Oxytocin is best known as the ‘love hormone’. Despite this, there are many other, less well known, effects that oxytocin has on the body which I will be discussing in this article.
Figure 1. oxytocin
Oxytocin is a neurotransmitter in the brain, and can act as a hormone. It has many roles in pair bonding, relationships and social interactions. It is released during sex, while giving birth and during a hug.
Oxytocin is also released in a positive feedback loop during breastfeeding. When the infant begins to suckle, oxytocin triggers the ejection of milk from a mother’s breast in order to feed her child. This occurs because the suckling of the baby at the nipple is detected and a signal is relayed by spinal nerves to the hypothalamus. This stimulation causes neurones to synthesise oxytocin in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and consequently release oxytocin from the posterior pituitary gland in recurrent bursts. These bursts of oxytocin correspond to the secretion of milk.
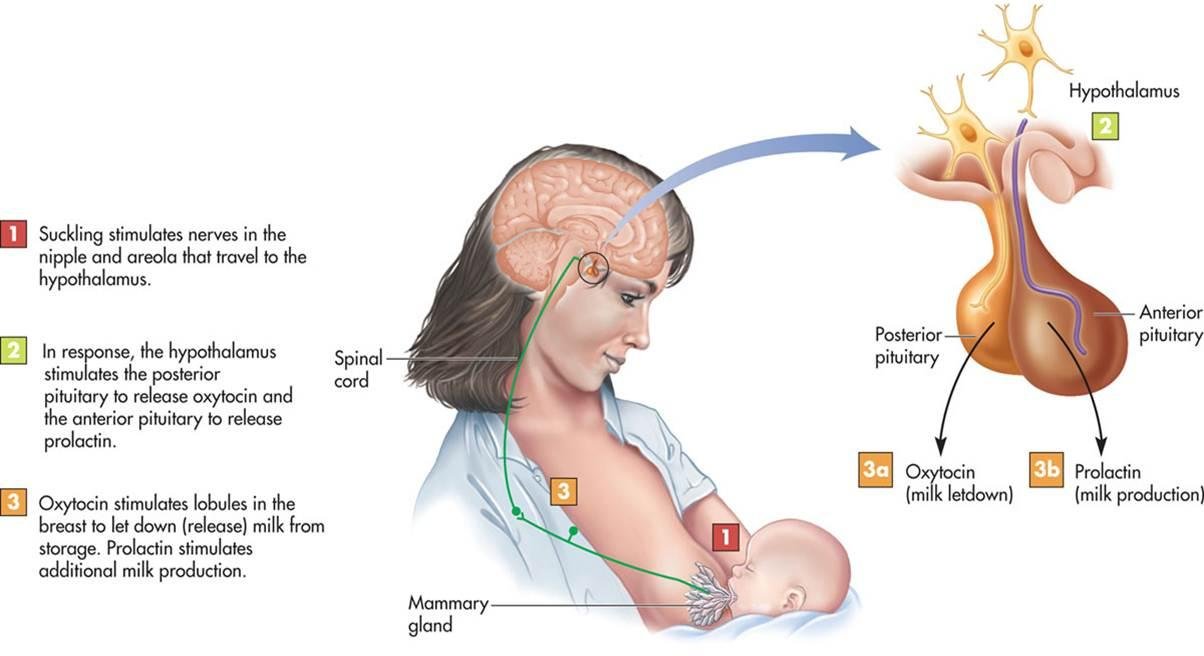
Figure 2. mechanism of oxytocin release during breastfeeding
In addition to this, oxytocin is released during an orgasm and unusual effects can occur if this is combined with a recent mother who is still breastfeeding her child. Since oxytocin is released during an orgasm, but also during lactation, when a mother (who is also breastfeeding) has an orgasm the sudden surge of oxytocin will simultaneously trigger the ejection of milk from her nipples.
This will cause the woman to eject milk upon orgasm!
But hold on, the oxytocin wouldn’t have an affect on breastfeeding if it is released in response to an orgasm would it?
The answer is, yes, of course it would. Unlike nervous responses to stimuli, which are very specific, hormones respond in a much more global manner across the entire body. As the oxytocin is released in response to an orgasm, it is circulated in the blood (like all hormones are). This means to have intracellular effects, oxytocin must bind to various receptors on the surface of cells. The way in which hormones like oxytocin bring about their effects is via these receptors, which have different intracellular responses. Each cell that is responsive to oxytocin will have a different receptor type. When oxytocin binds to these receptors, each cell will have a different effect depending on the cell type. Thus, in breast cells oxytocin binding to the receptor will produce lactation, but in other cells it will have different effects which will depend on the specific receptor that oxytocin binds to.
The ejection of milk from a mother during orgasm is an effect that results from the many roles of oxytocin throughout the body and the non-specific nature with which hormones act.
References:
Figure 1
Figure 2
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3183515/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxytocin
