
The first artificial satellite was launched October 4, 1957. Over the past 60 years more than 70 different countries and several private companies launched about 6,000 objects into the space.
1085 satellites are now in working condition, a large part belongs to the United States (450), then Russia (146) and China (135). The remaining 5,000 continue to rotate around the earth as debris.
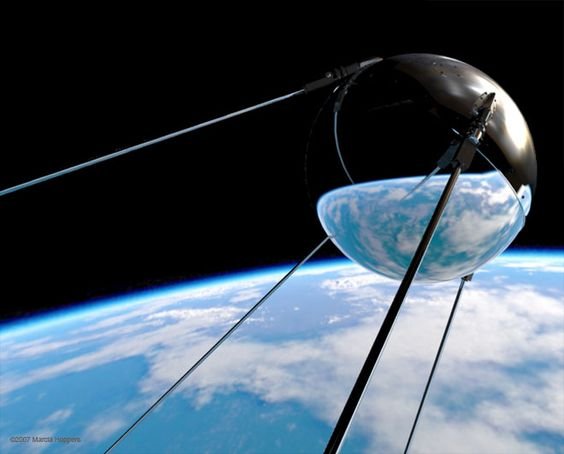

The first satellite Sputnik-1
The orbit on which the moving satellite, and its height depend on the purpose of the spacecraft. In rough form, we can divide orbits into three types, depending on their distance from the surface of the earth.
- Low-Earth orbit 160-2000 km, 500 operational satellites (the meteorological satellites and stations).
- Medium-Earth orbit 5000-20000 km, 50 operational satellites (communication and observation satellites)
- Geostationary orbit 20,000-50000 km. 535 operational satellites (satellites for weather, communication, monitoring solar activity).
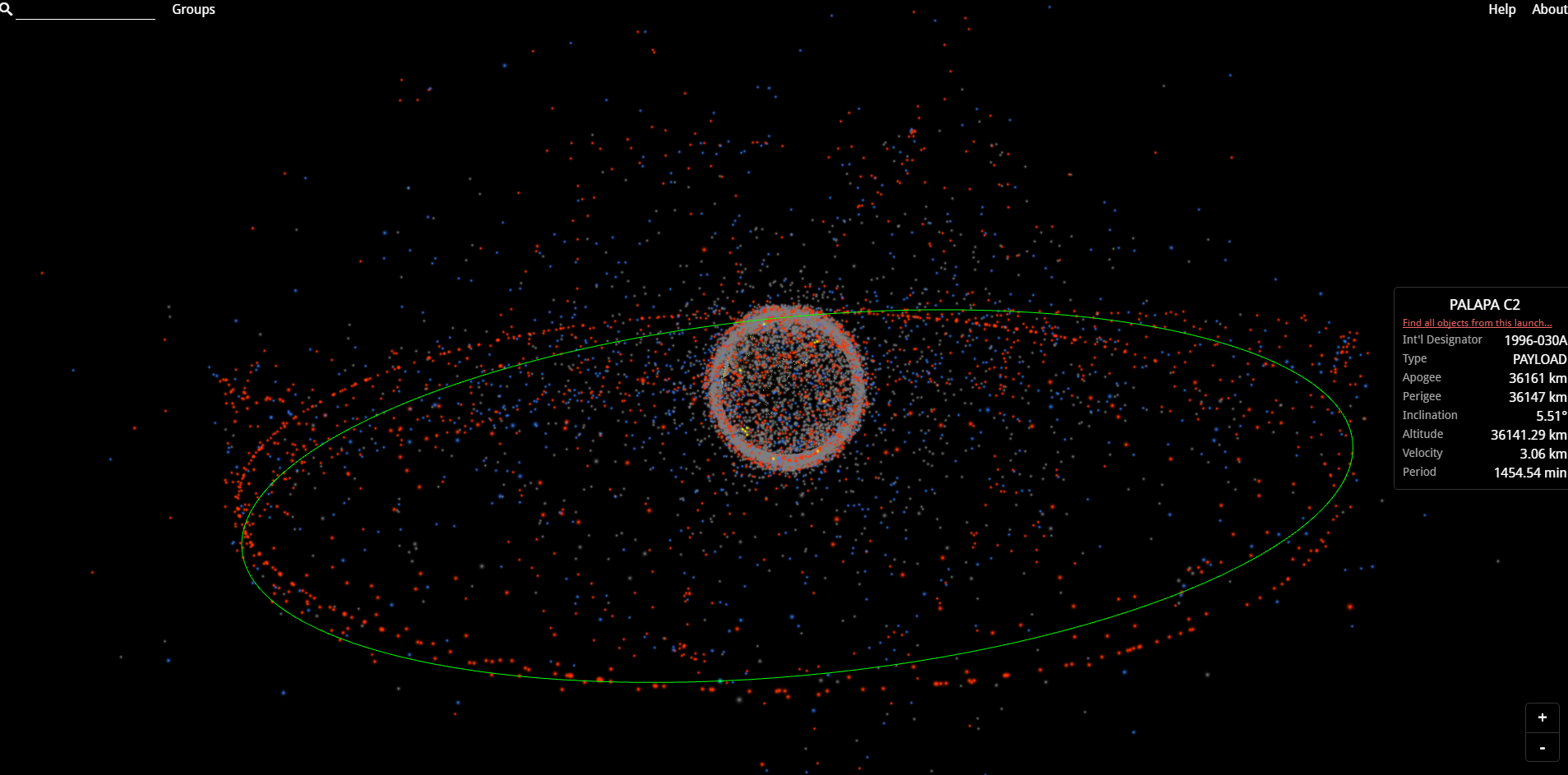
HERE you can use the interactive map to see all working and disabled satellites and their orbits.
