Archaeology as a Profession
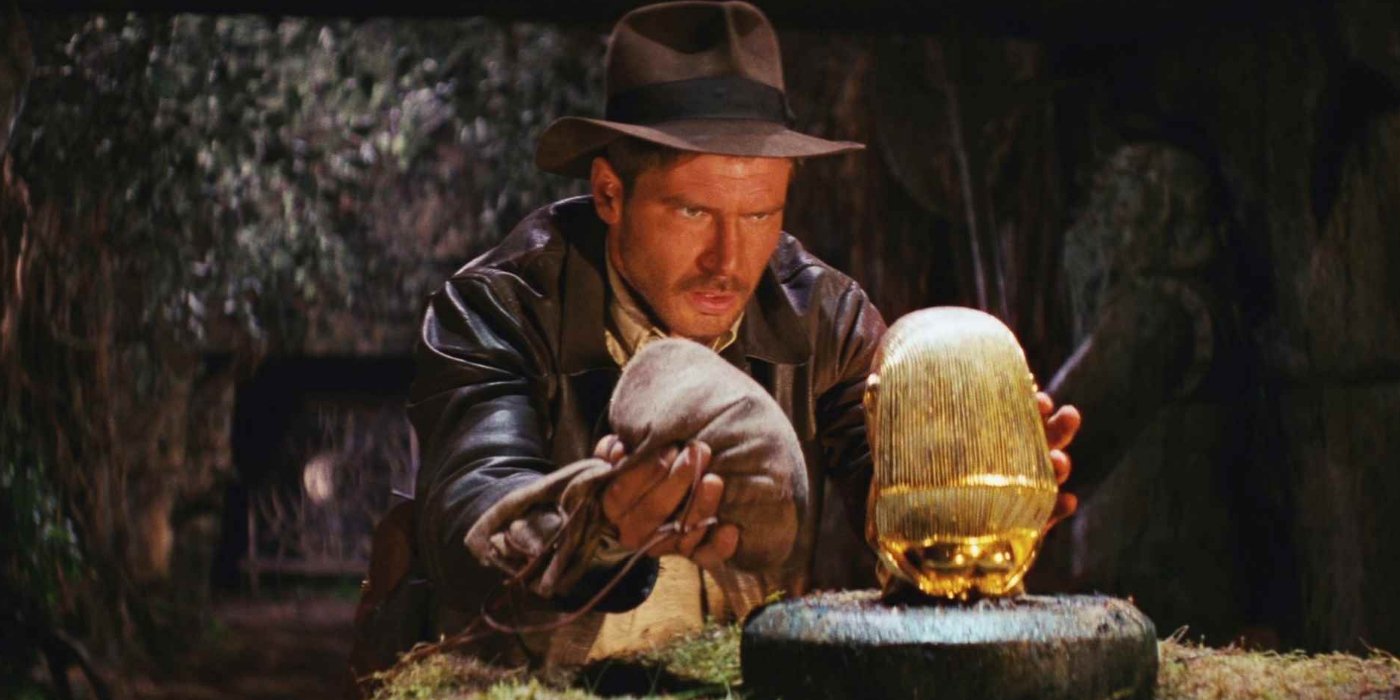

Archaeology is still thought of as a romantic and glamorous pastime by many people, even though, after almost two centuries of practice has been turned into a meticulous discipline. The excitement, however, still exists in the many diverse and highly detailed reconstructions of life in the past that result from scientific inquiry. Archaeology are continually developing new methods to reconstruct the life ways of prehistoric humans, to document the earliest art, to outline the process of plant and animal domestication and to investigate many other aspects of prehistoric existence.
Domestication
Although no consensus definition for domestication exists in archaeology, at a minimum it typically refers to the process whereby animals/plants subsist and survive