
Background
Finance(or Financial Health) is the very basis of our survival regardless of which ecosystem and which generation we belong to. That is why the financial use-cases are always powerful by default. The traditional financial system does not offer easy access to all. One has to go through the complex legal requirements and compliances. It does not stop here; if even if you gain access to the traditional financial system they will restrict you by imposing limits on financial transactions.
Not to mention you always have to trust a centralized entity(generally Banks) when you carry out a financial transaction. Blockchain (Bitcoin, being the first over to be powered with Blockchain technology) solves this problem interface of the traditional system by eliminating a third party, a centralized entity.
A financial transaction with Blockchain as the underlying technology is trust-less, p2p transaction is possible. It is completely decentralized, one does not have to rely upon a bank. As it is decentralized it ensures 100% up-time, there is no down-time and server maintenance like a Bank, because with Blockchain technology at any given time, not all the nodes will go down.
Easy and free access to the financial system is being ensured with the advent of Blockchain technology since 2009. It does not limit you on how much you want to send, it does not levy unnecessary fees when you send money across the globe. The best thing is that the fee is reasonable(not like percentage of what you are sending)--cost-effective, time-effective(as you can easily & quickly make a transfer abroad as compared to a Bank).

What inherent characteristics of Blockchain make a financial transaction better than the traditional financial system(Banks)
(1)Not possible to create a counterfeit token
The counterfeit token is impossible in Blockchain as the protocol will prevent any such attempt. If at all someone tries to counterfeit a token, the Blockchain will branch, and by principles, the longest chain is the valid chain. The valid transaction will always have the Blockchain attached to it.
Further, the protocol tracks every transaction, every single token that is being minted through the Blockchain algorithm.
So it is way better than the physical cash (of the traditional financial system).
(2)Time-stamp
Time-stamping in Blockchain guarantees that the data that is included in the Block is not previously created, which means unspent-before. Further, the consensus rule in any Blockchain does not recognize the time-stamp of a block too far from the past, that is why each timestamp includes the immediate previous timestamp.
(3) 100% Up time
There is no such downtime for Blockchain. Being decentralized in nature, a Blockchain is distributed over thousands of nodes, also distributed geographically. So it is not possible that all the nodes will go down at any given time.
(4) Immutability & Append only
The Blocks are produced in Blockchain through a consensus mechanism (defined for a particular blockchain), The Blocks in themselves are a chain of blocks as each block contains the hash of its own as well as the previous block. So "an ordered Blockchain". Further, it is append-only. You can only add a block. You can not erase a Block. Therefore the data that is recorded in a Blockchain is immutable.
This makes a financial transaction with Blockchain as underlying technology more transparent, fair for either party under consideration, whereas in a traditional financial system, it is quite possible to manipulate or erase it from the ledger leaving room for corruption.
(5)Auditability
Starting from the genesis chain, the Blockchain is an ordered chain, and un-broken chain and is a public ledger(permissionless) that is visible to all. It is transparent. It can be audited by anyone. An auditor does not have to take permission like a Bank.
(6)Authorization & Absolute Control
The legitimate owner of the coin(crypto) is the one who owns the private key. The private keys ensure absolute control of the fund. The owner of the coin always requires to sign the transaction with the Private key and then the public key and the signatures are verified, validated by the miners through the consensus mechanism.
In the traditional Bank, you don't have absolute control of the fund, which means you might run into the risk of a Bank failure or other similar risks. Crypto with Blockchain as underlying technology shields the owner from such risks.

