
In 1947, Claude Beck played god during a chirurgical operation.
As a doctor he was used to saving people.Whether it was the right treatment at the right time or a bypass in an artery, he usually got home every day knowing that one person was still among us because of his dedication and good work.
That night, Claude, during an operation, changed the destiny of that infarcted heart by using an electrical device called defibrillator. Applying electrical current to the heart ended up prolonging the life of that patient.
Electricity has become something essential in our life. Who would have told Tesla that seventy years after his dead the electricity would be bought, sold and traded, as it would be a kilogram of oranges.
Electricity is a commodity
The Electricity is a Commodity, meaning that it is a good that is been produced in mass by men although there is a huge amount of it in the nature.
Bids and offers are cleared by the market operator resulting in profits or losses. This market has its own particularities due to the nature of the commodity. Electricity is difficult to store. Demand and supply changes continuously. Therefore Electric companies are forced to have a number of engineers and mathematicians who work on demand forecast.
This people predict the use of the electricity in the short and long term taking into account different parameters as temperature and economic activity. If the next day the temperature if going to be high in certain regions that means that the energy required to supply energy to all the air conditioning devices will be higher than normal.
Electricity Industry evolution.
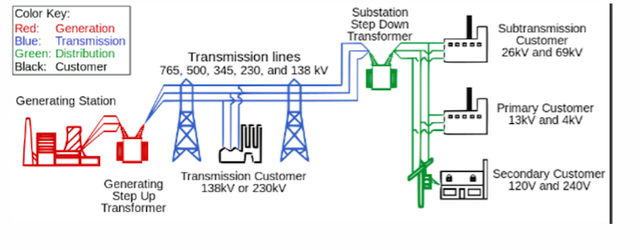
Historically the electric business is been a natural monopoly. That means that the transmission, supply and generation of the electricity is been provided by just one vertical integrated company and it didn´t have any competitors in a specific geographical area. This usually happened as well with the water services. In these network industries it would be very inefficient to develop and operate parallel infrastructures to transmit the electricity or water.
Today, the natural monopolies have been evolved into regulated network industries where companies compete to get a piece of the cake from the different legs of the electric industry table: Generation and retailing. The transmission and distribution remains as natural monopoly.
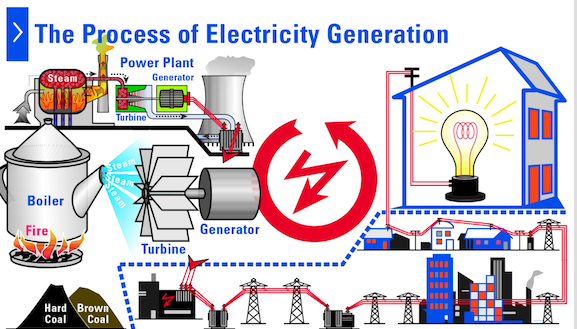
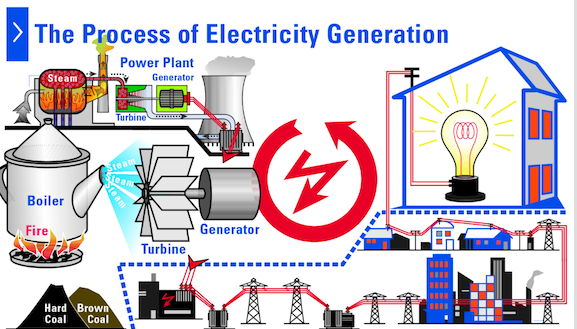
Generation of electricity
Turbines: 40% of all electricity on earth is generated with steam turbines where water is boiled by coal burned in a thermal power. There are also nuclear fission turbines (around 15% of all electricity on earth). And also renewables steam turbines where the steam is generated by biomass, solar energy or geothermal power.
There are also turbines generating electricity without steam. They work with gas where combustion does the job, with water where the energy is captured from the movement of water and wind where the wind moves the turbine.
Electric power transmission.
The electriticy is moved from the generation plants to electrical substations. The electricity is transmitted at very high voltage and the conductor is mainly aluminum.

