July 5th marked our first full year of living off-grid. We generate our own electricity with solar panels, and a backup generator that ran for a hour a day for the two darkest months of winter. We'll be adding more solar panels and batteries before the upcoming winter to lessen the use of the gasoline backup generator.
Why Off-Grid Solar Power ?
I'm not sure how much effect I will have on the natural climate change cycles, but energy Independence is one of the greatest benefits I've found. Not being effected - possibly for days - by storms that knock down power lines - or by electricity price changes. Another motivating benefit is energy cost savings - our calculated monthly bill went from $200 per month to $40 per month. This is including the cost of the current system, and assuming battery replacement at 6 years and solar panel replacement at 20 years. This also includes the family using electricity more efficiently. The solar power system that I am using - My Solar Power Setup - cost $6300.
Current Solar Power System Cost
+$2500 Solar Panels (1000 Watts)
+$500 Solar Charge Controller (60 amp)
+$1700 Deep Cycle 12 Volt Batteries (10 batteries, 800 Amp Hours Total)
+$800 Pure Sine Wave Inverter (2500 Watts)
+$400 Backup Generator (3000 Watts)
+$400 12 Volt Battery Charger (70 amp)
=$6300

Solar Power System Flow
Solar Panels create an electrical charge from light. The solar charge controller converts the electrical charge to a voltage that can charge the 12 Volt Battery Array for storing the energy for on-demand use. The Power Inverter changes the 12 Volt DC Battery power to Standard household voltage Alternating Current for powering household appliances, devices, tools, pumps, fans - and more. A Backup Generator and 12 Volt Battery Charger is used to charge the battery array when there is not enough light for the solar panels in the setup to charge the batteries.

Solar Panels - Mono Vs. Poly
There are two major types of solar panels - Monocrystalline and Polycrystalline. With mono solar panels, the panel acts as one. With poly solar panels, each cell on the solar panel acts independently. When both solar panel types have their entire panel exposed to light - sunny or overcast - the mono solar panel would generate more electricity. If both panels were in half light and half shade - like from a tree - the poly solar panel would generate more electricity. I am using monocrystalline panels because no objects will be throwing shade on any of the solar panels.
How many Solar Panels ?
That depends on the amp hours of battery array storage - and on the amount of sunlight received throughout the year. Currently I have 1000 watts of solar panels charging an 800 Amp hour battery array. In full sunlight the solar panels will fully charge the battery array in about a hour and a half. I live in Ontario, Canada - we have Spring, Summer, Fall, and Winter. In the winter it's dark before 6 PM and as early as 5 PM for two months. Those two dark months are the only months that I could really use more panels to keep the batteries charged. If you live closer to the equator, then you could probably get away with less panels to batteries ratio. If you rarely have clouds where you live, then you could most likely have an even less solar panel wattage to battery storage amp hours ratio.

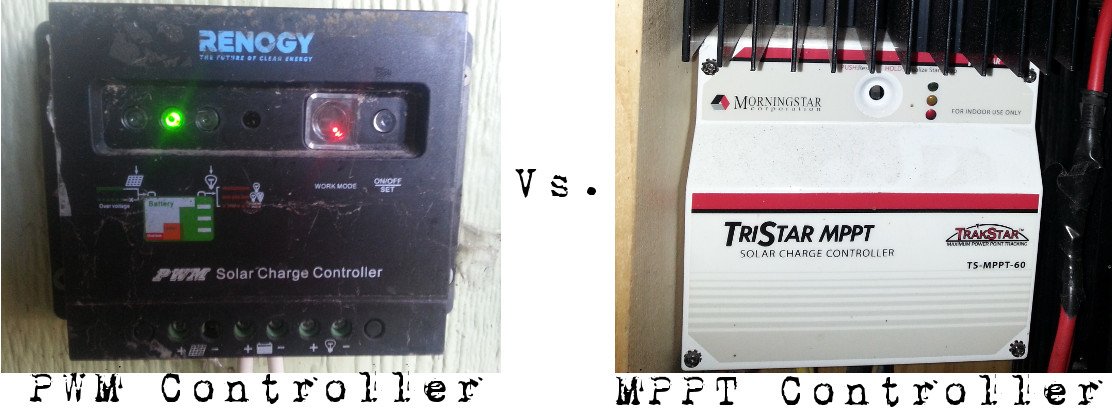
Solar Panel Charge Controllers - PWM Vs. MPPT
MPPT charge controllers are more efficient - and a little more expensive. They are most useful when you have a battery array larger than 200 amp hours - or have a lot of cloudy days. A larger current is required to charge a larger battery array. In lower light conditions, if the solar panels aren't producing enough current to charge the battery bank, the MPPT charge controllers basically have a large capacitor that a small amount of solar power would slowly fill. When full, the MPPT controller pushes the high amps from the capacitor into the battery bank.
For more information about solar panels and charge controllers, here is a link to a previous post - Tech Talk: Solar Panel Wattage Selection.