Blockchain wallet
A Blockchain is a distributed network. A ledger is a component of the Blockchain. All the financial transactions are immutably recorded in this ledger and are visible to all.
A Blockchain wallet is a decentralized application on top of the Blockchain, it facilitates the use case of financial transaction between the users in this distributed network.
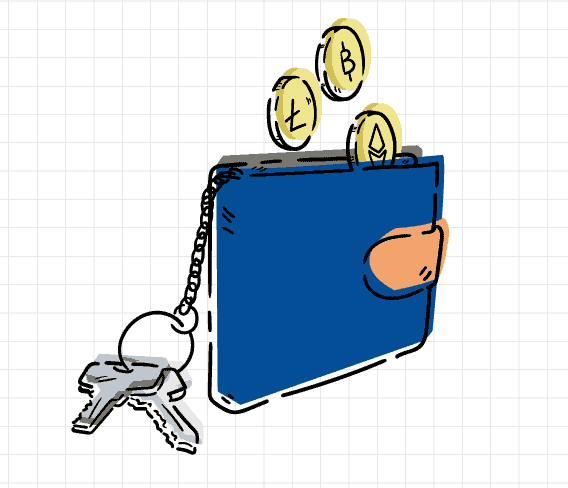
Any user can download and install a Blockchain wallet and identified with a wallet address which is done by hashing the public key via cryptographic algorithms. In other words, the wallet address is the simplified version of your public key that can be easily readable for humans.
Note- The hashing algorithms may be different for different Blockchains.
So public key and private key, these two keys are the most important thing of any Blockchain wallet. As the keys are named the Private key should remain private all the time, otherwise, you risks losing your assets. You should take care of your private key so that it remains safe and secure all the time. (we will discuss in details about private key, mnemonic key in the next chapter).
In the case of a Bank, you have the option of "forgot password" and further recovery of your password. It is not possible in a decentralized wallet as you are the absolute owner of the fund & no copy is saved anywhere else. So a decentralized wallet also brings additional responsibility-- take care of your key. Just remember this adage-- "Not your key, not your asset".
So a Blockchain wallet is associated with a wallet address which is obtained by hashing the public key. And the public key is generated from the private key using cryptography which is a one-way function, thus making it secure.
In the traditional financial system, when you issue payment by cheque you need to enter the Beneficiary name-- "In favor of" or "Pay to", then you put your signature in the check. That signature is unique to you.
When you transfer funds through Online Banking you enter Beneficiary Bank Account Number and then you authorize the transaction through OTP, Transaction Password.
When you make a payment through a Credit/Debit Card, you need to enter the CVV, PIN.
In all three cases, your Name or Account Number can be made public in order to receive payment from someone(in business). But your Signature or OTP or PIN or Transaction Password is private, which should be kept secret.
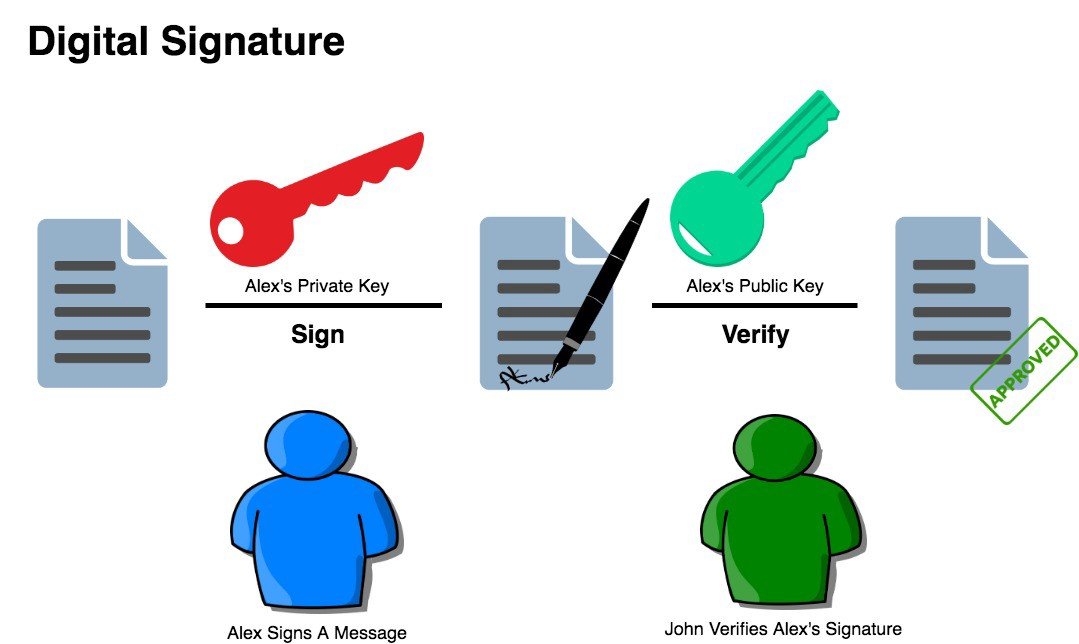
In Blockchain, you are issued with a key pair-- Private Key and Public Key.
The Public Key is just similar to a Bank Account Number or Beneficiary Name. You can share it with anyone in order to receive money, to remain in business with your counter-party.
The Private Key is similar to the Signature, OTP, PIN, Transaction Password, etc. It should be kept secret. It is used for Authentication & encryption.
The keys are created locally, stored locally either as a file or a database or simply as a wallet. The key is critical to your absolute control of the asset.
- You know the Private Key-- You can create digital signature(s)
- You know the Public key & signature-- You can verify a transaction
With your Blockchain wallet, you can send your crypto to another peer in the Blockchain network. When you send your crypto you would need the wallet address of the recipient. Then using your private key you would sign the transaction, once you sign it, it will create a unique digital signature & broadcasted to the network which will be then verified by the mining nodes, again they will use your public key to verify the transaction.

