PART 1: THREE TYPES OF IMPOSSIBLE

In this series, we will discuss wild stuff; going back in time, faster than light travel, giant insects, escaping black holes, non-locality, and perpetual motion machines. Scientists spend a large portion of their time thinking about the impossible. This may seem counter-intuitive, but by discovering which things are really and truly impossible they can define the line between possible and impossible. Things which are truly impossible always are so because of some law. If something was not impossible it would happen eventually. Things which never happen do so for a reason and understanding those reasons is the main way science expands its horizons. Scientists have developed a classification system to identify what degree of impossible something is.
1. Absolute Impossibility:
- Strongest type of impossible
- Involves a logical or mathematical contradiction
- Does not rely on any assumptions
- It is impossible on to itself
- Can not imagine any world where this could be true.
Greek mathematician Euclid of Alexandria,
author of the elements can be considered the father of Absolute Impossibility. He proved things impossible over a thousand years ago using a method he developed known as proof by contradiction.
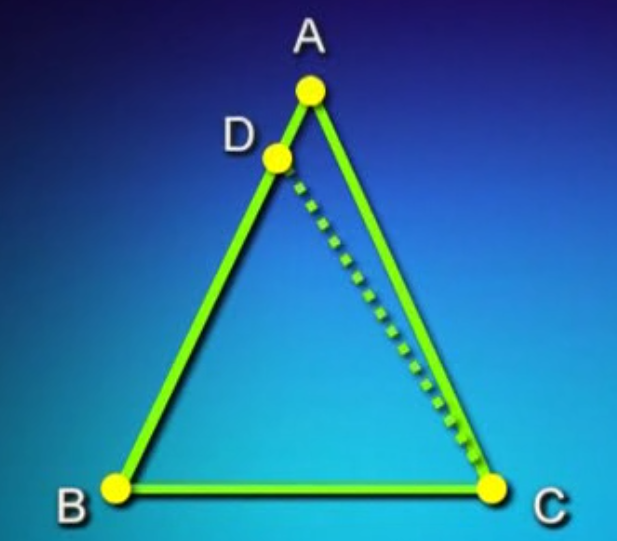
Proof by contradiction:
Prove X is true by assuming X is NOT true
If X being NOT true leads to contradiction
Then X must be true.
2. Derived Impossibility
- Not impossible by itself
- Impossible because it violates a known law of physics
- Contradicts accepted assumption about the world
- Imagine a world where such a thing could be true but not our world.
- Depends on the reliability of our assumptions and web of beliefs.
- Changes to our understanding of science can change status of these
Sir Issac Newton,
author of the Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica can be considered the patron of Derived Impossibility. His thought experience "Newton's Dumbell" explored the possibility of the law of action and reaction weren't true. He also used a variety of Euclid's proof by contradiction.

"Newton's Dumbbell"
Imagine two balls, ball 1 and ball 2 connected by a stiff rod.
If number 1 exerts a force on number 2
the force of number 2 on number 1 must be equal in strenth and opposite in direction.
What if one of the balls experiences a stronger force not equal and opposite?
This would create a Net force in one direction, accelerating the dumbbell without an outside force.
This violates the law of inertia, without an outside force, the dumbbell should not accelerate. This proves the law of action and reaction must hold true in the face of the law of inertia.
3. Statistical Impossibility
- Technically possible but practically impossible.
- Not impossible according to logic or laws of physics
- So overwhelmingly improbable that it can be regarded as "effectively impossible"
- The 2nd law of thermodynamics is an example of a statistical law.
Flip a coin 10,000x what are the chances you would get 10,000 heads?
Possible but odds 2 x 10 ^ 2010 or a 2 followed by 2010 zeros .
Scottish physicist James Clark Maxwell,
created the first color photograph and the thought experiment Maxwell's demon. To get more insight on this type of impossible we look to Maxwell when he postulated a thought experiment regarding a box with gas molecules in just the one side. Initially gas only fills one- half of the container. If we let time pass the gas will disperse and fill the whole container. What prevents the gas from going back to its original state? Nothing, it is just extremely improbable.

What are the odds that the gas molecules will all gather back in its original state on just one-half of the box?
The odds are 1 x10 ^150 billion trillion to 1 (a 1 followed by 150 billion trillion zeros) against that ever happening.
Given the amount of time before reaching a maximum entropy state of a universe, such things become statistically impossible.
We have learned today about the 3 types of impossible and how they shed new light on our understanding of reality. Next time you hear something is impossible you will be able to intelligently comprehend how and why that is true.
Stay tuned for Part 2.
follow @pjheinz
