that studies how our body’s natural cycles—mental, physical and emotional—are affected by solar and lunar rhythms. For example, the circadian rhythm, a 24-hour cycle of physiological processes that happen throughout the human body, is a vital cycle in the study of chronobiology.
Chronobiology refers to the day-night cycle that affects the human organism when the earth rotates
Basically chronobiology involves the study of different cycles or rythms, the most common of which are:
- Infradian Rhythms: which are rhythms that last over 24 hours and which would repeat in periods over a day. Some examples include bird migration, reproduction cycles of certain animals or plants, and human menstrual cycle...
- Ultradian Rhythms: which are ones that last under 24 hours. Those include REM sleep, food ingestion, 3-hour growth hormone cycle, or even tidal rhythms (around 12.4 hours)...
- Circadian Rhythms: which last approximately 24 hours, including human wake/sleep cycle, or the plant leaf movements.
The circadian rhythms constitute the area that mostly and directly affects humans, as it helps regulate sleep patterns, blood pressure, body temperature, feeding behavior, among other activities, and is the area of the recent findings and hence the Nobel Prize.
You can see one example below of an illustration of how our circardian rhythm / biological clock reflects on our daily activities. A fresher image can be found under reference 2 below, i just didn't copy it for potential copyright issues.
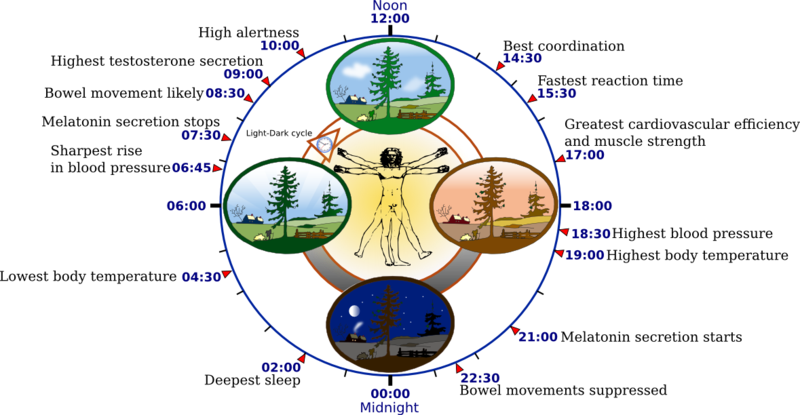
So what is the big news about?
For the first time, the 3 researchers were able to dig inside the biological clock and explain the "how" in the animals, plants and humans adaptation to the Earth's rotation.
In fact, they conducted their research using Drosophila melanogaster - the common fruit fly, which is a reliable genetic proxy to humans, and were able to isolate the gene responsible for controlling the normal daily biological clock and its internal workings.
In further details, this gene was found to encode a protein stacking up over the night, and then just like a sand clock, would decrease throughout the day. And then it would auto-repeat the same cycle of build up and then degradation, which is why the clock was termed as self-sustaining. And it is throughout this build up and release that the fruit fly was able to know when it should be awake, and when to sleep.
A similar pattern has been applied to cells, and through identifying additional protein components in this system, were able to apply this to multi-cellular organisms.
And why is it big news?
Due to its large influence over our daily lives, understanding how the biological clock operates is of key value to allow us to resolve and possibly control manifestations of biological clock into health, among other problems we face on a day to day basis. This includes learning further about morning v/s evening persons, coping with jet lags, as well as how much chronic misalignment with our biological clock can affect us generally, and particularly on blood pressure, hormone levels, metabolism, and any other health issues.
Thank you for reading through!
References:
- http://www.iflscience.com/health-and-medicine/three-americans-nobel-prize-physiology-decoding-lifes-biological-clock/
- https://www.chronobiology.com/
- https://www.chronobiology.com/circadian-rhythm-discoveries-win-nobel-prize/
- https://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/2017/press.html
Photo Credits:
A Proud member of MAP - Minnows Accelerator Project
MAP is a growing community helping talented minnows accelerate their growth on Steemit.
To join, check out the link at the home page of @accelerator account
One of my articles is featured in the MAP28 Contest "Six of the Best".
If you'd like to support me, please go to this post Minnow Accelerator Project MAP27 "Six of the Best" Contest. @accelerator/six-of-the-best-from-our-new-mapsters-map28-minnow-contest
And upvote my comment towards the bottom of the page, or just type the word "VOTE" under my comment.
Prior Posts:
If you enjoyed this post, you might want to check out some of my earlier posts:
- Misconception #9: Color of Mucus Determines if you Need Antibiotics (And Some Drs Still Believe It)
- Daily Mysteries #4: What Causes Left Handedness ? (New Study Findings)
- Daily Mysteries #3: Are you Missing a Muscle?
- Are Viruses .. Alive?
- Daily Mysteries #2: Why do we dream?
- Astro News: Gravitational Waves Detected for the 4th Time by 3 Observatories
- Daily Mysteries #1: Why do we often forget what we just left the room to do?
- Misconception #8: Caesarian C-Section Is Named After Julius Caesar
- Misconception #7: Nero Set Rome On Fire And Watched It Burn
- Misconception #6: Low Voltage Shocks Are Not Dangerous
My posts aim to be contribute to the following projects:
- #steemSTEM / @steemstem - A project to increase both the quality as well as visibility of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (and Health).
- #steemiteducation / @steemiteducation - A project to promote high quality educational posts on Steemit.