Battery Power Storage
Battery Power Storage is used to run appliances like fridges, lights, and other electrical appliances or devices at night time - when the sun is not shining - and for multiple cloudy days with little sunlight. A battery array is multiple batteries connected to make one larger capacity battery. With zero power input, my 800 amp hour battery array can run the refrigerator and other items for about 24 hours, so after a few cloudy summer days the generator may need to be turned on to top up the batteries. Every few days, a battery array should be brought to a full charge to equalize the battery levels. Deep Cycle Lead Acid Batteries are the most commonly used batteries for battery arrays. I went with an 80 Amp hour marine deep cycle lead acid battery from the local hardware store so I could slowly add batteries to the array. This flooded type of lead acid battery is mostly used for motor homes, boats, and starting engines.
For more information about off-grid battery types and how to decide the amount of battery storage to have, this previous post could be useful - How to Calculate the Battery Bank Size for Your Off-Grid and Emergency Power Needs.
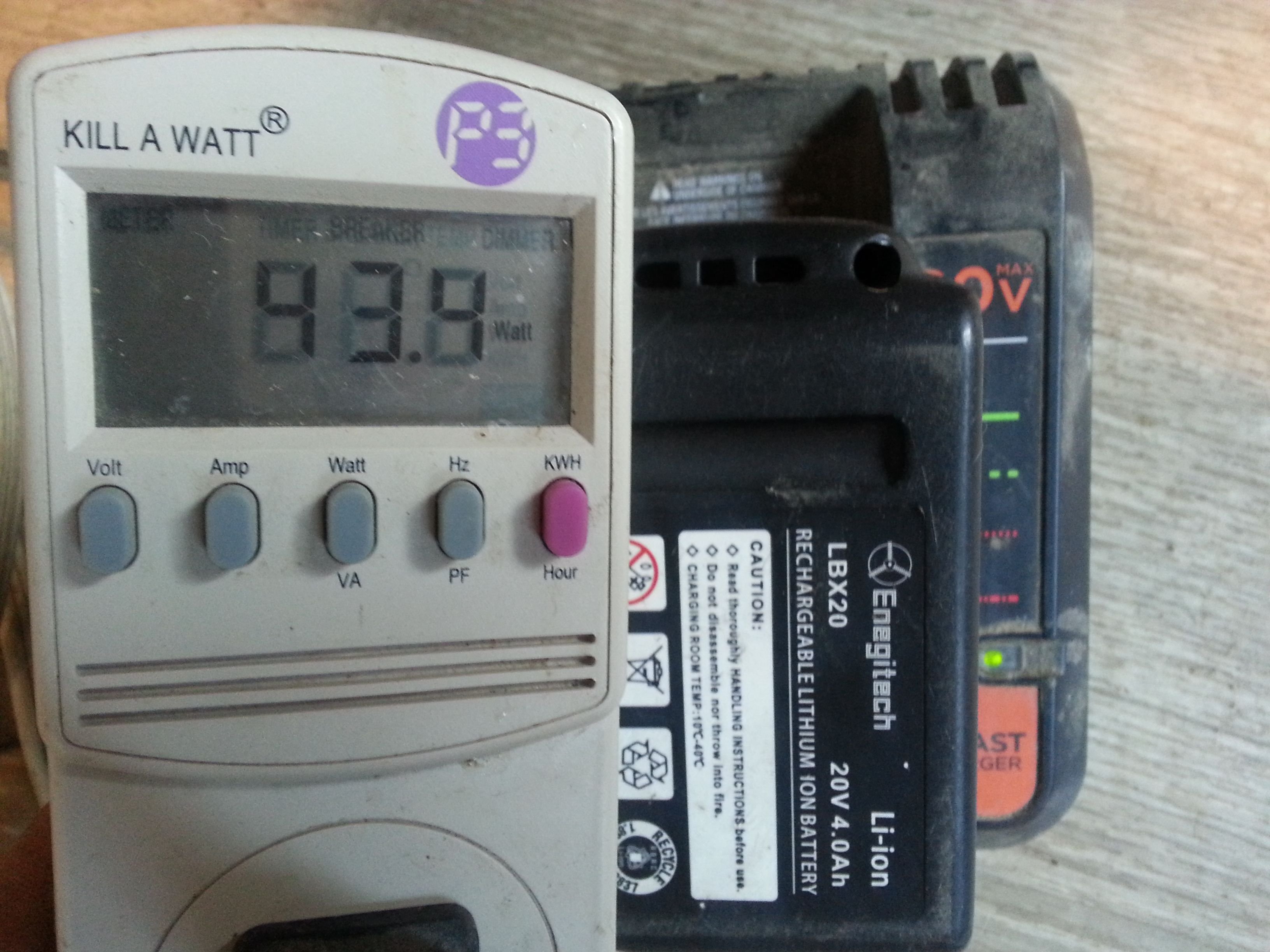

