
The internet. . .never meant to be in the hands of you and me!
Now that it is. . .they need to Control it!
See more on how they set the stage, stacked the deck if you will in the cabal's favor.
This is a rundown from a threat that got me pulled apparently permanently from Twitter because I dared to show his and his ex wife's true history.
Why is history or even Truth for that matter no longer allowed?
The White Hats dropped this article
https://qz.com/1145669/googles-true-origin-partly-lies-in-cia-and-nsa-research-grants-for-mass-surveillance/
It's a real eye opener.
It states this,
If the intelligence community wanted to conduct mass surveillance for national security purposes, it would require cooperation between the government and the emerging supercomputing companies.
To do this, they began reaching out to the scientists at American universities who were creating this supercomputing revolution. These scientists were developing ways to do what no single group of human beings sitting at work stations in the NSA and the CIA could ever hope to do: gather huge amounts of data and make intelligent sense of it.
In the 1970s, the agency responsible for developing emerging technologies for military, intelligence, and national security purposes—the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA)—linked four supercomputers to handle massive data transfers. It handed the operations off to the National Science Foundation (NSF) a decade or so later, ** which proliferated the network across thousands of universities and, eventually, the public,thus creating the architecture and scaffolding of the World Wide Web.**
They funded these computer scientists through an unclassified, highly compartmentalized program that was managed for the CIA and the NSA by large military and intelligence contractors. It was called the Massive Digital Data Systems (MDDS) project.
Because the challenges are not unique to any one agency, the Community Management Staff (CMS) has commissioned a Massive Digital Data Systems [MDDS] Working Group to address the needs and to identify and evaluate possible solutions.”
Guess who got two of those grants? Yes. . .Sergey Brin and Larry Page, who were grad students at Stanford when these were given out and of course became Google founders.
As people were doing their searching inside this vast data set. . .the intelligence community leaped upon the opportunity to uniquely identify and track individual users.
The grants were to be directed largely through the NSF so that the most promising, successful efforts could be captured as intellectual property and form the basis of companies attracting investments from Silicon Valley. This type of public-to-private innovation system helped launch powerful science and technology companies like Qualcomm, Symantec, Netscape, and others, and funded the pivotal research in areas like Doppler radar and fiber optics, which are central to large companies like AccuWeather, Verizon, and AT&T today. Today, the NSF provides nearly 90% of all federal funding for university-based computer-science research.
It was the beginning of what in just a few years’ time would become Google. The two intelligence-community managers charged with leading the program met regularly with Brin as his research progressed, and he was an author on several other research papers that resulted from this MDDS grant before he and Page left to form Google.
And isn't this part interesting and helpful?
The grants allowed Brin and Page to do their work and contributed to their breakthroughs in web-page ranking and tracking user queries. Brin didn’t work for the intelligence community—or for anyone else. Google had not yet been incorporated. He was just a Stanford researcher taking advantage of the grant provided by the NSA and CIA through the unclassified MDDS program.
NSF Grant IRI-96-31952 Data Warehousing and Decision Support
This states Google along with Amazon were indeed supported by an NSF grant!
The 1998 Report mentioned several achievements of the PI and students supported by previous NSF grants.
Last year, we mentioned two startups that developed from research under this and predecesor grants, Junglee Corp., bought by Amazon.com in 1998, applied information-integration technology to the Web. Google is a search engine company whose growth has brought it to the first rank, and that is growing faster than any of its competitors. Its core technology, which allows it to find pages far more accurately than other search engines, was partially supported by this grant.
This year, Enosys has started operation to provide XML-based information-integration in a particular vertical marketplace; it uses semistructured-data technology partially suppored by the grant.
source here http://db.cs.pitt.edu/idm/reports/1998/9631952.html
Research paper titled
What can you do with a Web in your Pocket?
