
Introduction
This is the time for a great genius. Of all the participants of the 5th Solvay Conference, he is the best known to the general public. For many considered the greatest man of all time. Did he deserve such a title? I will try to answer this question in the fourth part of the IQ overload series. If somehow you do not know who I'm talking about, you didn't read the title of the article - in this post you will be able to read about the life and achievements of Albert Einstein, one of the most important physicists of the XX century.

image credits: Wikipedia
Early years
It all started on March 14, 1879 at 11:30 in the city of Ulm, where Albert Einstein came into the world. By the way, I have always been curious whether the parents of great people - such as Einstein - have a sense of how important a person in the future will be. Returning to parents, both father Hermann and mother Pauline were Jewish. Hermann Einstein had been selling featherbeds until the idea of his brother that they will produce gas installations. The creator of the theory of relativity had one sister - the younger Maja.
Next years Albert spent in Munich, where his father's production plant was. However, after some time Albert's father's business ceased to generate satisfactory profits and in 1894 the family of a young genius went to Milan. Albert was to stay in Munich under the care of a distant family to complete a school where, contrary to universally valid myths, he had very good results and was one of the best students. However, young Einstein managed to be without parents for only half a year, then left school and decided that he will prepare himself for the university.
The first attempt was in 1895 and he failed. Einstein tried to get to Swiss Federal Polytechnic in Zürich where he needed special approval because he was two years younger than the minimum age allowed. However, he got permission, but he failed to pass the examinations in the humanities subjects and did not get into a polytechnic (tests in mathematics and physics went very well to him). The next year he spent in Aarau, where he graduated from high school and thus prepared for his second attempt to join the Swiss Federal Polytechnic in Zürich. This time he succeeded.

image credits: Wikipedia
Swiss Federal Polytechnic and Mileva
At the same time as Einstein at the Swiss Federal Polytechnic study began a Serbian woman Mileva Marić, who also was a passionate physicist. Albert Einstein was very interested in Mileva, because she was one of the few women in Polytechnic and in addition she was really fascinated by physics. The young fell in love and it is assumed that since then Mileva has helped Einstein with a few physics ideas. This relationship, however, wasn't approved by Einstein's mother (presumably because of the origin of Mileva).
In 1900 it was time for the final exams at the Polytechnic that Albert passed and Mileva did not. A year later, Einstein's partner became pregnant. Mileva spent the last part of her pregnancy and childbirth in her homeland - Serbia, where a daughter of a couple - Lise - had been born. Mileva probably gave her for adoption and Einstein could have never seen her. The couple married in 1903, a few months after Einstein's father death. A year later was born the first of two sons of Albert and Mileva. Returning to Polytechnic time; Einstein offended many lecturers, accusing them of not being open to new ideas. After graduating from the Polytechnic, Albert was looking for a work as a lecturer, but he did not succeed. After some time he found a job, but in a patent office, where he had contact with interesting ideas. However, Einstein believed that it was not work for him, he thought he should deal with theoretical physics.

do you admire my drawing skills? ;D
Year 1905
Most people when hear the name Albert Einstein think of the famous equation E=mc2. This dependence was discovered in a year called Annus mirabilis (wonderful year) of Einstein. Let's start with the fact that in this year Albert got his PhD at the University of Zurich. In the same year he explained Brownian motion - the random movements of the particles in the fluid. He also explained the photoelectric effect using photon, for which he later won the Nobel Prize. Finally, the most important publication - "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies" - introducing a special theory of relativity.
Special theory of relativity
Both the special theory of relativity and its generalized version have already many publications with explanation, so I will present them only briefly. Einstein wondered what would happen if he sat down at the end of the beam of light and traveled with it. He wondered if he would see its end. Years later he published a paper in which he presented two basic assumptions:
- The laws of physics are the same in all inertial systems.
- The speed of light in the vacuum is constant, independent of the observer, and is the maximum speed of information transfer.
What did Einstein mean by saying that the speed of light does not depend on the observer? Imagine the situation from the picture above. By observing the rays of light from the Earth we see that they are moving at the speed of light c. Looking at the light from a rocket that moves at 0.9c, according to classical physics we should infer that we observe that the light is moving at 0.1c. This is not a valid reasoning, however. Einstein explained that the observer on the rocket also sees the light moving at c speed! Out of these two assumptions, he made some interesting consequences, such as the time dilation.

