Even if we aren't aware of it, our function of hearing is formed as a result of many chain events. Even if we don't like the shape of our auricles, even some people realize its presence when they have pain caused by otitis and even many of us don't know how a sound wave is turned into electrical signals in our inner ears and sensed by our brains, physiology of hearing is a miracle that I learned with admiration and admired as I learned.

Let's look at this miracle from a little closer and technically. I hope this draws your attention and I can be able to raise awareness. Today, I want to talk a little about outer ear and middle ear.
First, let's look at the stages of hearing, I think a general look at the rings of this chain will help us understand the concept better.
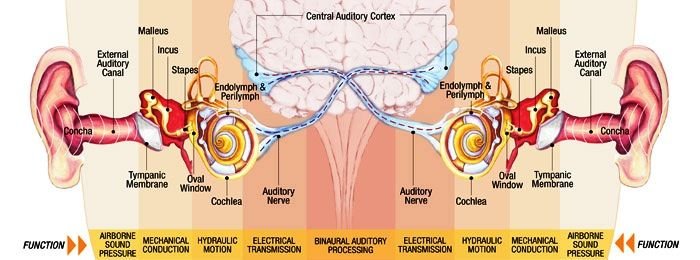
The part where the sound is collected from the atmosphere and transferred to the organ of Corti, we call this transmission. My topic for today's post.
Transduction: The process of turning a sound wave into neuronal energy.
Neural coding: The process of transmitting sound energy to nerve fibers.
Association: The combining and decoding process of nerve transmissions in the hearing center.
In the journey of sound till the organ of Corti, the body and the head have a blocking effect and the outer ear canal, the auricle and the middle ear have guiding and enhancing effects.
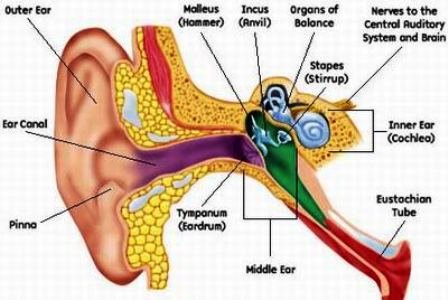
Outer ear canal, auricles, and the head
The outer ear plays a passive role in the process of hearing. It affects the spreading of sound in free space together with the body and the head and it ensures the acoustic signals reach the tympanic membrane. Some specialties of the head, body and the outer ear are thought to be important in ensuring the localization of sound. In this point, we come across the baffle effect and the shadow effect.
The pressure of the sound wave on the side of the ear that sound hits will increase and on the other side of the ear the sound wave pressure will decrease. This is called "Baffle effect". The interaural distance (the distance between 2 ears) is an important factor for the head's blocking effect. The distance between two ears is 0.6msn.
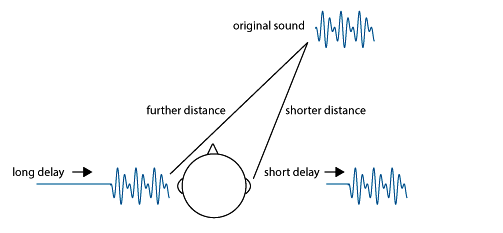
Another effect of the head is the shadow effect. The shadow effect is seen when the width of the head is bigger or smaller than the length of the sound wave. Let me tell you the function of the shadow effect in finding direction; The wavelengths of high-pitched sound are smaller than the width of the head and high-pitched sounds travel to the ear that is further away. So we can find the directions of high-pitched sounds easier than the low-pitched sounds.
The auricles: They collect all the sounds at about 135 degrees, frequency or wavelength, without discrimination of meaningful or meaningless. Most of this collected sound is just noises. It densifies the sound waves in the outer ear canal and provides an enhancement of around 6dBs. The outer ear canal acts as a resonator for the sound waves and the difference of temperature between the outer ear canal and the middle ear effects the transmission thus affecting hearing.
