~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
[ENGLISH]
19-11-2023 - Technical contents - Isolated, closed and open systems [EN]-[IT]
Purpose of thermodynamics
Thermodynamics focuses on the study of the "internal" state of a system.
Isolated system and closed system
The isolated, closed and open systems are represented below.
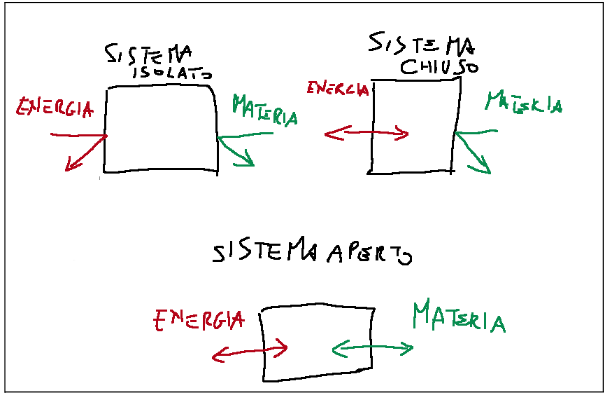
The isolated system differs from the closed system in that in the isolated system there is no exchange of energy, while in the closed system this occurs. In both systems there is no exchange of matter.
The first law of thermodynamics for isolated systems
In thermodynamics, the isolated system is a system which, across its boundary, does not allow a flow of energy with the external environment or even a transfer of mass.
The first law of thermodynamics is taken as a postulate, that is, as a statement accepted as true.
The formula that identifies the first law of thermodynamics is the following:
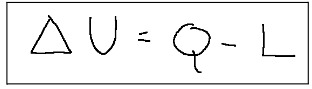
Where:
ΔU = Change in internal energy
Q = Heat exchanged with the environment
L = Work exchanged with the environment
The statement is as follows:
During any thermodynamic transformation, the change in internal energy ΔU of a system is equal to the difference between the heat Q and the work L exchanged with the environment.
The equation establishes an energy balance and therefore can be considered as a thermodynamic principle of energy conservation.
Therefore we can say that the internal energy ΔU acquired or lost by the isolated system is given by the difference between the heat Q, which can be absorbed or released, and the work L that can be done by the system on the environment or by the environment on the system .
Conclusion
An isolated system is a thermodynamic system, consisting of the system and its environment.
The internal energy of an isolated system is constant, therefore energy is neither created nor destroyed, but transformed. In a thermodynamic system, energy passes from one form to another and can therefore be transferred through exchanges of heat and work.
The first law of closed system thermodynamics
In thermodynamics, a closed system is a system that, across its boundary, allows a flow of energy with the external environment, but there is no mass transfer.
The statement of the first law of thermodynamics states that the internal energy (U) of a closed thermodynamic system is constant.
The formula is the same as before.
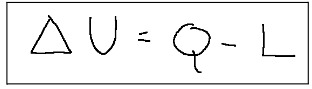
Conclusions
Systems in dynamic thermodynamics are divided into three categories: isolated, closed and open.
Request
Through the study of thermodynamic systems, the insulation of homes can be studied. Do you also think that thermodynamics will be used more and more in building design?

[ITALIAN]
19-11-2023 - Contenuti tecnici - Sistemi isolati, chiusi e aperti [EN]-[IT]
Scopo della termodinamica
La termodinamica si concentra sullo studio dello stato “interno” di un sistema.
Sistema isolato e sistema chiuso
Qui di seguito sono rappresentati i sistemi isolati, chiusi e aperti.

Il sistema isolato differisce dal sistema chiuso dal fatto che nel sistema isolato non c’è scambio di energia, mentre in quello chiuso questo invece avviene. In entrambi i sistemi non avviene lo scambio di materia.
Il primo principio della termodinamica per sistema isolato
In termodinamica il sistema isolato è un sistema che, attraverso il suo confine, non consente un flusso di energia con l'ambiente esterno e nemmeno un trasferimento di massa.
Il primo principio della termodinamica viene assunto come postulato, cioè come un’affermazione accettata per vera.
La formula che identifica il primo principio della termodinamica è la seguente:
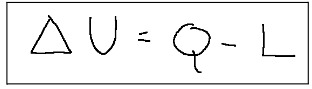
dove:
ΔU = Variazione di energia interna
Q = Calore scambiato con l’ambiente
L = Lavoro scambiato con l’ambiente
L’enunciato è il seguente:
Durante una qualsiasi trasformazione termodinamica, la variazione di energia interna ΔU di un sistema è uguale alla differenza tra il calore Q ed il lavoro L scambiati con l’ambiente.
L’equazione stabilisce un bilancio energetico e quindi può essere considerato come un principio termodinamico di conservazione dell’energia.
Quindi possiamo dire che l’energia interna ΔU acquisita o persa dal sistema isolato è data dalla differenza tra il calore Q, che può essere assorbito o ceduto, e dal lavoro L che può essere svolto dal sistema sull’ambiente o dall’ambiente sul sistema.
Conclusione
Un sistema isolato è un sistema termodinamico, costituito dal sistema e dal suo ambiente.
L'energia interna di un sistema isolato è costante, quindi l'energia non si crea né si distrugge, ma si trasforma. In un sistema termodinamico l’energia passa da una forma ad un'altra e può cioè essere trasferita attraverso scambi di calore e di lavoro.
Il primo principio della termodinamica per sistema chiuso
In termodinamica il sistema chiuso è un sistema che, attraverso il suo confine, consente un flusso di energia con l'ambiente esterno, ma non c’è trasferimento di massa.
L'enunciato del primo principio della termodinamica afferma che l'energia interna (U) di un sistema termodinamico chiuso è costante.
La formula è la stessa di prima.
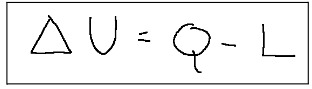
Conclusioni
I sistemi in termodinamica dinamica vengono racchiusi in tre categorie: isolati, chiusi e aperti.
Domanda
Tramite lo studio dei sistemi termodinamici si possono studiare gli isolamenti delle abitazioni. Pensate anche voi che nell'ambito della progettazione edile la termodinamica verrà usata sempre di più?
THE END