Sergey Brin
Rajeev Motwani y
Lawrence Page z
Terry Winograd
In the work presented in this paper we take advantage of one central idea: the Web provides its own metadata
through its link structure, anchor text, and partially redundant content. This is because a substantial portion of the
Web is about the Web. To take full advantage of this data would require human intelligence or more. However,
simple techniques that focus on a small subset of the potentially useful data can succeed due to the scale of the
web. A technique that might capture only one percent of the available information might still be very useful.
Because size is so crucial to these techniques, and the amount of publicly available information is likely to grow
rapidly, it is important to maintain a large Web repository like our Stanford WebBase.
The size of the World Wide Web is an elastic number. There are many automatically generated infinite Web
spaces, there is a large amount of duplication, and the Web changes every day. Nonetheless, a recent estimate
has put its size at about 200 million web pages in November 1997 [BB98].
In 1994, one of the first web search engines, the World Wide Web Worm [McB94], had an index of 110,000
web pages and web accessible documents. As of March, 1998, the largest search engines claim to index from 2
to 110 million web documents [Sul]. It is foreseeable that by the year 2000, a comprehensive index of the Web
will contain over a billion documents.
The Stanford WebBase is designed to store a significant subset of the text content of the Web for research
purposes. It currently holds roughly 25 million web pages and will soon expand to approximately double that
size. The repository itself is roughly 150 GB of HTML (stored compressed in 50 GB). Additionally, we keep an
inverted index of the text, which includes word position and font information, occupying an additional 50 GB.
Finally, various metadata including URL’s and link structure occupy another 10 GB .
Source here http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.36.2806&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Written in 2015 by Dr. Bhavani Thuraisingham
January 25, 2015

The challenges remain the same; we have to develop data management and analysis technologies to handle massive amounts of data.
However the massiveness has changed. From several terabytes to a few petabytes of data back in the
1990s, we have now moved on to several petabytes to exabytes and even zetabytes of data. Why?
Because of the World Wide Web, social media, mobile technologies and developments in the human
genome project, as well progress in bioinformatics, geoinformatics, security informatics, and
multimedia/video processing, among others. Massive amounts of data about entities and the relationships
between them and the evolution of these relationships have to modeled, stored, managed, queried and
analyzed. The world population has increased by over 25% in the past 20 years and hundreds of millions
of people from all over the world are joining social media. It is expected that by 2020 50 billion devices
will be online and that’s only seven years away. Therefore we need to be able to securely and efficiently
handle the zetabytes of data without violating the privacy of individuals. This is a daunting task.
And They all Sure do Work Together as stated here. . .
I am very pleased
to see that not only federal agencies such as the National Science Foundation and the Defense and
Intelligence organizations are focusing on big data, practically every large company such as Google,
Facebook. Microsoft, Oracle and IBM are starting initiatives. We all have to work together to tackle the
big data challenge and make the world a better place to live.
Source,
https://www.utdallas.edu/~bxt043000/Motivational-Articles/Big_Data-Have_we_seen_it_before.pdf
So Brin and Pages story of Googles creation Does mention This grant,
https://www.nsf.gov/awardsearch/showAward?AWD_ID=9411306
And the fact that it was over $4.5 million
So why in their research paper titled,
“The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine,” did they thank NSF and DARPA for their grant to stanford, but not the MDDS program or Massive Digital Data Project which were managed by large military and intelligence contractors for the CIA and NSA?
Now remember, this grant was designed exactly for what Google became and is what we know today.
Remember when Wired claimed this in 2010?
It's not the very first time Google has done business with America's spy agencies. Long before it reportedly enlisted the help of the National Security Agency to secure its networks, Google sold equipment to the secret signals-intelligence group. In-Q-Tel backed the mapping firm Keyhole, which was bought by Google in 2004 – and then became the backbone for Google Earth.
U.S. spy agencies, through In-Q-Tel, have invested in a number of firms to help them better find that information. Visible Technologies crawls over half a million web 2.0 sites a day, scraping more than a million posts and conversations taking place on blogs, YouTube, Twitter and Amazon. Attensity applies the rules of grammar to the so-called "unstructured text" of the web to make it more easily digestible by government databases. Keyhole (now Google Earth) is a staple of the targeting cells in military-intelligence units.
Recorded Future strips from web pages the people, places and activities they mention. The company examines when and where these events happened ("spatial and temporal analysis") and the tone of the document ("sentiment analysis"). Then it applies some artificial-intelligence algorithms to tease out connections between the players. Recorded Future maintains an index with more than 100 million events, hosted on Amazon.com servers. The analysis, however, is on the living web.
"We're right there as it happens," Ahlberg told Danger Room as he clicked through a demonstration. "We can assemble actual real-time dossiers on people."
Both Google Ventures and In-Q-Tel made their investments in 2009, shortly after the company was founded. The exact amounts weren't disclosed, but were under $10 million each. Google's investment came to light earlier this year online. In-Q-Tel, which often announces its new holdings in press releases, quietly uploaded a brief mention of its investment a few weeks ago.
Both In-Q-Tel and Google Ventures have seats on Recorded Future's board. Ahlberg says those board members have been "very helpful," providing business and technology advice, as well as introducing him to potential customers. Both organizations, it's safe to say, will profit handsomely if Recorded Future is ever sold or taken public. Ahlberg's last company, the corporate intelligence firm Spotfire, was acquired in 2007 for $195 million in cash.
Still back in the day prior to Schmidt building his robot army or possibly in conjunction with. . .
Google CEO Eric Schmidt hosted a town hall at company headquarters in the early days of Obama's presidential campaign. Senior White House officials like economic chief Larry Summers give speeches at the New America Foundation, the left-of-center think tank chaired by Schmidt. Former Google public policy chief Andrew McLaughlin is now the White House's deputy CTO, and was publicly (if mildly) reprimanded by the administration for continuing to hash out issues with his former colleagues.
In some corners, the scrutiny of the company's political ties have dovetailed with concerns about how Google collects and uses its enormous storehouse of search data, e-mail, maps and online documents. Google, as we all know, keeps a titanic amount of information about every aspect of our online lives.
But unease has been growing. Thirty seven state Attorneys General are demanding answers from the company after Google hoovered up 600 gigabytes of data from open Wi-Fi networks as it snapped pictures for its Street View project. (The company swears the incident was an accident.)
"Assurances from the likes of Google that the company can be trusted to respect consumers' privacy because its corporate motto is 'don’t be evil' have been shown by recent events such as the 'Wi-Spy' debacle to be unwarranted," long-time corporate gadfly John M. Simpson told a Congressional hearing in a prepared statement. Any business dealings with the CIA's investment arm are unlikely to make critics like him more comfortable.
Source: https://www.wired.com/2010/07/exclusive-google-cia/
Very quickly. . .In-Q-Tel
States this on their page,
Bridging technology, venture, and intelligence
STARTUPS
IQT identifies startups with the potential for high impact on national security.
VENTURE CAPITAL
IQT works side-by-side with the venture capital community to identify great startup technology for our customers. Our areas of interest include cybersecurity, biotechnology, novel materials, remote sensing, deep learning for data analytics, and much more.
NATIONAL SECURITY
IQT accelerates cutting-edge technologies into the U.S. Intelligence Community to protect and preserve national security.
So Not for Profit. . .
IQT is the not-for-profit strategic investor that accelerates the development and delivery of cutting-edge technologies to U.S. government agencies that keep our nation safe. Our work bridges the gap between the challenging technology needs of the national security agencies, the rapidly changing innovations of the startup world, and the venture community that funds those startups.

And for now they also have IQT Labs which states,
IQT Labs explore the art of the possible in emerging technology areas of interest to national security. These include cybersecurity, biotechnology, commercial space, and advanced data analytics.

Source: https://www.iqt.org/
You will recall Q pointing towards keyhole. Do you remember what they were known for?