For a given transmitted power the higher the voltage the lower the current is lost and therefore the lower energy loses due to the Joule Effect.
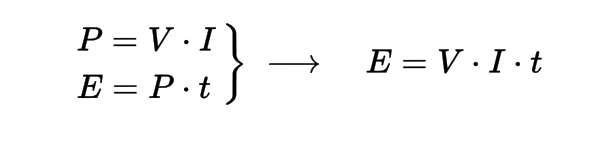
Where P is is the power
I is the current traveling trough the resistor of other element
V is the voltage drop across the element
(Energy dissipated per unit time) = (Energy dissipated per charge passing through resistor) × (Charge passing through resistor per unit time)
Electric power distribution
This is the final stage of the process where the electricity is delivered to customers. The voltage is reduced from hundreds of thousands to 127 V in EEUU or 220 V in most of the countries in Europe.
Electric retailing
This is quite new. In the last 25 years there is been a deregulation of the electric markets where companies buy electricity on the whole sale market facing the price volatility and sale it to the customers. In order to reduce the risk exposure of this volatility they can edge the risk by signing different types of financial contracts.
Nowadays, customers can choose different suppliers, including those where the electricity is been generated from renewable energy like solar power or wind power

FUTURE:
###There are two tendencies at the moment:
###The supergrid tendency.
Also known as super grid. A huge network that connects all countries over the world in HVDC (high voltage direct current. This would lead to a world where all countries would have electricity.
A world where the sahara dessert would be filled with solar panels and the north see filled with off-shore wind farms and this energy could be transmitted in real time to all places where the energy is required.
Distributed generation.
This tendency is a breakthrough because the adoption of this tendency would mean the change of the electrical business, as we know it nowadays. It would lead to the end of electrical companies if they don´t adjust their business lines. Here, there are many points of electricity generation.
Almost in every house, electricity would be generated trough solar panels or they will be connected to local wind farms.
The batteries to store electricity have been improved recently being the Tesla Company one of the mains driving forces for this technology.
The adoption of the electric cars would also play a significant role.

Cars could act as electricity storage and generator devices providing electricity to the network when necessary.
This new era would lead to Smart Cities
Electrical Companies have been predicted that by year 2050, electricity would be generated and sold at a very local level. They will need to adjust their business activities. For example focusing on the creation of micro-grids if they don´t want to lose the train.
Neighbors will sale electricity to each other.
Is that an utopia or a coming reality?
SPANISH

En 1947, Claude Beck jugó a ser Dios durante una operación quirúrgica.
Como doctor, estaba acostumbrado a salvar vidas. Ya fuera por el tratamiento apropiado en el momento correcto o por un bypass coronario, solía volver a casa sabiendo que una persona aún estaba entre nosotros gracias a su dedicación y buen trabajo.
Una noche, Claude, durante una operación de rutina, cambió el destino de un corazón infartado usando un aparato eléctrico llamado desfibrilador. Aplicó corriente eléctrica al corazón y esto tuvo como consecuencia la supervivencia del paciente.

La electricidad se ha vuelto algo muy esencial en nuestras vidas. Quien le habría dicho a Tesla que setenta años después se su muerte la electricidad iba a ser comprada, vendida e intercambiada como si fuera un kilo de naranjas.
La electricidad es una commodity
La Electricidad es una Commodity, significando esto que es un bien producido en masa por el hombre pero que también existe en grandes cantidades en la naturaleza.
Oferta y demanda se balancean gracias a un operador de mercado donde se producen un beneficio o una perdida. Este mercado tiene sus propias particularidades debido a la naturaleza de la commodity.
La electricidad es difícil de almacenar y la demanda y abastecimiento cambia continuamente. Por esta razón, las compañías eléctricas se ven forzadas a tener un equipo de ingenieros y matemáticos que trabajan en la previsión de demanda.
Esta gente predice el uso de la electricidad a corto y largo plazo, teniendo en cuenta parámetros como la temperatura y la actividad económica. Si al día siguiente va a hacer mucho calor en algunas regiones, entonces esto significará que la demanda energética va a ser mayor por el uso de todos los aires acondicionados.

Evolución de la industria energética
Históricamente, el negocio eléctrico ha sido un monopolio natural. Esto significa que la transmisión, el abastecimiento y la generación de electricidad han sido proveídos solo por una compañía vertical integrada y no ha tenido competencia en áreas específicas. Lo mismo ha pasado también con las empresas de abastecimiento de agua. En este tipo de industrias es muy ineficiente y costoso desarrollar infraestructuras paralelas de transmisión de electricidad o agua
Hoy en días, los monopolios naturales han evolucionado en industrias reguladas de red donde las compañías compiten por conseguir un trozo de la tarda en cualquiera de las 4 patas que conforman el mercado eléctrico: Generación y venta. La transmisión y distribución permanecen como monopolios naturales.

