How Life of a High Mass Star Ends?

In my previous posts on Life Span of Stars we discussed the journey of a Star from the part of a Nebula then becoming a Proto-Star, then turning into a Main-Sequence-Star.
After the Main-Sequence phase, the next phase depends upon the original mass of the star. There are two ways, stars can enter into the next phase based on their masses;
- If the mass of the Star is low (Stars with the mass equal to 0.08mass of Sun to 8masses of Sun are known as low mass stars), then the Star enters the next phase which is called The Red Giant Phase. After Red Giant Phase the star puffs off its outer gases into the space and the highly compressed core left which is named as the White Dwarf.
- If the original mass of the star is more than 8 Solar Masses then the next phase is known as Red Supergiant Phase. Red Supergiant Stars are the largest known stars (but not massive). They are very similar to Red Giants but larger in size.
Betelgeuse is the Red Supergiant Star held in the constellation Orion. It will explode as a Supernova in the future.
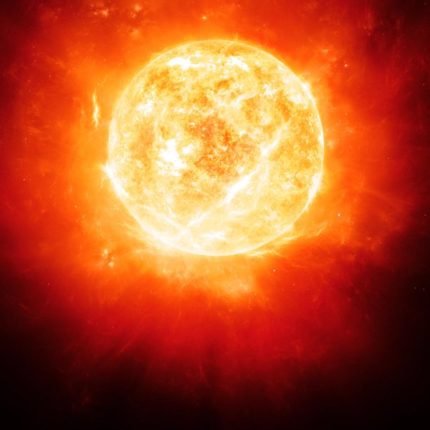

Why such a humongous explosion happens in Red Supergiant Stars?
Well, due to larger size of the star once all the Hydrogen is used up in the core then all left in the core is Helium. Due to very high mass of the core, it starts to collapse very fast due to gravity and fusion of Helium into Carbon starts rapidly. The reaction is known as triple alpha reaction.
But due to the large size again, the Gravity is still compressing the core and Carbon Starts to Fuse into Oxygen. Fusion of lighter elements into heavier elements keep going until it reaches the Fusion of Silicon into Iron.
As the fusion goes higher it gets faster and faster. For example a Star with a mass of 20 Suns can fuse its Carbon into Oxygen in about 10,000 years but it can fuse all its Silicon into Iron in days and Iron Core only lasts a few hours and you know what happens next!! A huge explosion we name Supernova Explosion.
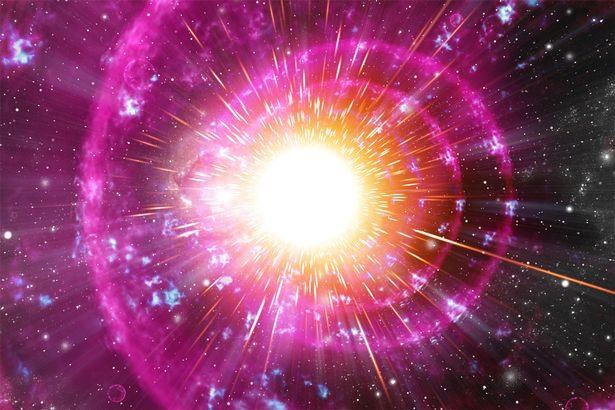