This written in 2005,
In a continued effort to connect searchers with the information they need whether it’s across the Internet or in their neighborhood, today, Google announced the integration of Keyhole, a digital mapping service acquired by Google in 2004, into Google Maps. The integration enables Google Maps users to view maps and directions through Keyhole’s satellite and aerial high resolution digital photos. The new functionality is also available on the maps shown through Google Local.
The traditional graphical maps provided by Google Maps are still available through the service, as well as, Google Local. In addition, users can now select ‘Satellite’ mode and see actual overhead views of the area or route they have selected. As with the original Google Maps, the Keyhole maps enable users to zoom in and out, and navigate the satellite and aerial high resolution digital maps dynamically in any direction.
Keyhole will continue to offer its Keyhole 2 LT and PRO software products that provide interactive access to a streaming 3D global database of imagery and mapping information.
Source: https://www.searchenginejournal.com/keyhole-now-live-on-google-maps/1527/
detailed map of Keyhole and near places
Google Local — Keyhole mapWelcome to the Keyhole google satellite map! This place is situated in Delta County, Colorado, United States, its geographical coordinates are 38° 41' 35" North, 108° 18' 30" West and its original name (with diacritics) is Keyhole. See Keyhole photos and images from satellite below, explore the aerial photographs of Keyhole in United States.
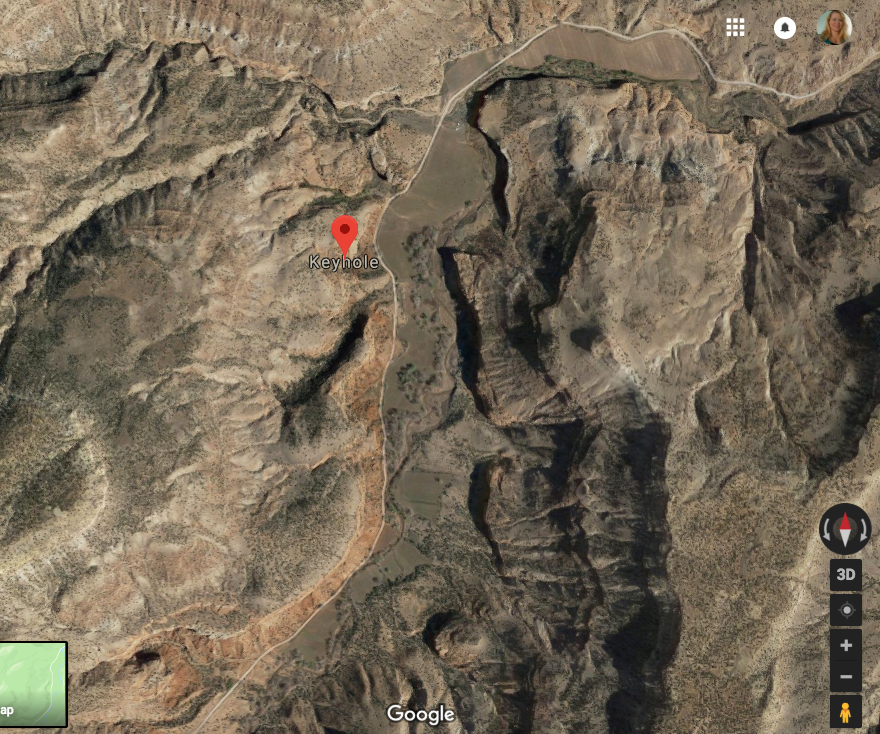

Source: http://www.maplandia.com/united-states/colorado/delta-county/keyhole/
A follow up is coming out on the rest of this Qanon drop as this is the mother of Anne Wojcicki, who was married to Brin. . .Anne herself started a genomics and biotechnology company named 23andme.
23 based on human's 23 chromosomes. Now why do they want to tamper with it? What do they want to mix it with?
Do they already have a way to do so? You know the answer!
Now, this is her mother. . .