Generación de electricidad
Turbinas: El 40% de la electricidad en la tierra es generada a través de turbinas de vapor, donde el agua es evaporada con carbón en una planta termal. También hay turbinas de fisión nuclear (sobre el 15% de la electricidad total, energía solar y geotermia)
También hay turbinas que generan electricidad sin vapor. Estas funcionan con gas donde la combustión hace el trabajo y también las hay donde la energía se captura por el movimiento del agua y viento.

Transmisión de la energía eléctrica
La electricidad se mueve desde las plantas generadoras hacia las subestaciones eléctricas. Se transmite a un voltaje muy alto y normalmente el conductor utilizado es el aluminio.

Para una electricidad transmitida a más alto el voltaje más baja es la perdida de corriente y consecuentemente más baja es la perdida de energía debido al Efecto de Joule:

Donde P es la energía
I es la corriente viajando a través de una resistencia de otro elemento
V es el voltaje.
(La energía disipada por unidad de tiempo) = (Energía disipada por carga a través de una resistencia) x (carga pasando por resistencia por unidad de tiempo).
Distribución de la energía eléctrica
Esta es la parte final del proceso donde la electricidad es llevada hasta los consumidores. El voltaje se reduce desde cientos de miles hasta 127V en estados unidos y 220V en la mayoría de países europeos.

Venta Eléctrica
El Retail de la electricidad es un negocio bastante nuevo. En los últimos 25 años ha habido una desregulación de los mercados energéticos dónde las compañías compran electricidad en el mercado eléctrico afrontando altas volatilidades de precio y luego venden a clientes. Para reducir el riesgo de esta volatilidad las compañas se benefician de productos financieros específicamente creados para este mercado.
Hoy en día, los clientes pueden elegir diferentes proveedores, incluyendo aquellos donde la electricidad es generada a través de plantas solares o granjas de viento.

Futuro
Hay dos tendencias en este momento:
La tendencia supergrid:
Es una red que conecta todos los países en el mundo a través del HVDC (high voltaje direct current). Esta tendencia derivaría a un mundo donde todos los países tendrían electricidad.
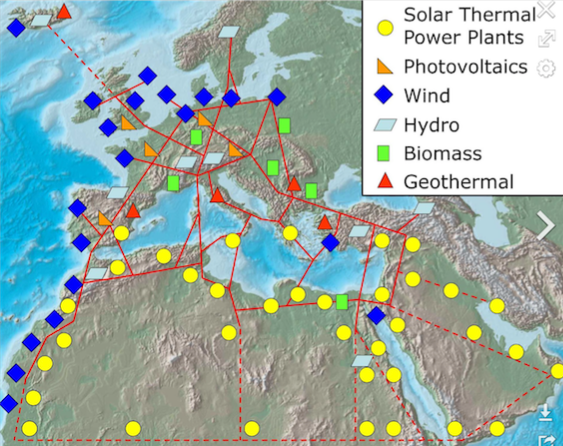
(http://www.friendsofthesupergrid.eu)
Un mundo donde el desierto del Sahara estaría lleno de paneles solares y el mar del norte lleno de turbinas de viento. Toda esta energía se transmitiría en tiempo real según el requerimiento de cada país.
Generación distribuida
Esta tendencia supone un punto de inflexión en lo que ha sido el marcado energético hasta ahora. Significaría el final de las compañías eléctricas como las conocemos hoy en día, ya que tendrían que adaptar totalmente su modelo de negocio. Aquí habría muchísimos puntos de generación de energía.
Casi en cada casa, la electricidad se generaría por paneles solares y las mismas casas podrían estar conectadas a granjas de molinos de viento.
Las baterías de almacenamiento de energía han sido mejoradas últimamente sobre todo gracias a la empresa de coches eléctricos Tesla
La adopción de los coches eléctricos también jugaría un papel muy importante.
Los coches podrían actuar como almacenes y generadores de energía ya que también estarían conectados a la red y podrían proveer su energía en caso de que fuera requerida.

Esta nueva era podría llevarnos a la consecución de ciudades inteligentes
Las compañías eléctricas han predicho que en el año 2050 toda la electricidad será comprada y vendida a nivel local. De esta forma se tendrán que adaptar sus actividades de negocio y centrarse más en la creación de micro-grids si no quieren perder el tren de lo que será el futuro del mercado eléctrico.
Vecinos vendiendo y comprando energía entre ellos
Es esto una utopía o una realidad cercana?