So, if consider that 1085 satellites are distributed into these three orbits, you might think that we have enough free space to launch of thousands of new units… but it's not true. Inactive satellites (5000), boosters, and parts of spacecraft left in orbit as space debris, which can cause serious problems in subsequent launches.
The danger of space debris: The speed of movement of objects in earth orbit is at least 11,18 km/s (or 30.000 km/h). Such high rates of speed make even very small particles devastating.
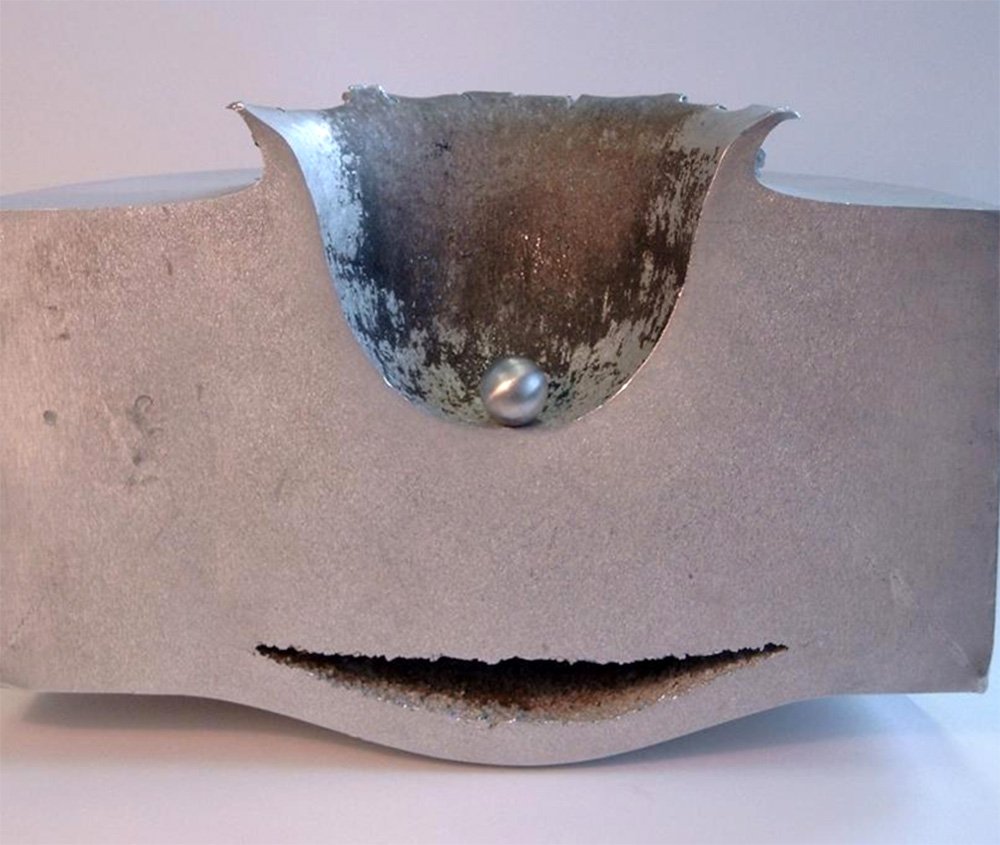

The ball (size of 1cm) crashed into a steel plate at speeds of 6.7 km/s
In 1983, the grain with diameter is less than 1mm left a crack in the window of the space Shuttle. If its size was 1 cm, the collision could lead to the destruction (power-on collision is equivalent to the explosion of anti-tank grenades).