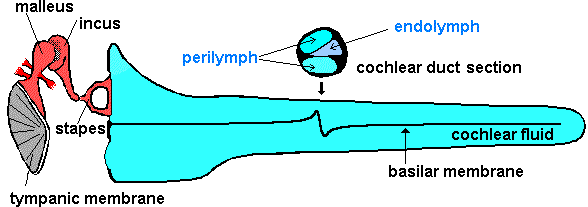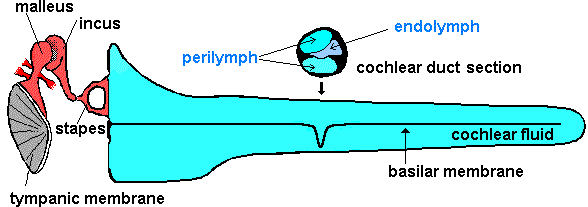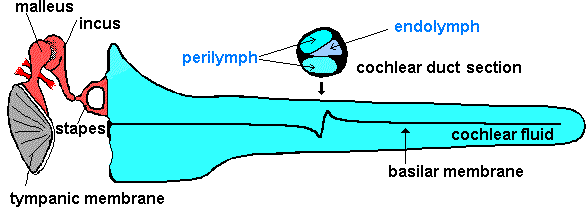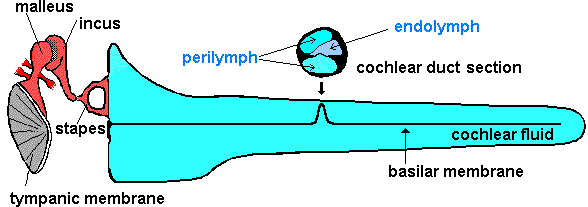
The sound waves we collect at the outer ear and determine the direction will face resonance in the outer ear canal. When they are going to the middle ear, the first thing that they encounter is the tympanic membrane. This oval shaped tense membrane vibrates at the same frequency as the sound waves. It is sensitive to pressure changes. The tympanic membrane has about 65mm2 area and a 0,0002dyne/cm2 stimulant will be enough to vibrate the tympanic membrane.
Middle ear ossicles
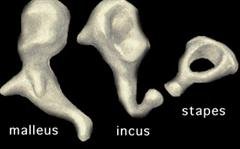 image source
image source
The sound vibrations are transmitted to the oval window through the ossicle chain. But because there will be a transmission from air to liquid during this transfer; the sound waves will lose energy while passing from air to liquid where air has a much smaller acoustic resonance than the liquid. The main part of the energy is absorbed by the liquid and only 1 in 1000 will pass to the inner ear. There will be approximately 30 dB of loss. The middle ear ossicles rise the incoming sound by 30 dB and tolerate this loss. How?
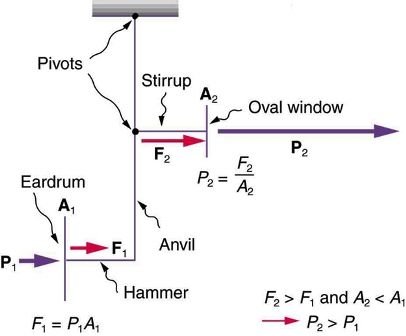
- Malleus and the incus will move as levers and enhance the sound proportional to 1/1.3, that's about 2.5 dB.
- The actual sound enhancing mechanism is; the surface difference between the tympanic membrane and the stapes bone.
The area of actively vibrating tympanic membrane is 55mm2. And the base area of the stapes bone is 3.2mm2. The meaning of the 17 times difference is that the sound will be 17 times enhanced. This provides about 27.5 dB of gain and at the total, the 30 dB will be compensated.
And there is a secret hero in the ear; the stapedius muscle. This muscle will pull the stapes bone by contracting and block the sound from entering the inner ear when it encounters high volume sounds. This protective reflex is very important. Because the pathologies caused by traumas can result in irreversible damages...
Goodbye for now...
)
references:
- https://www.britannica.com/
- http://www.who.int/occupational_health/publications/noise2.pdf
- Handbook of Clinical Audiology, Jack Katz,Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2002