image credits: Wikipedia
Next years of genius
Over the next years, Einstein continued to work in the patent office and developed his thoughts. In 1909 he received the title of professor theoretical physics at the University of Zurich, and in 1913 Max Planck offered him a place at the Prussian Academy of Sciences. All this time Einstein couldn't live with that if he suddenly removed a massive object like the Sun, then according to classical physics, it would immediately remove its gravitational influence even between objects that are miles away. This would mean that we can transfer information at a speed faster than the speed of light, with what Einstein could not agree with. So he published in 1915 the theory of gravity - the general theory of relativity. He showed that spacetime is curved. He said that objects which have mass deform spacetime. For example, while staying near a very massive object, time flows more slowly than for an observer that is not near a massive object.
Nobel Prize
Einstein's Nobel Prize has been a subject of controversy. He received it not for great theories (special and general theory of relativity), but for explaining the photoelectric effect, and for the indefinite "for his services to theoretical physics" From 1910 to the award in 1921 he was nominated 10 times, but each time someone else was rewarded. However, Genius never received a prize money, because in 1919 he divorced Mileva and one of the conditions was that if Albert wins the Nobel Prize, then the whole amount will be paid to Mileva.
What did he think of quantum mechanics?
In the 1920s there was a rapid development of quantum mechanics. What was Einstein thinking about it? Of course, he accepted it, but in the year of the 5th Solvay Conference, where a group of supporters of Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics led by Bohr announced that quantum mechanics was already complete. Einstein disagreed. He did not accept the probabilistic nature of the microworld. He also did not acknowledge that entangled particles can interact with each other immediately - according to quantum mechanics by checking the state of one we have instant information about the state of the other. He called it "a spooky action at a distance". He thought there must be hidden variables that we just do not know yet.
Einstein in the USA
When anti-Semitism grew in Germany and the Nazis seized power, it was obvious to Einstein that he could no longer stay in Berlin, where he had worked since 1914. At the end of 1933, Albert went to the United States permanently, where he began work at the Institute for Advanced Studies at Princeton. In the same year he renounced German citizenship, still possessing Swiss citizenship. I'm sure that not everyone knows about the letter that Einstein wrote to US President Franklin Delano Roosevelt in 1939, in which he urged the United States government to begin work on the atomic bomb because he thought Nazi Germany could already begin work on it. Well, at least I've never heard of it before.
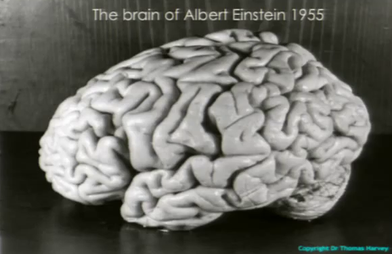
image credits: Wikipedia
The Einstein's brain
Albert Einstein ordered his body to be cremated as quickly as possible, and his ashes scattered at not known place. However, not everything went according to his plan, because of the pathologist Thomas Stoltz Harvey who... stole his brain. He thought that he can't allow the brain of such a great genius to remain not studied. So he fragmented the brain of the creator of the theory of relativity, and some fragments were sent to research. What is interesting, while he was changing his place of residence, Einstein's brain traveled in a small refrigerator for beer. Now the brain of genius is at Princeton University Medical Center. If you want to read about the results of the research, I recommend you look at the article in the References section.
Conclusion
Albert Einstein was a great physicist, I am not afraid to use the statement that he was the greatest genius of the twentieth century. There was made many books, films and even TV series about him. Not only were his achievements fascinating, but also life.
References:
- more about Einstein: Wikipedia and the Nobel Prize website
- more about special relativity: Wikipedia
- more about general relativity: plus.maths.org
- more about Einstein's brain and results of research: National Geographic webiste
0. IQ overload: the story of one photo
1. IQ overload: Maria Skłodowska-Curie
2. IQ overload: Niels Bohr
3. IQ overload: Albert Einstein (this post)
Don't forget to follow me, otherwise you can miss my new entries ;)
