
In the Chapter-1 & Chapter-2 of Blockchain wallet, we have already discussed Private Key+Public Key and various forms of Private key. Today in Chapter-3 we will discuss various types of Blockchain wallets, the difference between an exchange wallet and a decentralized crypto wallet, Web 3.0 wallet, etc.
Safety, security, self-custody/non-custodial, etc are always paramount in Blockchain wallets. But what type of Blockchain wallet can be ideal for you depends on the requirements, portfolio size, and frequency of use. For that, we must know the different types of wallets, ease of use, security advantages of the one over the others, etc.

Different types of the crypto wallet
Non-custodial or self-custody is a fundamental term in a Blockchain wallet. So any classification of Blockchain wallet must conform to that principle. Further, this classification is based on the prevalence of modern days use of a wallet.
The crypto ecosystem has also evolved over the last decade and in that process, many other types of use of a Blockchain wallet are obsolete these days. For instance, these days Non-deterministic wallets are not being used with the proliferation of HD wallets, similarly despite being safe, and having security advantages people hardly use Paper wallets(once popular until 2016/17) these days.
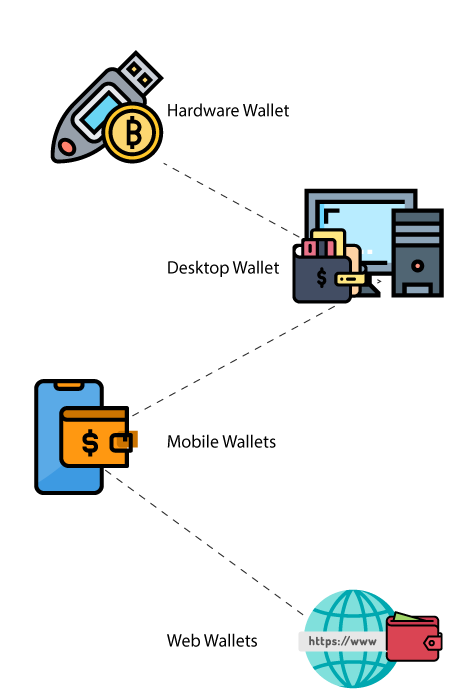
Hardware Wallets
A Hardware wallet is a portable electronic device that uses randomness to generate Private+Public Key pair and gives secure access to the crypto asset. So they remain in the off-line environment and they can be connected to a computer/laptop via USB port or Bluetooth.
A hardware wallet does not risk disclosing sensitive information to an internet-connected device even when you connect and sign a transaction. That is how they have better security advantages over the software wallets. Alongside it always creates a feeling that you own that asset, that is in your hand, in your hardware device.
There are different hardware wallets available in the market supporting many other cryptocurrencies along with Bitcoin, Etherum with the popular ones being Ledger Nano X, Trezor, KeepKey, BitBox, etc. Ledger Nano X supports more than 30 cryptocurrencies plus over 500 ERC-20 tokens.
Software Wallets
A software wallet can be either in the form of a web wallet or a desktop client or a mobile client. In both desktop(Computer/Laptop) and mobile clients(Android, iOS) you have to download and install it, whereas, in the case of a web wallet you don't need to download anything, you just need to set up your wallet; and they run on the browsers. Whether you install it on a Desktop/Smartphone or you set it up on the web, always back up your private key. Even if it is connected to the internet, don't forget to back up and store your private key offline.
Note- Extension- Metamask, TronLink, etc(installed in Chrome, Firefox, Brave, etc) can be categorized as Web wallets.
A web wallet may be easy and convenient for general users, but vulnerable to hacking. In the case of a Desktop/Mobile client, make sure your Computer/Laptop/Smartphone is free from virus/malware.
Out of the three forms, these days people prefer a mobile client over the other forms of Software wallets as Smartphone by nature is mobile, so users can carry it anywhere and can use as per their convenience.
Multichain wallet
In a Bitcoin core client, you are being able to store Bitcoin. Similarly in Etherum, you are being able to store ETH, ERC-20 tokens, etc. So these are single coin wallets, which means they can only store a coin which belongs to that family. These days as wrapped tokens are gaining popularity you can also find W-tokens in that family, but technically they don't belong to the original chain.
A general user always deals with cryptocurrencies of heterogenous Blockchains. So a single coin wallet can't fulfill the requirement of such users. A Multichain wallet ideally solves this problem interface and simplifies things for the general user by supporting coins of heterogenous Blockchains.
A Multichain wallet can be a hardware wallet or can be a software wallet. They also offer Web 3.0 features.
Example- Trust Wallet, Atomic Wallet, Guarda Wallet, etc
In Multichain wallets, you need to back up the Mnemonic key(generally 12 words), the private key of every supported coin can be derived from this recovery phrase.
In Atomic Wallet, you can back up the Mnemonic key as well as the private keys of individual coins supported by the wallet. Similarly, Guarda wallet is another Multichain wallet which I consider a comprehensive Multichain wallet supporting a wide list of coins and you can also import an existing coin balance(wallet) if that is supported in Guarda Wallet.

