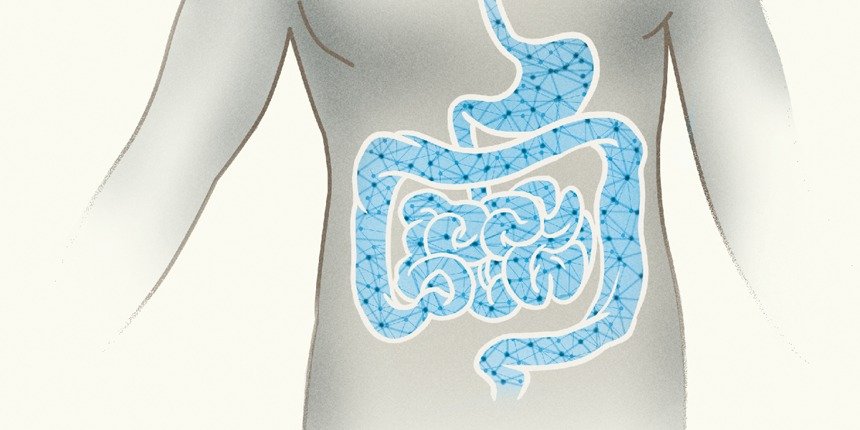
The enteric nervous system (ENS, shown in blue) is embedded in the digestive tract.
HOW many brains do you have? If you answer “one,” you are correct. Yet, there are other nervous systems in your body. One network of neurons is so extensive that some scientists have referred to it as a “second brain.” It is the enteric nervous system (ENS) and is located, not in your head, but mostly in your belly.
It takes an enormous amount of coordination and effort for the body to transform food into fuel. Hence, it is fitting that the brain is designed to delegate, as it were, most digestive control to the ENS.
While much simpler than the brain, the ENS is immensely complex. In humans, it is made up of an estimated 200 to 600 million neurons. This complex network of neurons is built into the digestive system. Scientists believe that if the function of the ENS were to take place in the brain, the needed nerves would be too thick. According to the book The Second Brain, “it is thus both safer and more convenient to let the [digestive system] look after itself.”
Think of the digestive tract as a factory line managed mostly by the ENS. Your “second brain” moves food through the digestive system by directing the muscles along the wall of the digestive tract to contract. The ENS varies the strength and frequency of these muscle contractions as needed to make the system function like a line of conveyor belts.
The ENS also supervises safety functions. The food you swallow is likely to contain potentially harmful bacteria. It is no wonder that about 70 to 80 percent of your body’s lymphocyte cells—a vital component of your immune defense system—are housed inside your belly! If you ingest high levels of harmful organisms, the ENS protects the body by triggering powerful contractions that expel most of the toxic matter through vomiting or diarrhea.
While the ENS seems to function independently of the brain, these two nerve centers engage in constant communication. For example, the ENS plays a role in the regulation of hormones that tell the brain when you should eat and how much you should eat. ENS nerve cells signal the brain when you are full and may possibly trigger nausea if you eat too much.
Another example of communication between the brain and the digestive system is what has been described as having butterflies in one’s stomach. This feeling may be the result of the ENS diverting blood away from the stomach when the brain experiences tension or stress. Nausea can be another result, as during stress the brain triggers the ENS to change the gut’s normal contractions. According to experts, this brain-gut connection might also be the basis for so-called gut instincts.
While the ENS may generate such gut feelings, it cannot think for you or direct your decisions. In other words, the ENS is not really a brain. It cannot help you to compose a song, balance your bank account, or do your homework. Still, this marvelous system continues to amaze scientists for its complexity—much of it perhaps still undiscovered. So the next time you are about to eat a meal, pause and think about all the monitoring, data processing, coordination, and communication that is about to take place in your digestive system!
So many amazing things to learn about the our body system.
Article Credit: Awake No. 3 2017