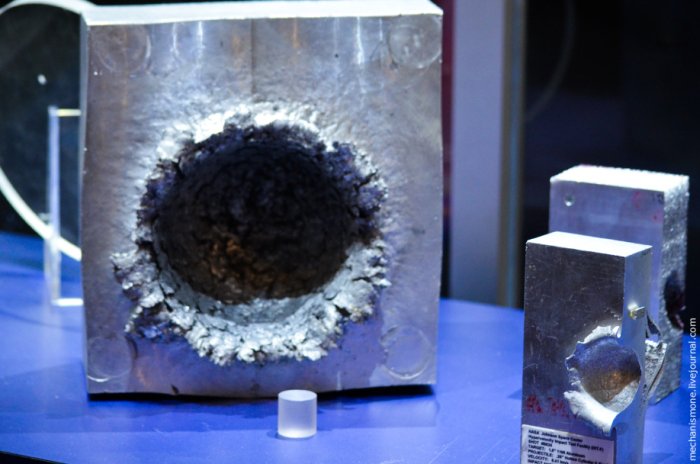

The result of the collision of the plastic piece of garbage (the size of 3cm) with aluminum protective shell of the satellite, at the speed of 7 km/s.
According to the latest data, today there are 300.000 objects at altitudes up to 2000 km, which belong to the category of dangerous space debris. Their total weight is 5000 tons.
- 20,000 objects have a size greater than 10 cm. Any spacecraft will be destroyed in the collision.
- 500,000 objects the size of 1-5 cm. In a collision can seriously damage a satellite or spaceship and destroy a portion of the compartments.
- 10.000.000 objects are smaller than 1 cm. Gradually reduce the strength of the hull and can destroy the solar panels.

These particles continue to face with old satellites, creating more debris after the collision and increasing the area of its distribution, is the Kessler syndrome.
This map shows the orbits of all objects larger than 5 cm.
