▲ Image for thumbnail
첫 글
First post
안녕하세요~ 자기소개 후 제대로 작성하는 첫 번째 글이라 두근두근합니다. 오늘은 제가 하는 연구 중 최근 출판된 (사실 몇 달 지났지만) 논문 내용을 소개하는 시간을 가져보겠습니다. 최대한 이해하기 쉽고 간결하게 전달해보도록 노력하겠습니다.
Hello~ steemit friends! I am thrilled to write my first post after my introduction. Today, I will take some time to review the contents of my recently published work (Although it has been several months since). I will try to make it as simple and understandable as possible for our steemit friends.
다이오드?
Diode?
전자 소자의 기능과 효율을 결정하는 가장 중요한 물리적인 현상들은 대부분 서로 다른 물질들이 맞닿는 접합면에서 발생합니다. 전자 및 광전자 소자 응용에 있어 매우 중요한 금속/반도체 접합은 반도체 소자에서 전하가 주입되고 빠져 나오는 관문인데요. 소자의 동작 특성과 소비전력을 결정하는 데 중요한 역할을 할 뿐 아니라, 그 자체로도 정류 작용을 하는 다이오드입니다.
The most important physical phenomena that determine the function and efficiency of electronic devices arise mostly at the junction where different materials touch. A very important metal/semiconductor junction in electronic and optoelectronic device applications, so-called Schottky contact is the gate which charge is injected and escaped from the semiconductor device. It is a diode that not only plays an important role in determining the operating characteristics and power consumption of a device, but also acts as a rectifier itself.
image reference: https://www.carit-automotive.com/
따라서 제작된 반도체 소자를 설계한 대로 작동시키려면 금속/반도체 접합의 전기적 특성을 임의로 조절하는 일이 필수적이라고 할 수 있죠. 그런데 기존 반도체 공정을 사용하여 금속/반도체 접합을 형성하면 접합면에서 금속 및 반도체 원자들의 상호 확산이 일어나는데요. 이로 인하여 접합면의 물질 간 경계가 불분명해져 접합의 전기적 특성이 예측 불가능하게 변화되는 현상이 발생합니다.
Therefore, in order to operate the fabricated semiconductor device as designed, it is essential to arbitrarily adjust the electrical characteristics of the metal/semiconductor junction. However, when metal/semiconductor junctions are formed using conventional semiconductor processes, mutual diffusion of metals and semiconductor atoms occurs at the junctions. As a result, the boundary between materials on the interface becomes unclear and the electrical characteristics change unpredictably.
그래핀 확산 방지막
Graphene diffusion barrier
저와 제 연구팀은 이와 같은 금속/반도체 접합면에서 원자 확산을 방지하면서도 접합면의 전하 이동에는 영향을 주지 않는 확산 방지막 역할을 할 수 있는 물질로써 그래핀에 주목하였습니다. 접합면 사이에 단일 원자층 그래핀을 삽입하여 물질 간 경계가 분명한 이상적 구조의 금속/반도체 접합을 제작하여 접합의 전기적 특성이 이론적 예측과 얼마나 부합하는지 알아보고자 했죠.
I and my team have focused on graphene as a material that can prevent diffusion of atoms in the metal/semiconductor interface and act as a diffusion barrier that does not affect the charge transfer on the interface. We attempted to investigate how the electrical properties of the junctions match the theoretical predictions by fabricating ideal metal/semiconductor junctions with a graphene insertion layer.
실리콘 반도체 표면에 단일 원자층 그래핀을 얹은 후, 금속 박막을 증착해 ‘금속/그래핀/반도체 접합’을 형성했는데요. 그 결과, 그래핀이 접합면에서 금속과 반도체 원자들의 상호 확산을 방지하여 접합면을 통한 누설전류를 현저히 감소시킨다는 것을 확인했습니다.
After depositing a single atomic layer of graphene on the silicon semiconductor surface, a metal thin film was deposited to form metal/graphene/semiconductor junctions. As a result, we have confirmed that graphene prevents inter-diffusion of metal and semiconductor atoms at the junction plane, significantly reducing leakage current through the junction plane.