In a similar way, the recipient can use the private key associated with the public key to unlock and spend the asset.
Therefore a Blockchain wallet is a tool, a decentralized application that runs on the top of Blockchain network to store crypto, send/receive crypto, manage the crypto for simple to sophisticated financial use-cases(DeFi), your wallet may or may not perform those DeFi use-cases and that all depends on the types of wallet(we will discuss in the subsequent chapters).
In simple words, a Blockchain wallet is your Bank account, but with absolute control. It holds the necessary keys(Private & Public) to manage the crypto assets. It can track all the transactions that are associated with the wallet address, but it can't track all the transactions of the Blockchain network and if you want to track all the transaction of a Blockchain network, you would need a Block Explorer which is just like a search engine of a particular network.

Block Explorer
In the traditional financial system(Banks), if someone says he/she has sent money to you, you can't independently interrogate a bank database. The only way is that the sender will send a screenshot of the payment voucher and only a Bank official can check the database. Neither it can be audited by anyone independently.
Blockchain definitely solves this issue and a Blok explorer is another tool or a search engine that comes to your rescue as you(or anyone) can independently check whether a transaction goes through or not. This brings more transparency to the table.
A Block Explorer is a search engine of a particular network that offers a structured and organized database(easily readable for a common man) of a Blockchain so that anyone can interrogate a Blockchain transaction in a searchable format.
What do I check with a Blockchain explorer?
- A wallet address is valid or not
- The status of a transaction
- Time & Date of transaction
- Transaction Hash
- Sender and Recipient Address
- Cost of the transaction(Actual Network Fees)
- Explore Genesis Block
- Latest Transactions in a Blockchain
- Wallet Balances
- Spending on Smart Contracts

Homework-Task
How do I find(or What is the easiest way to find) the block explorer of any Blockchain? Examples? How do I check the number of confirmations? How do I find the transaction hash, sender address, receiver's address, network fees of a particular transaction? How do I check whether a wallet address is valid for a network or not(using Block explorer)? Examples?
Guidelines
- Your article should be at least 300 words.
- It is always better to gain user experience (in any Blockchain network) before submitting your article.
- Refrain from spam/plagiarism. Use images from copyright-free sources and showcase the source.
- This homework task will run till 14th-Feb'2021.
- Add tag #sapwood in your post, so that I can easily find your submission. Use #cryptoacademy, so that Steemit Team can find you. You can also use other relevant tags like #blockchain #crypto #wallet.
Thank you.
(Please feel free to join the comment section if you have any doubt on Homework-Task)

Cc:-
@steemitblog
@steemcurator01
@steemcurator02