It may seem that given the distances in space all this junk poses no threat- in this moment, pieces of debris fly in a radius of 8 km from the satellites every 2 minutes.
But when you consider how many satellites we continue to launch (for example: 4500 satellites for Elon Musk's WiFi project), you will understand that this range will be significantly reduced very fast.
Leaders in the pollution of the orbit: China- 40% (due to the weak technology), USA - 27.5%, Russia- 25.5%. The low-Earth orbit is the most contaminated, because it is here we show the most of cosmic activity.
Some debris will burn in the atmosphere, but it's not enough. Today, no country and no private company don’t have at their disposal a working space- scavenger. There are a number of projects, none of which has clear dates and even budget.
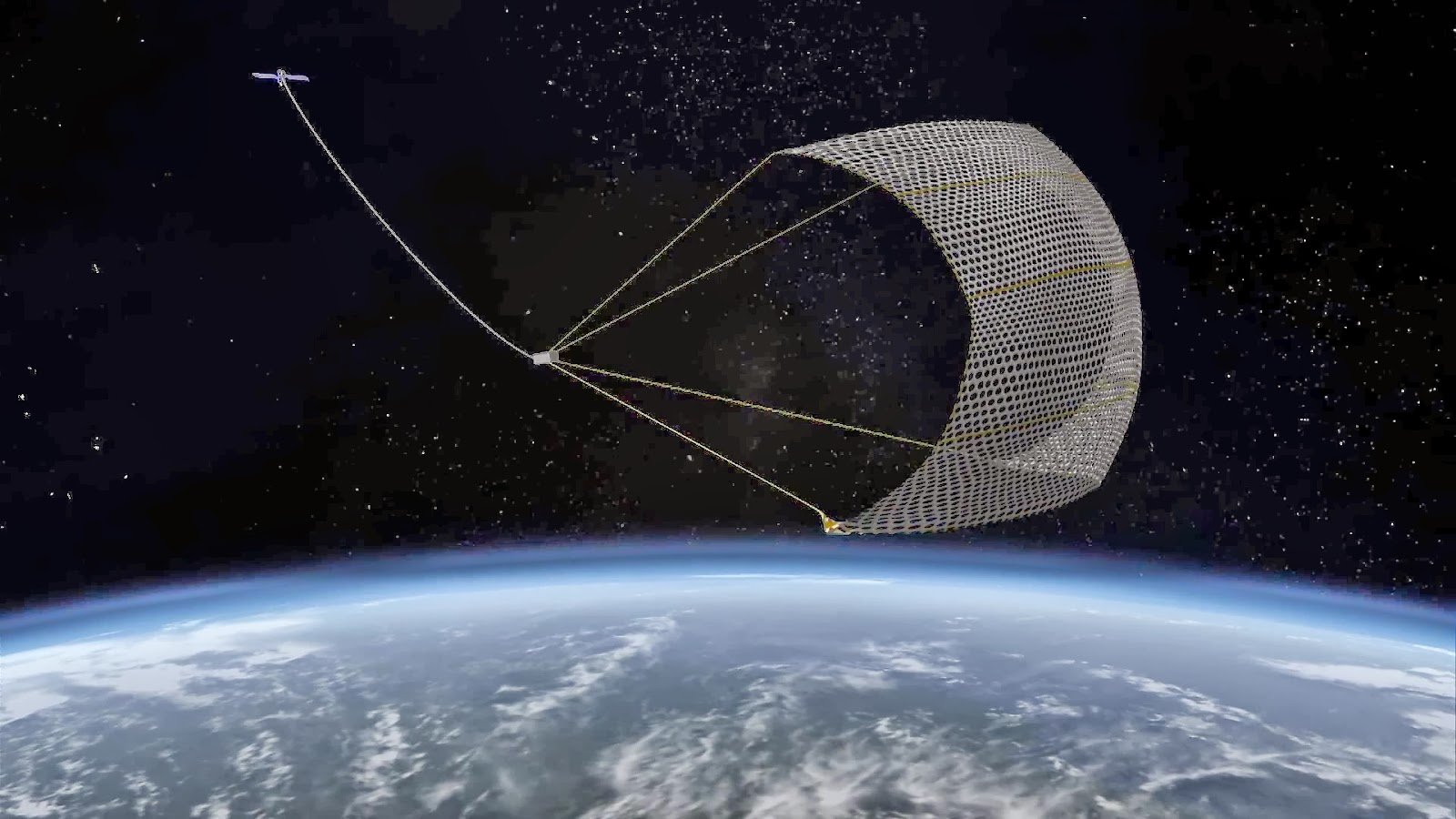
The program e.DeOrbit