This explosion is extremely luminous in order of Billions times more luminous than our Sun. Once Supernova explosion happens it is one time event, there is nothing remaining, no star no core, all left is an expanding cloud of gases we name it as A Nebula.
What? A Nebula? Didn’t we hear this name before? Did we?
Yes, all stars start their journey from the part of a Nebula and many massive stars end their journey with Supernova Explosion giving birth to a new Nebula, which is a fertile ground for new stars to take birth.
Yes, a nebula named Crab Nebula is result of a Supernova explosion happened in the year 1054.
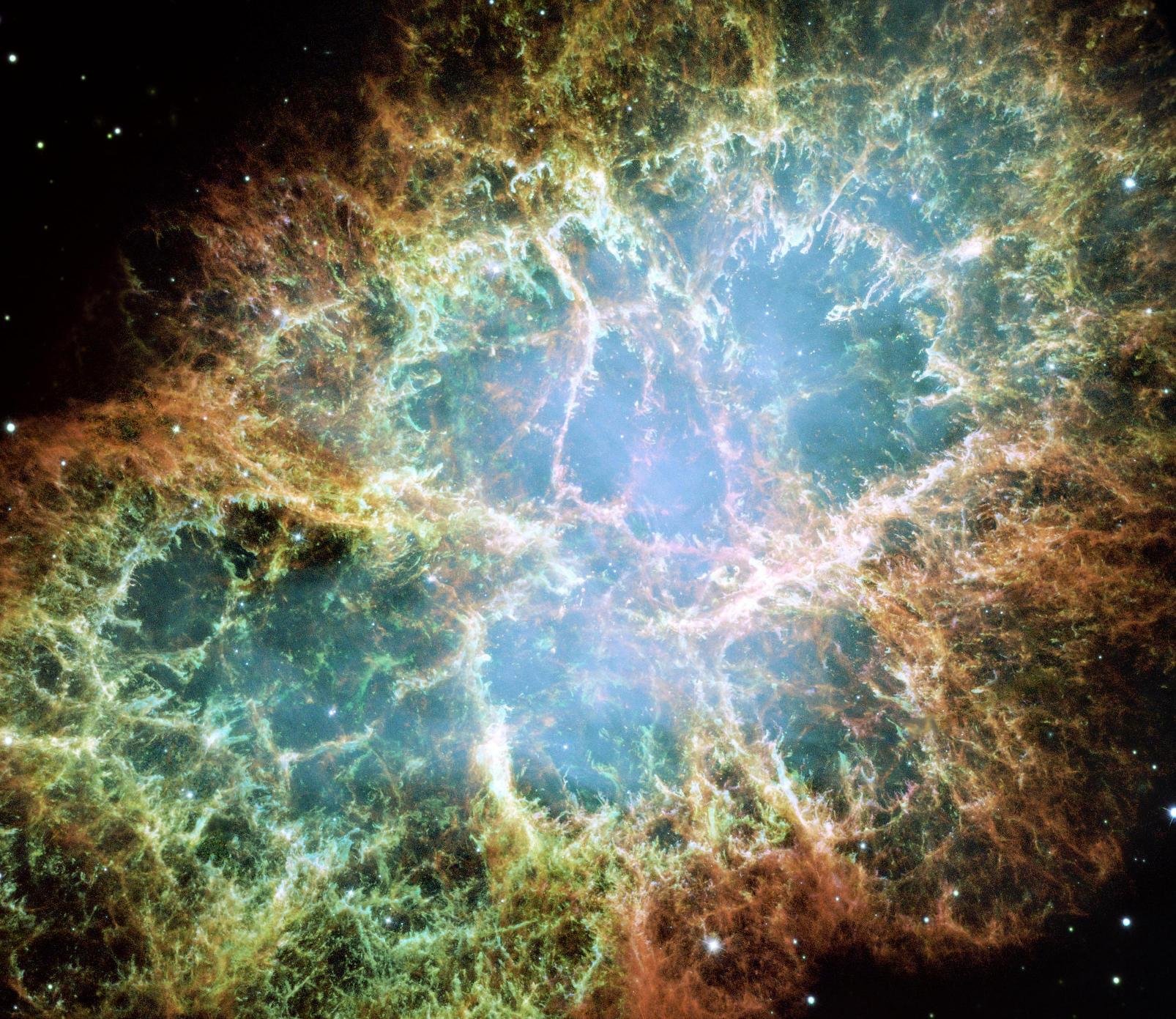
Yes, all the elements other than hydrogen and helium are formed in Stars. Hence I can say that my body is part of a Star, went through all the stages of a star life.
Following are the links to previous posts on Story of a Star:
@mathworksheets/story-of-a-star-in-the-womb-of-a-nebula
@mathworksheets/a-star-story-forming-the-protostar
@mathworksheets/story-of-a-star-a-brown-dwarf
@mathworksheets/fate-of-our-sun-story-of-a-star-continues
/@mathworksheets/our-sun-from-red-giant-phase-to-a-white-dwarf
That's all from me on life cycle of a star, folks. Will come back with some more interesting cosmology topics.
