Image link
Image link
These days, many farmers and producers use vermiculture to develop their crops,  since it contains unique and pure nutrients, so much so that it could even advance the plant cycle, although it is true that worm farming is the worm breeding of different ways and these in turn will provide organic fertilizer. Earthworms process organic waste that tends to be polluting the environment, such as restaurant waste, excrement, kitchen shells and fallen leaves in the garden.
since it contains unique and pure nutrients, so much so that it could even advance the plant cycle, although it is true that worm farming is the worm breeding of different ways and these in turn will provide organic fertilizer. Earthworms process organic waste that tends to be polluting the environment, such as restaurant waste, excrement, kitchen shells and fallen leaves in the garden.
Starting with the vermiculture
If you are new to this topic, it does not matter come see what I explain  ...
...
 there are endless species of worms but it has been proven that the Californian Red Worm is a species that adapts to any climate or temperature, so it is efficient to breed this lineage.
there are endless species of worms but it has been proven that the Californian Red Worm is a species that adapts to any climate or temperature, so it is efficient to breed this lineage.Now, we must first  consider the purpose of worm breeding, that is, for whats to raise worms; worms have different uses in the industry as well as in the home, solid humus, liquid humus, animal feed and food for human consumption can be obtained. Once the end is clear, we will build the place where we will deposit the earthworms, it must be a shaded place, with good drainage and the stonecutters should be easily accessible, then we will place a layer of substrate as 15cm high (this varies depending on the design of the stonecutter), then we will deposit all organic material: shells or other materials; then we deposit the worms with 2 worms
consider the purpose of worm breeding, that is, for whats to raise worms; worms have different uses in the industry as well as in the home, solid humus, liquid humus, animal feed and food for human consumption can be obtained. Once the end is clear, we will build the place where we will deposit the earthworms, it must be a shaded place, with good drainage and the stonecutters should be easily accessible, then we will place a layer of substrate as 15cm high (this varies depending on the design of the stonecutter), then we will deposit all organic material: shells or other materials; then we deposit the worms with 2 worms  to start the breeding, this happens because the worm is asexual, so it can be reproduced alone; but for the process to be faster, we will put several and finally we do a superficial irrigation to maintain the temperature suitable for the breeding.
to start the breeding, this happens because the worm is asexual, so it can be reproduced alone; but for the process to be faster, we will put several and finally we do a superficial irrigation to maintain the temperature suitable for the breeding.
Structure of the red worm
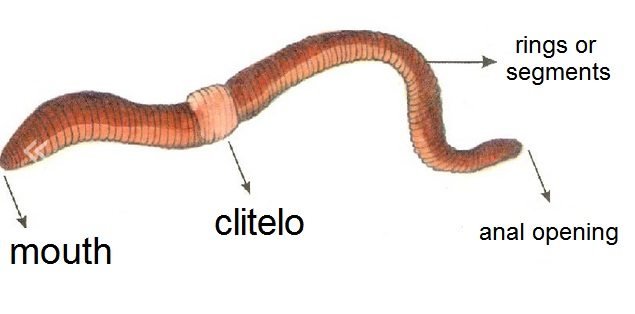
The earthworm is characterized by having a body formed by rings, on the outside are identified external structures such as: external segments; mouth; arrows; genital pore; dorsal pore; clitelo; pubertal tubers; and the anus.
 (link)
(link)Applications in agriculture and others
- Solid humus: it is the substrate already processed
 by the worms, when applying solid humus in the crops, the microorganisms begin to degrade the soil, attributing the nutrients and minerals that the plant needs.
by the worms, when applying solid humus in the crops, the microorganisms begin to degrade the soil, attributing the nutrients and minerals that the plant needs.
- Humus liquid: semitransparent liquid substance that is drained
 from the vermiculture, the application is of foliar way, bone by the sprinkling of the leaf, its proportion of prepared is 2 liters of humus liquid for 16 liters of water, It is recommended to apply in the crops weekly .
from the vermiculture, the application is of foliar way, bone by the sprinkling of the leaf, its proportion of prepared is 2 liters of humus liquid for 16 liters of water, It is recommended to apply in the crops weekly .
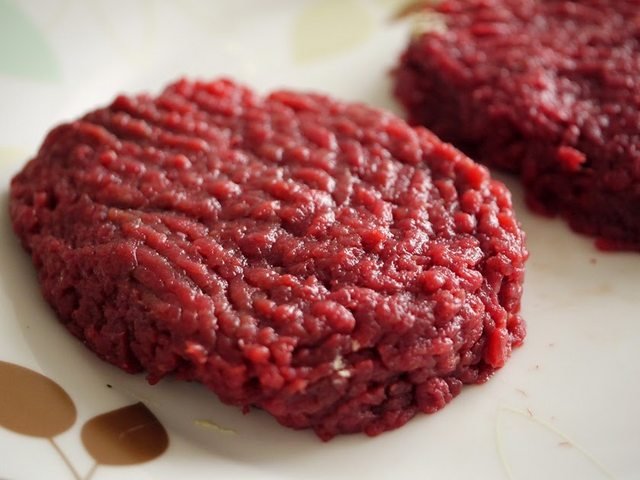
- Food for animals and humans: since the worm contains raw protein, in some cases it can be processed for different consumption, animals can be dehydrated to be used in concentrated
 feed for mono-gastric animals and in human consumption meat can be prepared based worm rich in nutrients with high protein value.
feed for mono-gastric animals and in human consumption meat can be prepared based worm rich in nutrients with high protein value.