the small spacecraft, which with the help of tentacles, nets or harpoons will collect the debris. What spacecraft will do with garbage after – unknown. On the one hand: all ingenious is simple, on the other hand: such a project could come up with a child.

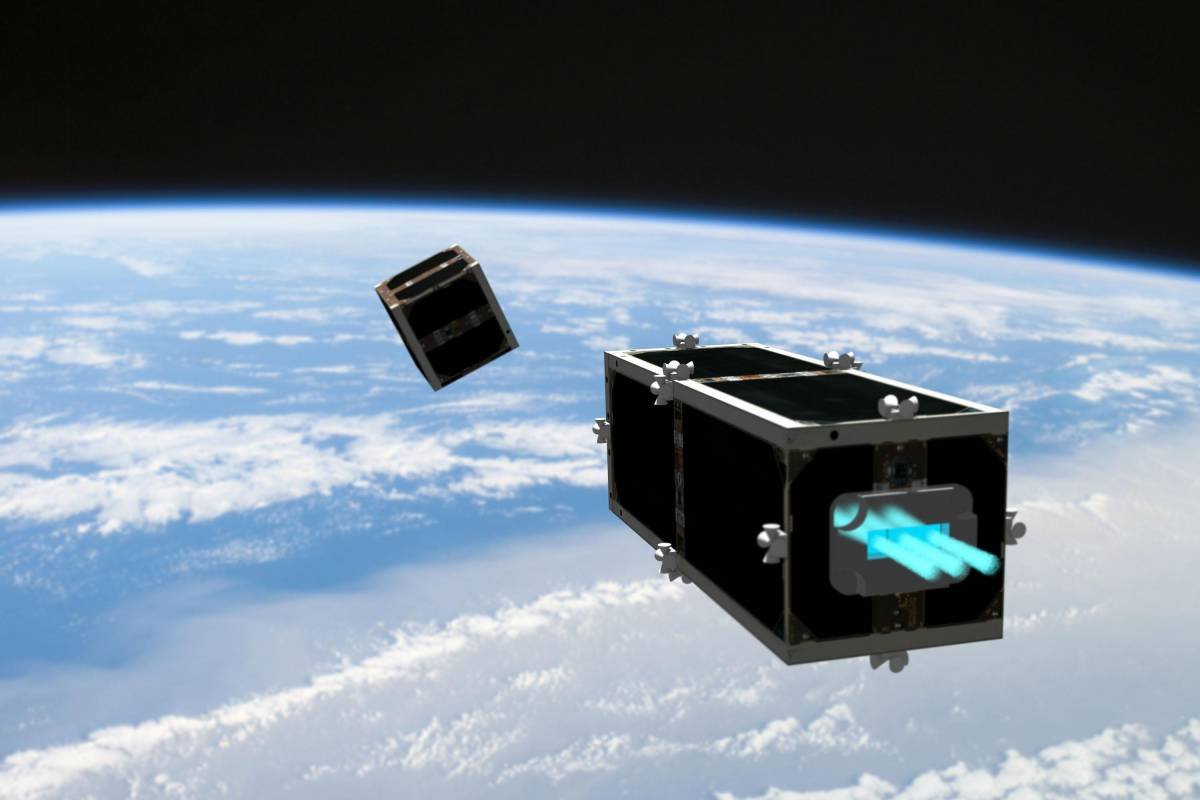
CleanSpace One
suggest using a small spacecraft, about the size 300х100х100 mm in the form of a cube. The cube is attached to the useless satellite, or debris and using thrusters sends the object to the ground, so it will burned in the atmosphere.

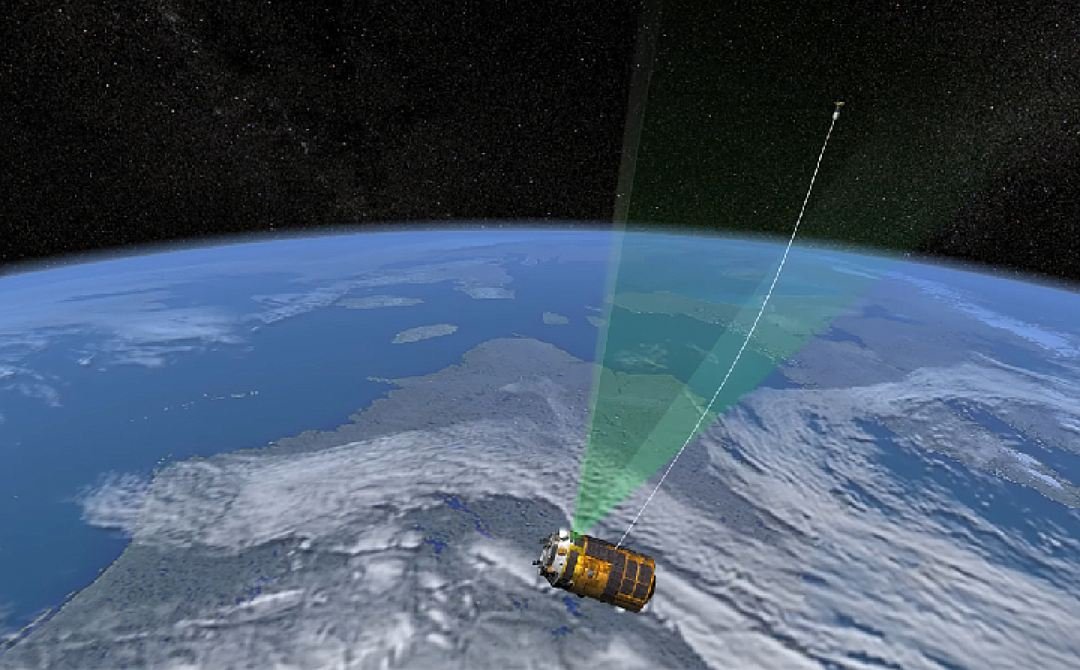
The Japanese company JAXA
proposes to use electrodynamic rope. The rope is attached to the satellite or debris and under the influence of earth's magnetic field starts to reduce the speed of the object. Once the speed drops below the first space, the object falls to earth, burning up in the atmosphere. This option is suitable only for satellites, not for debris with a size 10 cm.