Exchange Wallet(Centralized) & Decentralized crypto wallet.
Although an Exchange can be both Centralized or Decentralized, here, by default we are taking Centralized Exchange into account, with the reason being-- "most of the trading volumes are still concentrated in Centralized Exchanges with the likes of Binance, Huobi, Coinbase, Bittrex, etc".
Furthermore, centralized Exchanges like Binance, Huobi, Poloniex, etc lowers the barrier to entry with easy registration. Naive users always find it easy to get started with such an exchange. So they have their relevance despite being centralized.
When you register an account with a centralized exchange you get an exchange wallet with a list of supported coins by that exchange. You can perform spot trade(buy/sell), deposit, withdraw, p2p trade, Futures & Options Trading, etc.
Buying, Selling, Deposit, Withdrawal, etc all are integrated into the Exchange server, making it easy and convenient for the Newcomers in particular.
In general, when you set up your exchange account, you need an Email account, a Mobile Number and you also need to set up 2FA for additional security.
Any operation such as withdrawal or transfer of coins from an exchange wallet requires you to enter the OTP/2FA. So if you have access to your email account and mobile number then you are in good standing with the withdrawal/transfer of crypto assets from an Exchange wallet.
.png)
Please do note that in an Exchange Wallet(Centralised) you don't have control of the keys. You gain access to your Exchange wallet and perform withdrawal/transfer with the login credentials/OTP only. So an Exchange Wallet is just like a Bank Account. That's a custodian wallet.
In contrast, a decentralized crypto wallet is a self-custody or non-custodial wallet. You have absolute control. You and only you know the private keys of the wallet, hence only you can unlock and spend the crypto asset.
With the fundamental difference between an Exchange(Centralized) wallet and a Decentralized Crypto wallet in place, we have the requirements and use of both types on day to day basis.
Ideally, an Exchange Wallet(Centralized) should be used to fulfill the short-term objective(spot trading, p2p, Futures, etc, liquidity pool, etc) and a decentralized crypto Wallet should be used for the long-term objective (HODL, better security, absolute control, etc).
Now, what should you do if you have lost your phone/2FA/forgot password in the case of an Exchange Wallet and if your device got malfunctioned in the case of a decentralized crypto wallet?
In the case of an Exchange Wallet, you can still gain access to an Exchange Wallet if you have lost your mobile phone/2FA/forgot password. You may not be able to perform withdrawal for 2/3 days in some of the exchanges when your reset the password/or reset the 2FA or added a new mobile number. But you are still safe, and you gain access to the Exchange wallet once again. In the rarest event if you lose access to your Email Account, and if they can verify your identity they will restore the account for you(however in such a case, it might take a lot of time).
Put simply, when you set up an Exchange wallet keep your Email Account, 2 FA secure(back up the 2 FA code), make sure you have your mobile number active for a seamless experience with an Exchange.
In contrast, if you dealing with your decentralized crypto wallet, only and only your private key can bring you home(in case your device gets malfunctioned or if you have lost the device). We have already discussed in Chapter-2, how to secure your private keys(Keep your private keys off-line).

Web 3.0 Wallet & its specific use
Let's go back to the era of 1991(Web 1.0) when the content and web page used to be static, may not be relevant to your need also. And only produced by a select few. There is no room to engage with such a publisher.
Then comes Web 2.0 in the year 2005 when you begin to interact with a publisher, content creator with the likes of Youtube, Facebook, etc. So here the interface is a little better as you can interact with another user/publisher. But it is not absolutely user-centric as the monopoly still prevails by the platform owners.
So the next evolution of the web is Web 3.0. Semantic Web+AI +Blockchain can produce the best ever experience of the web where it will be absolutely user-centric. It is up to the user to opt-in or opt-out of data trading.
In essence web 3.0 is ubiquitous(but not limited to Computer or Smartphone only, rather Internet-of-Things), absolute ownership- hence absolutely user-centric, 100% up-time(distributed servers), permissionless, interoperable, automated, etc.
Now coming to Blockchain wallet, if we can recollect the early days of crypto(2013/14), the Blockchain wallet also used to static, we did not have a plethora of decentralized applications. In today's reality, Blockchain wallets have really made significant improvements; Interacting with a dApp powered by Smart-contract has become a reality. In 2020, the DeFi brought fresh impetus to the crypto ecosystem. Almost all DeFi apps can be accessed with a web 3.0 wallet.
.png)
So what are the key features of a web 3.0 wallet?
- Fundamentally a web 3.0 wallet has to be non-custodial-- Absolute ownership.
- A web 3.0 wallet is always a key(Private Key+Public Key) based wallet.
- It should be able to interact with other dApps(Gaming, DeFi, Exchange, Loan, etc) of the same family(at least).
- It should be compatible, seamlessly integrated, and must operate through Smart contracts.
Examples of Web 3.0 wallet
Metamask- A web browser extension. One can interact with the dApps(e.g popular DeFi applications like Uniswap) of the Etherum family from the browser using Metamask(powered by Smart-contract)
Tron Link- A web browser extension. One can interact with the dApps like JustLend, JustSwap of Tron Family using TronLink wallet(powered by smart contracts).
Trust Wallet- A Multichain wallet. One can browse dApps and interact with a dApp without having to leave the wallet.
Homework Task
(1) Have you ever used a Hardware/software wallet? Which one is having a better security advantage?
(2) What are the important points to consider when you deal with an Exchange(centralized) Wallet & Decentralized wallet. How do you secure/restore both types?
(3) Give an example of a Web 3.0 wallet and what are the distinct uses of a web 3.0 wallet? Have you ever used any Web 3.0 crypto Wallet? Examples?
Guidelines
- Your article should be at least 300 words.
- It is always better to gain user experience (in any Blockchain wallet) before submitting your article.
- Refrain from spam/plagiarism. This task specifically requires screenshot(s) of your own experience with a wallet. Use images from copyright-free sources and showcase the source, if any.
- This homework task will run until 28th-Feb'2021.
- Add tag #sapwood-week3 #cryptoacademy in your post and should be among the first five tags. You can also use other relevant tags like #blockchain #crypto #wallet or any other relevant tag.
Thank you.
(Please feel free to join the comment section if you have any doubt on Homework-Task)

Cc:-
@steemitblog
@steemcurator01
@steemcurator02