under the control of humans. Many archaeologists also consider animals/plants to be domesticated if humans are somehow involved in the breeding patterns of the species.
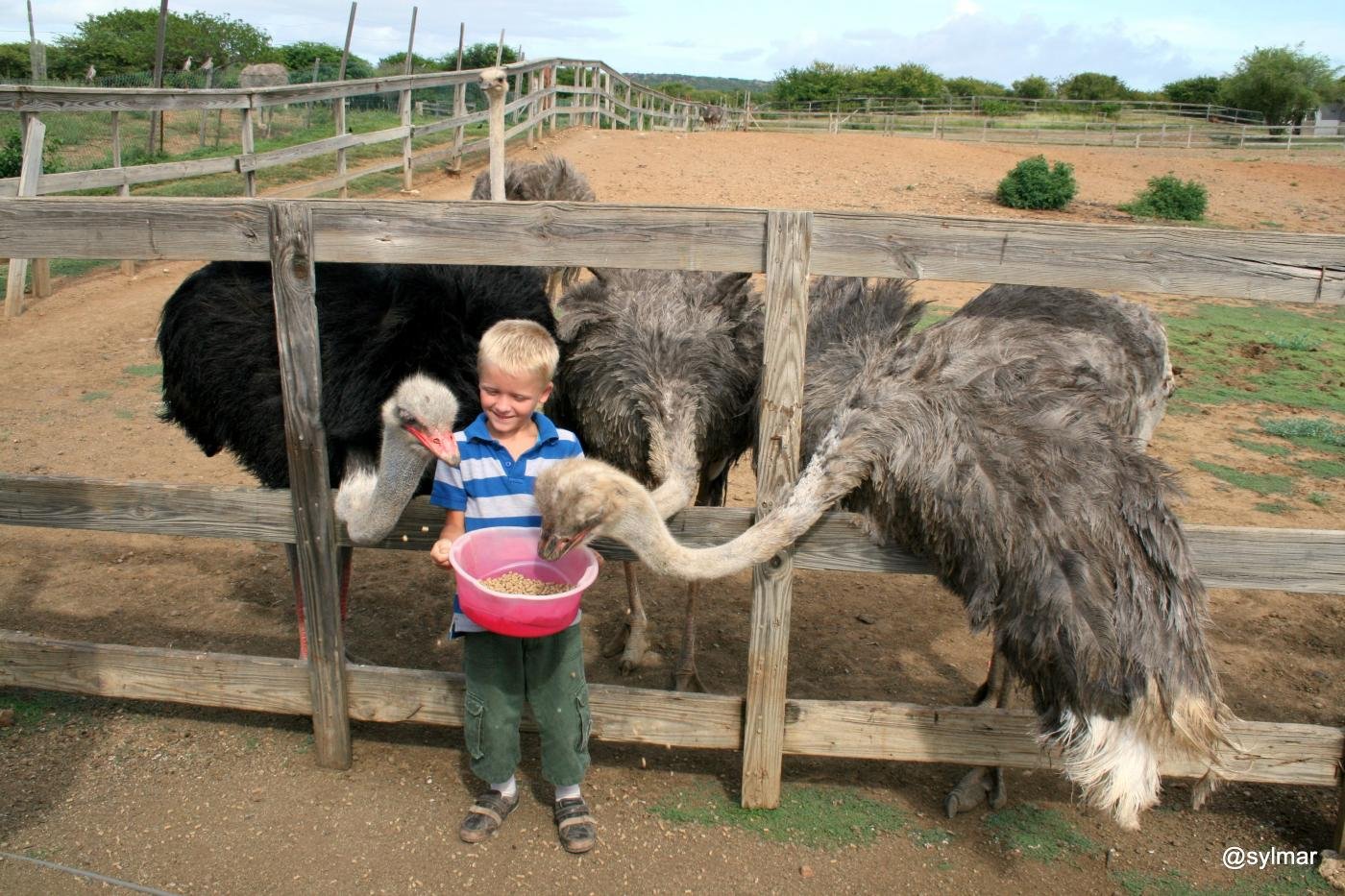

It is suggested that, at the present in sub-Sahara Africa, the Ostrich (Struthio camelus) is in the process of being domesticated.
By developing these new research methods archaeology has become a refined "high tech" discipline, with many professional archaeologists working in highly specialized fields. Specialists are necessary as no one person can possibly be an expert in the entire diverse practice of archaeology. This resulted in not only a knowledge explosion but also the development of ever more sophisticated methods for studying the specific aspects of the past.
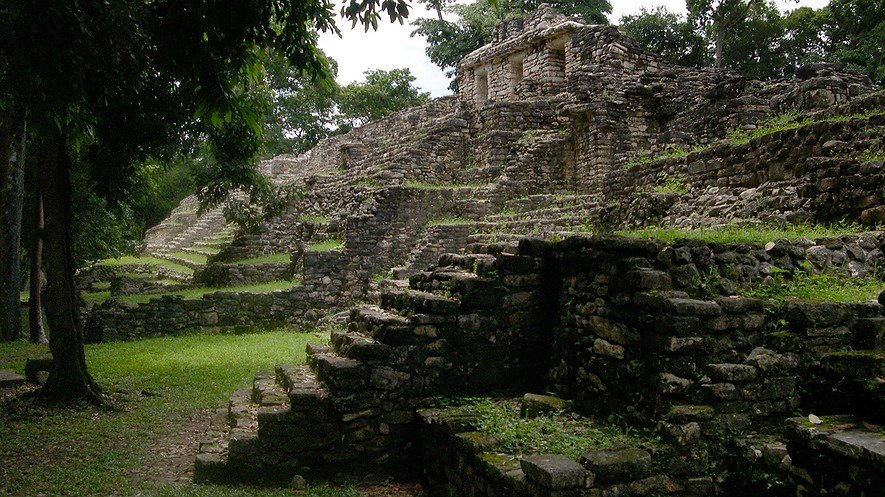