Raytheon BBN Technologies
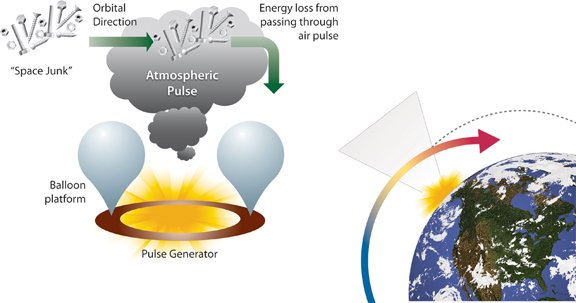
propose a method Space Debris Elimination – SpaDE. Satellites and debris will shoot down to a lower orbit using a special atmospheric gas explosions. It is expected to carry out directed explosions with a balloon near the object, the object will change its trajectory and fall to the atmosphere. However, developers do not explain how they will be able to make directed explosions for objects that move at a speed of 11,000 meters per second.
Star Technology and Research
offers as a solution a net of nano-satellites (net width is 3 kilometers). When interacting with the magnetic field of the earth the net generates a voltage, which changes the trajectory of the debris, sending it into the net. According to the developers, complete cleaning of the space within the Earth will take 12 years. Also not specified how the full net will be output from the orbit.

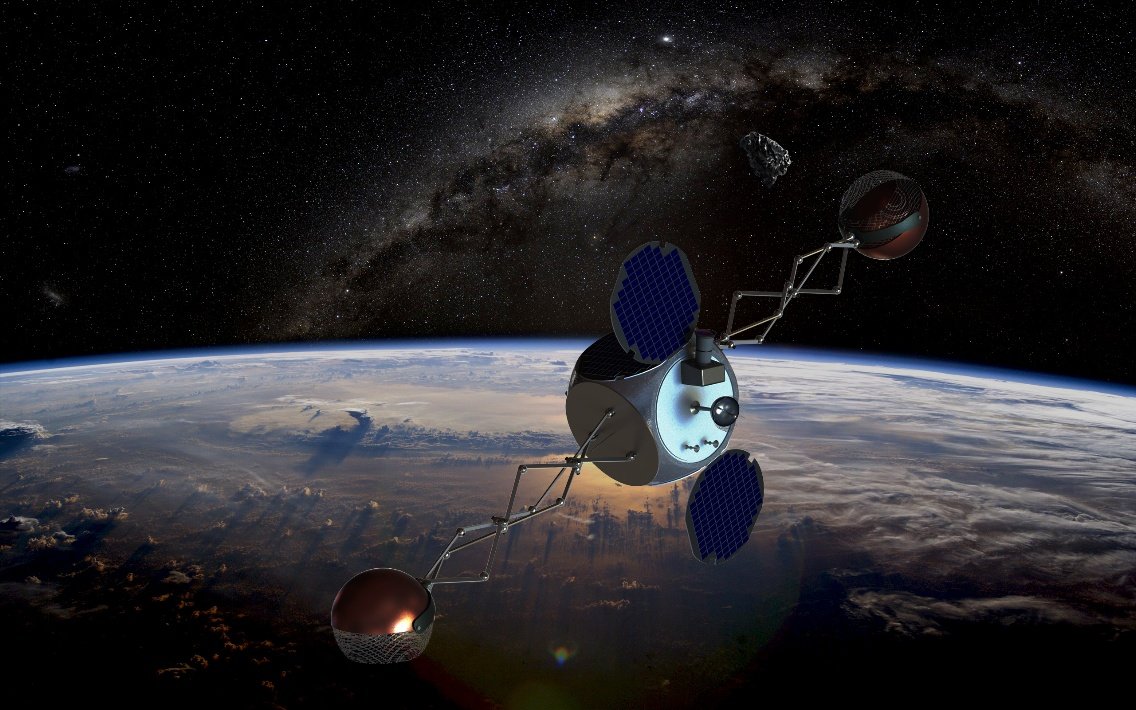
Sling-Sat Space Sweeper
Scavenger, which with the help of special manipulators arms catches the object and change its trajectory, sending to the earth. Sling-Sat will use the energy from the cast to move to another object. The project has no deadline and budget.

***
According to preliminary estimates of scientists, if do not start to clean up all this debris today, then after 50-60 years we will not be able to hold the launches of medium and big spacecraft. They will be destroyed by the space debris in low orbit. So, we still have time to find a solution.
sources: Satellites, Space debris, Kessler syndrome, Space cleaners, Satellite map, The world of fiction, EESA, images from Google search.