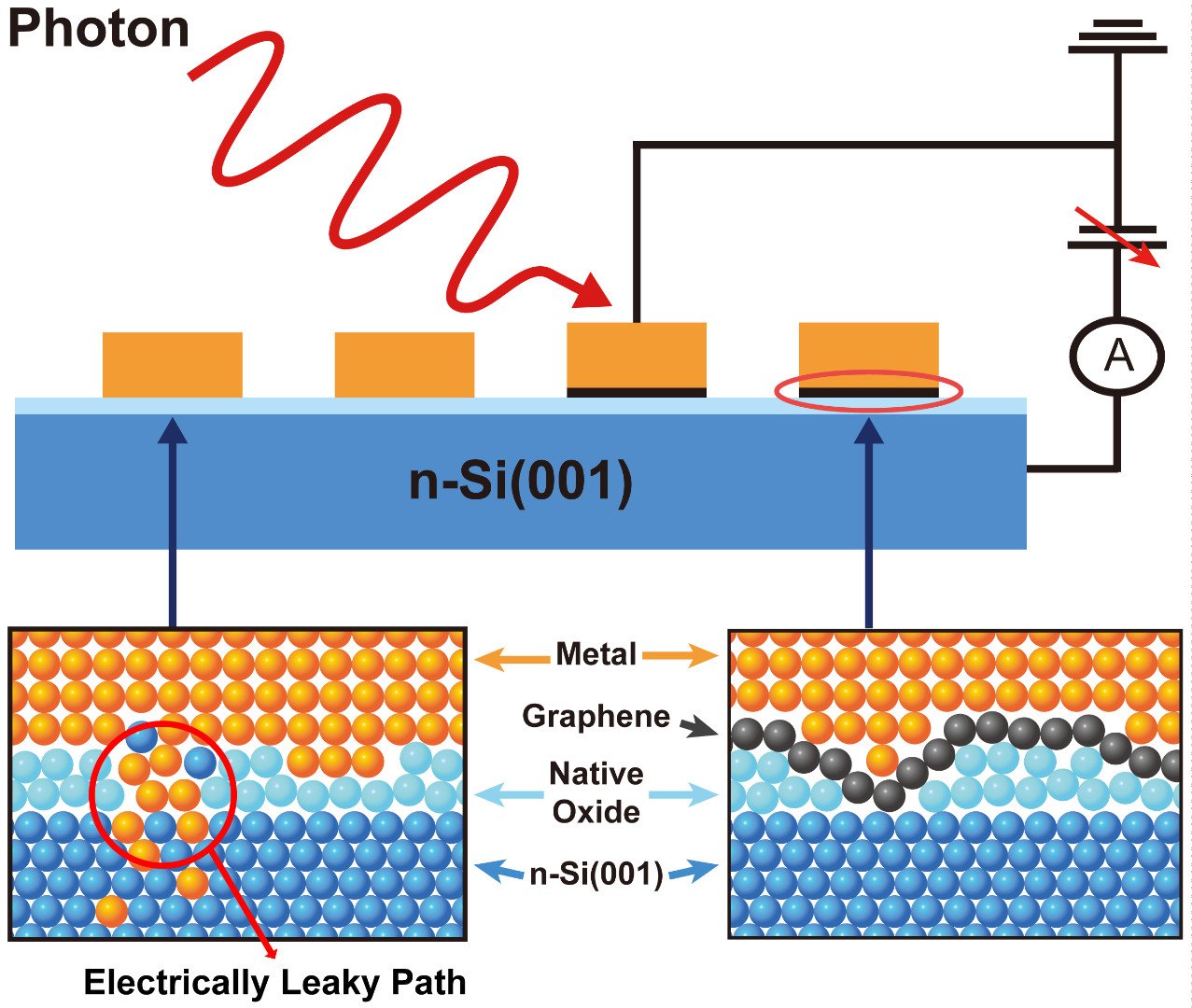
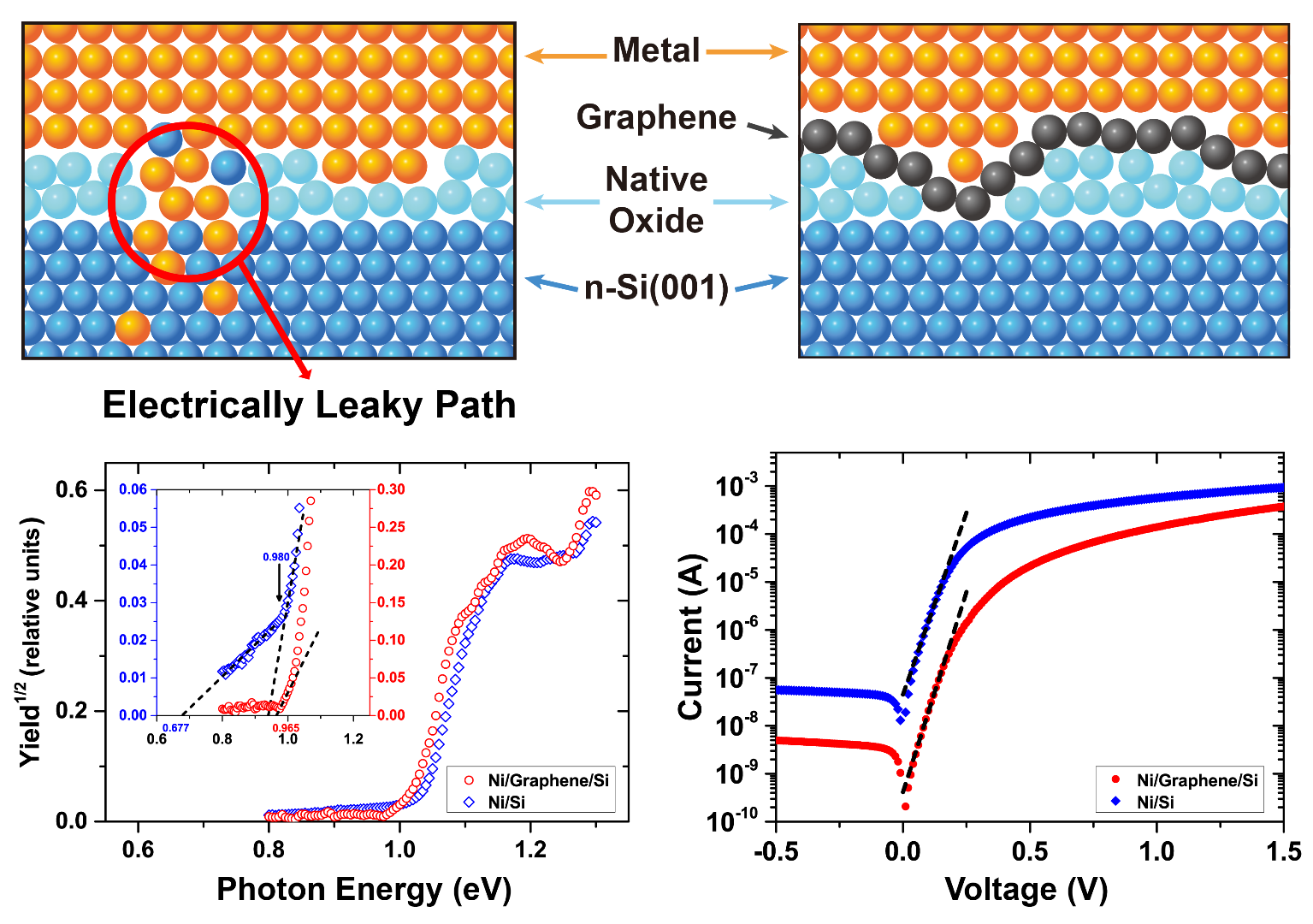
▲ 그래핀 삽입층이 있거나 없는 금속/n형-실리콘(001) 접합에서의 내부광전자방출 측정에 대한 모식도. 두 개의 확대 이미지는 금속/실리콘 및 금속/그래핀/실리콘 접합 계면의 원자 배열을 보여줍니다.
Schematic view of internal photoemission measurements on metal/n-Si(001) junctions with and without a graphene insertion layer. The two zoomins illustrate the atomic arrangements at the metal/Si and metal/graphene/Si interfaces.

▲ 그래핀 확산 방지막의 효과를 보여주는 모식도. 그래핀 확산 방지막이 없는 경우(좌상), 금속/반도체 접합면에서 금속 및 반도체 원자들의 상호 확산이 일어납니다. 접합면에 그래핀을 끼워 넣을 경우(우상), 이와 같은 원자 확산 현상이 방지됩니다. 아래쪽 그래프는 그래핀 확산 방지막을 사용할 경우 금속/반도체 접합면의 전자 에너지 장벽이 공간적으로 균일해지고(좌하) 접합의 누설전류가 현저히 감소하는(우하) 것을 보여줍니다.
A schematic diagram showing the effect of a graphene diffusion barrier. In the absence of graphene diffusion barrier (top left), inter-diffusion of metal and semiconductor atoms occurs at the metal/semiconductor interface. When a graphene layer inserted at the interface (top right), such atom diffusion phenomenon is prevented. The lower graph shows that when the graphene diffusion barrier is used, the electron energy barrier at the metal/semiconductor interface is spatially uniform and the junction leakage current is significantly reduced (lower right).