Archaeologists investigate the preserved remains of ancient societies. It is not the "Treasures" that interest them, but the data that result from the excavating and properly recording archaeological sites. Today's archaeologists is as interested in why people lived the way they did as in the objects they made or the buildings they erected on basic archaeological research and and on archaeological excavations. In addition to research and theoretical approaches, archaeologists are increasingly concerned with the management and conservation of the rapidly vanishing archaeological record. Daily activities include strategies to combat looting, measures to mitigate the destruction and potential plunder caused by thousands of tourists' feet at places like Egypt's pyramids, as well as finding ways to preserve our cultural heritage and ensure the long-term survival of the archaeological record.
Fields Of Specialization in Archaeology

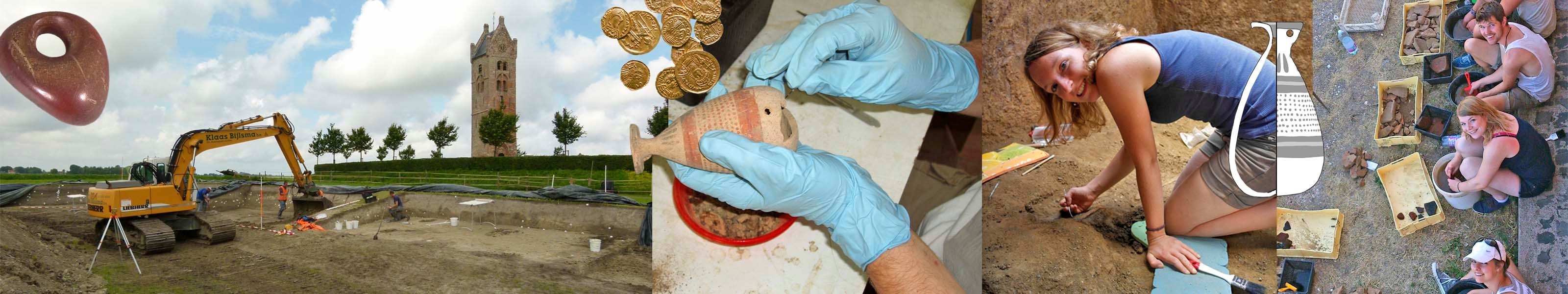
* Cultural resource management
Cultural Resources are the human-made and natural and physical features associated with human activity. These are unique and not renewable and include sites, structures and artefacts significant in history and prehistory. Cultural resource management (CRM) is the application of management skills to utilize, preserve and/or document important parts of our cultural heritage, both historical and prehistoric, for the benefit of all, at present and in the future.

Assessment of Archaeological Areas

- Pre-Phase 1 : An initial pre-assessment ( scoping) phase, where the specialist establishes the scope of the project and the terms of reference for the developer.
- Phase 1 : An impact Assessment which identifies sites, assess their significance and comments on the impact of a given development on the sites. Recommendations for the site mitigation or conservation are also made during this phase.
- Phase 2: Mitigation/Rescue involves planning the protection of significant sites, Recommendations for the sites or sampling through excavation or collection ( in terms of a permit) at sites that may be lost as a result of a given development.
- Phase 3: A Heritage Site Management Plan (for heritage conservation), is required in rare cases where the site is so important that development will not be allowed and sometimes developers are encouraged to enhance the value of sites retained on their properties with appropriate material or displays.
Cultural resource management, and the archaeological research that goes with it, are components of a much larger enterprise: the study of the effects of the human activity on the total landscape. It is part of a much larger concern for the fragile ecology, and the finite archaeological record is only part of the context in which decisions are made about projects that affect the landscape.
The Three Major Procedures executed during CRM involve:
- An overview of cultural resources in the area.
- An archaeological assessment report.
- The proposal of a management plan.