Spanish / Español 

Por estos días, muchos agricultores, campesinos y productores usan la lombricultura  para desarrollar sus cultivos, dado que contiene nutrientes únicos y puros, tanto así que pudiera hasta adelantar el ciclo de las plantas, si bien es cierto la lombricultura es la cría de lombrices de diferentes maneras y estas a su vez nos proporcionaran abono orgánico. Las lombrices procesan los residuos orgánicos que tienden a ser contaminantes para el medio ambiente, como desperdicios de restaurantes, excrementos, conchas de la cocina y hojas caídas en el jardín.
para desarrollar sus cultivos, dado que contiene nutrientes únicos y puros, tanto así que pudiera hasta adelantar el ciclo de las plantas, si bien es cierto la lombricultura es la cría de lombrices de diferentes maneras y estas a su vez nos proporcionaran abono orgánico. Las lombrices procesan los residuos orgánicos que tienden a ser contaminantes para el medio ambiente, como desperdicios de restaurantes, excrementos, conchas de la cocina y hojas caídas en el jardín.
Empezando con la lombricultura
Si eres nuevo en este tema, no importa ven que te explico  …
…
 lombrices, existen un sinfín de especies de lombrices pero se ha demostrado que la Lombriz roja Californiana es una especie que se adapta a cualquier clima o temperatura, por lo cual es eficiente criar este linaje.
lombrices, existen un sinfín de especies de lombrices pero se ha demostrado que la Lombriz roja Californiana es una especie que se adapta a cualquier clima o temperatura, por lo cual es eficiente criar este linaje.Ahora bien en primer lugar debemos  tener en cuenta cual es el propósito de la cría de lombrices, es decir, para que criar lombrices; la lombricultura tiene diferentes usos tanto en la industria como domestico, se pueden obtener Humus solido, humus liquido, alimento para animales y alimento para consumo humano. Una vez claro la finalidad, construiremos el lugar donde depositaremos las lombrices, tiene que ser un lugar sombreado, con buen drenaje y los canteros debe estar de fácil acceso, luego colocaremos una capa de sustrato como 15cm de alto (esto varía dependiendo del diseño del cantero), después depositaremos todo material orgánico: conchas u otros materiales; posteriormente depositamos las lombrices basta con 2 lombrices
tener en cuenta cual es el propósito de la cría de lombrices, es decir, para que criar lombrices; la lombricultura tiene diferentes usos tanto en la industria como domestico, se pueden obtener Humus solido, humus liquido, alimento para animales y alimento para consumo humano. Una vez claro la finalidad, construiremos el lugar donde depositaremos las lombrices, tiene que ser un lugar sombreado, con buen drenaje y los canteros debe estar de fácil acceso, luego colocaremos una capa de sustrato como 15cm de alto (esto varía dependiendo del diseño del cantero), después depositaremos todo material orgánico: conchas u otros materiales; posteriormente depositamos las lombrices basta con 2 lombrices  para empezar con la cría esto sucede porque la lombriz es asexual, por lo que se puede reproducir sola; pero para que el proceso sea más rápido colocaremos varias y por ultimo hacemos un riego superficial para mantener la temperatura idónea para la cría, se tapan para que el sol o algún enemigo acabe con ellas.
para empezar con la cría esto sucede porque la lombriz es asexual, por lo que se puede reproducir sola; pero para que el proceso sea más rápido colocaremos varias y por ultimo hacemos un riego superficial para mantener la temperatura idónea para la cría, se tapan para que el sol o algún enemigo acabe con ellas.
Estructura de la lombriz roja
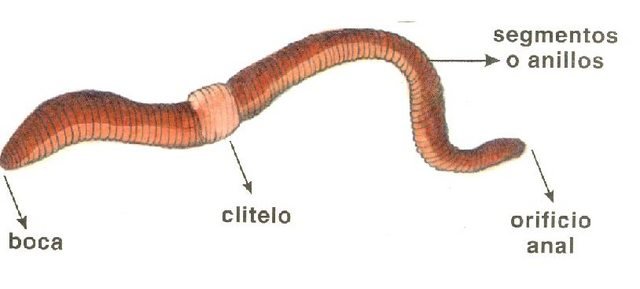
La lombriz de tierra se caracteriza por tener un cuerpo formado por anillos, en su exterior se identifican estructuras externas como: segmentos externos; boca; setas; poro genital; poro dorsal; clitelo; tubérculos puberales; y el ano.
 Enlace de imagen
Enlace de imagenAplicaciones en la agricultura y otros
- Humus solido: es el sustrato ya procesado por
 las lombrices, al aplicar humus solido en los cultivos empiezan los microorganismos a degradar el suelo, atribuyéndole nutrientes y minerales que la planta necesita.
las lombrices, al aplicar humus solido en los cultivos empiezan los microorganismos a degradar el suelo, atribuyéndole nutrientes y minerales que la planta necesita.
- Humus liquido: sustancia liquida semitransparente que
 se drena del cantero, la aplicación es de manera foliar, ósea por el roció de la hoja, su proporción de preparado es 2 litros de humus liquido para 16 litros de agua, Se recomienda aplicar en los cultivos semanalmente
se drena del cantero, la aplicación es de manera foliar, ósea por el roció de la hoja, su proporción de preparado es 2 litros de humus liquido para 16 litros de agua, Se recomienda aplicar en los cultivos semanalmente
- Alimento para animales y humanos: puesto que la lombriz contiene proteína cruda, en algunos casos se puede procesar para distintos consumo, en los animales se pueden deshidratar para ser utilizado en alimentos concentrados para animales mono-gástricos y en el consumo humano se puede preparar carne a base de lombriz rico
 en nutrientes con alto valor proteico.
en nutrientes con alto valor proteico.