Vaccines And The Immune System
In my last paper I wrote about skin vaccination in which cowpox pus is used to infect people to build their immunity to smallpox. If there wasn’t an infected cow to use, the doctors would infect a healthy cow not around the udder but in the belly where they could collect the most pus. Quart jars full of pus! A sharply pointed hollow prong was used to puncture the skin which was full of cow pus. And the doctor would puncture many people without disinfecting the hollowed out prong.

A spot, usually on the upper arm, is scraped by a lancet, so that the outer layers of the epidermis are removed; the spot is then rubbed with an ivory point, quill or tube, carrying the virus. A slight and usually unimportant illness or indisposition follows, and the arm is sore for a time, a characteristic scar remaining
An abscess would form and that’s when the doctors of the 1750-1800 declared that the patience had developed immunity to smallpox.
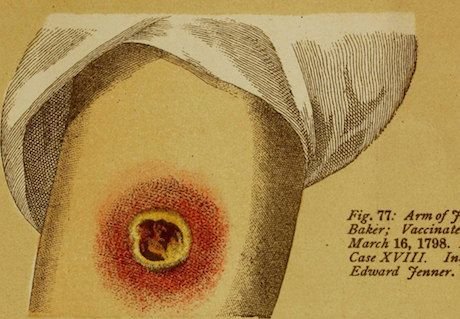
What I did not know at the time I started reading the history of medicine, so many people died of the vaccine. I don't know how many but it was enough for whole towns to refuse to get vaccinated. Check out my link at the bottom of my article which goes into the method developed by the town of Leicester. At that time no one knew how long one was immune to smallpox after surviving the vaccination.
The theory was that you would develop cowpox infection which is related to smallpox you would become immune. There were doctors at that time who were against this theory and warned there would be horrible deaths from infections. I will go into their arguments in my next article along with the conditions most poor people lived in which raised alarms among the more wealthy population. Huge portions of the population were stricken down by many diseases and these diseases didn't care about social and economic boundaries. The industrial revolution not only gave us assembly line products it gave us polluted cities and plagues.
The people who worked in the factories were paid little, couldn’t afford the basics people needed to live a healthy life. They lived in deplorable filthy conditions that lacked the basics we have today like clean running water and waste disposal systems. People were packed together like rats in a cage and had to work 12 hour days, this includes women and children. Children were allowed to run free on the streets because both parents and their older sibs had to work just to be able to eat.

During Edward Jenner’s time 1850-90s no one understood cellular or humoral immunity. The skin type of vaccine produced humoral immunity.

When the adaptive immune system is activated by the innate immune system, the humoral immune response (also: antibody-mediated immune response) triggers spe- cific B cells to develop into plasma cells. These plasma cells then secrete large amounts of antibody. Antibody circulate in the lymph and the blood streams. (Hence the name: humoral immunity.
Cellular immunity (also: cell-mediated immunity (CMI)) is an adaptive immune response that is primarily meditated by thymus-derived small lymphocytes, which are known as T cells. Here, two types of T cells are considered: T helper cells and T killer cells. T helper cells are particularly important because they maximize the capabilities of the immune system. They do not destroy infected cells or pathogens, but they activate and direct other immune cells to do so. Hence their name: T helper cells.
Cytokines are the hormonal messengers responsible for most of the biological effects in the immune system, such as cell mediated immunity and allergic type responses. Although they are numerous, cytokines can be functionally divided into two groups: those that are proinflammatory and those that are essentially anti-inflammatory but that promote allergic responses, link to NCBI Article
Vaccines don’t affect the innate immune system as much as I thought. Vaccines actually affect the adaptive immune system to a greater degree.
An example is giving infants vaccines they will usually develop more T helper 2 rather than Th1, Th1 is the cellular immune system that balances out inflammatory responses and tells the immune system where to go and what to attack. But if the child is older and given the same vaccine they develop more Th1.
How come the vaccine industry does not develop a protocol to check if the cellular immune system has been activated with a vaccine? I read that it is too expensive!
The cheap way to go is just to look for antibody. But that is a hit and miss type search because diseases like measles, you can have agammaglobulinemia, a disease which you cannot make antibody, but if you are infected with measles your immune system will still respond and your will recover just fine. Why? Because you don’t need that antibody for measles in order to become immune and you will have 75 years of immunity. Antibody just gives one a look at an immune response not a look at immunity. Antibody is produced by humoral immune system but have nothing to do with long term immunity which is the cellular immune system. Talk about a hit and miss protocol!
Vaccine science is still a hit or miss science like back during Edward Jenner’s time. Maybe not as gross with a needle like object dripping cowpox pus being jabbed into you skin.
But once you dig down into the data it’s not only imprecise, the science of vaccination for immunity is inaccurate. An example a patient can have high antibody levels for tetanus. There are people who developed high levels of antibody but got the worst case of tetanus. I’ve read of causes where there are people without any antibody for polio respond to the virus as if they were already immune. The antibody is the wrong marker when looking for immunity.

 A link to My Blog
A link to My Blog