Link: Power Audit with the Kill-A-Watt Power Meter
Household Power Audit
A great way to calculate your daily power needs is with a power audit. The Kill-A-Watt power meter is a great way to audit the appliances and devices in the household to see how much power they really use. The link above to a previous post has more information about the Kill-A-Watt power meter use. The efficiencysmart.org's Efficiency Smart Usage Chart PDF File has the power usage of the most commonly used household appliances and devices - useful for a household power audit.

Power Inverters
Power inverters change the 12 volt DC battery power to a household Alternating Current for powering household appliances, devices, tools, pumps, and fans - anything that would plug into the wall outlet of a house. If you are wanting to power a high power device like an 1800 watt compressor, then you would want at least a 2500 watt power inverter to be sure the inverter can provide enough power. If you are only trying to charge a laptop, some power tools, and small devices, a 300 watt power inverter would be sufficient and more efficient.
Pure Sine Wave Vs. PWM Inverters
Pure Sine Wave inverters put out a cleaner electrical current than Pulse Width Modulation inverters. Some computers and electrical equipment may be sensitive to this. The electrically noisy PWM inverters have electrical waves that look like jagged up and down staircases - when compared to the smooth up and down curves of the pure sine wave inverters - see the picture below.
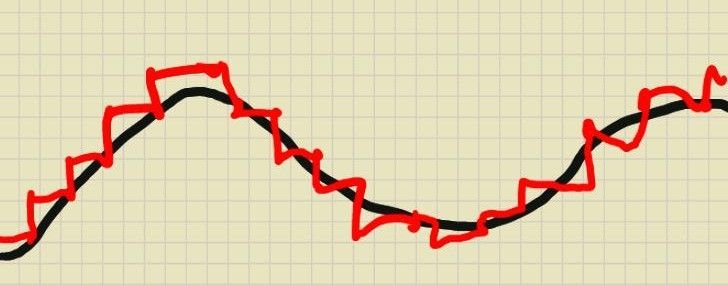
Link: Choosing the Right Inverter for Your Power Needs
I personally view PWM inverters as a short term solution and Pure Sine Wave inverters as a long term solution for more delicate electronics. For more information about power inverters, click the post link above.

Backup Generator and Battery Charger
It's always good to have a backup for many short cloudy days. A backup generator and battery charger help smooth out a solar power system that is being added to over time. I have a 3000 watt gasoline generator that powers a 70 amp -12 volt battery charger. Running the generator and charger for a hour fully charges up the 800 amp hour battery array. With a fully charged set of batteries the generator is turned off. The generator is decently efficient, it uses about a dollar worth of gasoline to run for an hour. Knowing How to Pull Start a Small Engine may be useful.

Off-grid Solar Power Strategy
The most difficulty with smaller battery storage systems have is running the refrigeration - because it could be running at any time, day or night. After the refrigeration can be kept running, most other appliances and devices can be run and charged during the daytime when there is ample power. Hot water we currently heat on the wood stove top in the winter and the rocket stove in the summer. On demand propane and small tank electric water heaters are possible substitutes. We currently use wood stove top, outdoor propane burners and pizza oven, and an electric bread machine for cooking. With enough solar panels, electric cooking could soon be an option. For clothes cleaning we have a small capacity and low power washer and spinner designed for apartments without laundry facilities. The clothes are hung outside to dry on the clothesline in the summer, or near the wood stove in the winter. As you can see, much of the solar power strategy is to use available electricity more efficiently and scheduling most of the power usage during the ample sunlight time of the day.
Global Homesteading Collective Radio Coming Soon...
 GHS Collective Radio
GHS Collective Radio
|

|
Many thanks to @ghscollective for the above podcast opportunity :)
Have a great day!