Esther, 77, who herself has become an international figure in education and the founder of Palo Alto High School’s media program, the largest in the nation. Affectionately called “Woj” by students (including actor James Franco), Esther, who raised her ultra-successful daughters on Stanford U.’s campus where her husband Stanley worked as a respected physicist, is sought after by parents and teachers looking for advice on how to raise children. She’s even currently writing a book on the topic (expected to come out in spring 2019 from Houghton Mifflin Harcourt called "How to Raise Successful People”).
As Q stated, Susan is Anne's sister and
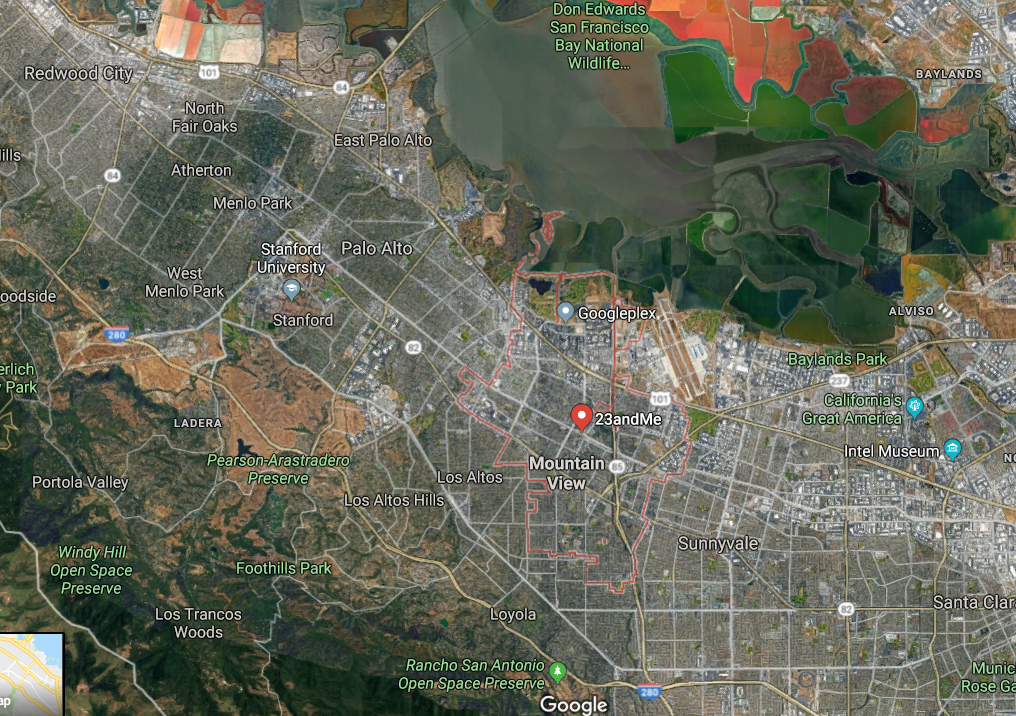
Did I mention. . .not only did Brin get those grants needed to lay the foundation and Platform for Google from Stanford where Anne's father worked, but the company Anne started is right there in Mountainview, CA where the Googleplex headquarters are and NASA Ames Research Center where they say on their page, "NASA Researchers Find Evidence of Planet-Building Clumps."
Location, location, location. Isn't this convenient for them?
Source:
https://www.nasa.gov/feature/nasa-researchers-find-evidence-of-planet-building-clumps
Won't that be useful for carrying out the Great Deception?
Oh the places you can go and the connections you Will Find!

Now if you look into Sergey Brin. . .as Q pointed out, he was born in Moscow.
He came here with his parents at the age of 6 and attended the University of Maryland.
His father is a mathematics professor at the University of Maryland, and his mother a researcher at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center.
Both parents are of Russian Jewish heritage.
More on these families and connections in a later post.
What are your thoughts on Qanon's latest drop concerning Google? Were they a CIA construct? Do you feel they have citizens' best interests at heart? Let me know in the comments below. Keep #FightingTheGoodFight in spite of all those haters out there! Good Will Overcome the evil ones!