In the face of development, CRM practitioners are expected to perform set procedures to fulfil the criteria laid out by the countries legislation to protect its archaeological heritage.
These procedures are designed to fulfil two sets of expectations. First, to provide the necessary expertise to ensure that adequate steps are taken to protect and conserve archaeological remains. Second, to ensure that assessments are based on comprehensive field data focusing on the nature and extent of the site, that representative samples are taken, that provision is made for the proper conservation and curation of these samples, and that interested and/or affected parties, such as local or archaeological communities, are informed and consulted.
Rock Art Conservation and Interpretation

Unquestionably Africa is one of the prime rock art regions within the global context. There thousands of documented rock art sites and more than double that still waiting to be discovered. It is thus imperative to understand and preserve this unique and nonrenewable cultural resource. If a site is damaged or destroyed the archaeological information is permanently lost.
All rock art, even currently undocumented art, is protected by law. There exists an increasing demand for CRM practitioners to specialize in rock art management.Because rock art is exposed to weather unlike the cave art in Europe, it can be accessed by all who take the trouble to reach it.
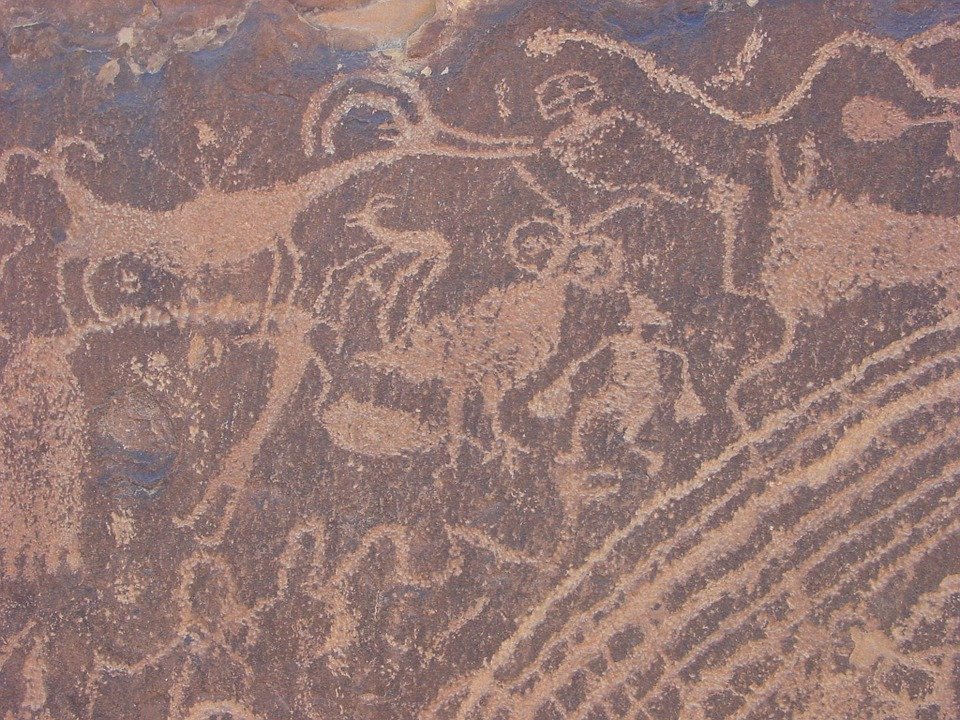

Rock art is not only about " pretty pictures", it is an extremely valuable source of archaeological information. By "decoding" these images much can be learned about the past life ways of the people who inhabited that land. Prehistoric people did not leave written texts or Steemit Posts , and in many cases rock art gives the only clues to their presence. Rock art can inform about dress-code, hunting and food gathering, social behaviour, such as dancing and making music, religious practice, gender issues, political issues etcetera.
Finding ever more ways of understanding and interpreting rock art thus become a specialized field which largely contributes to our overall understanding of the past.
Please Follow me for more information on Archaeology and History
Please check out my other posts:
To Become or Not Become an Archaeologist? - Introduction to Archaeology Part 2
I would like say a special Thank You to all those who have supported my previous posts and a Special Thank You to @kryptik and @ocd team for all the support!