내부광전자방출 측정
Internal photoemission
나아가, 금속/반도체 접합면의 전자 에너지 장벽을 가장 정밀하게 알아낼 수 있는 측정법 중 하나인 내부광전자방출 측정을 수행했습니다. 금속/반도체 접합면에 그래핀을 끼워 넣으면 접합면 전체에 공간적으로 균일한 전자 에너지 장벽을 얻게 되고 이론적으로 예측한 경향을 정확히 따른다는 것도 실험적으로 입증했죠.
Furthermore, internal photoelectron emission measurement, which is one of the measurement methods that can determine the electron energy barrier of the metal/semiconductor junction most precisely, was performed. It has been experimentally proven that, when the graphenes are embedded in the metal/semiconductor junction surface, a spatially uniform electron energy barrier is obtained over the junction surface and theoretically predicted behavior is exactly followed.
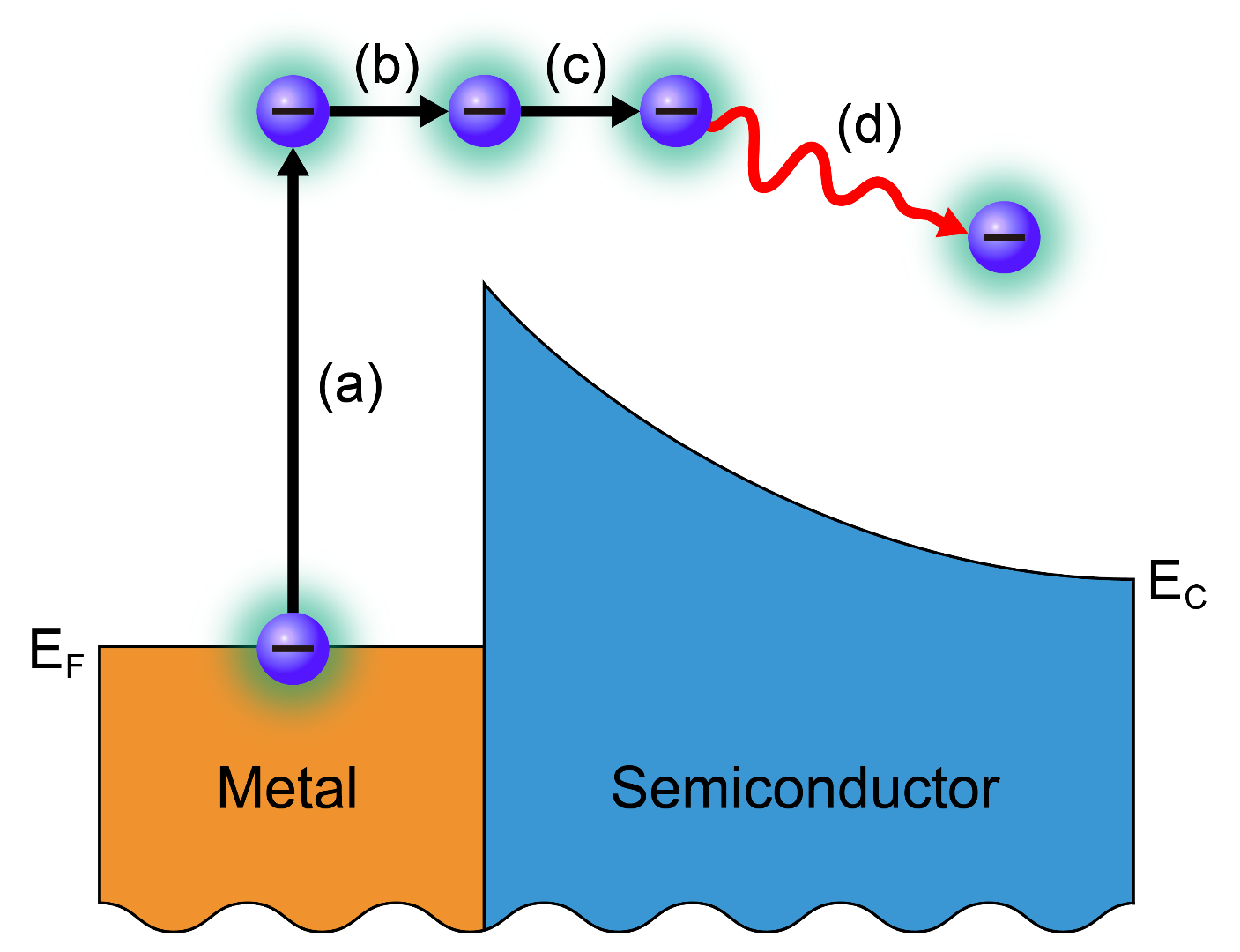
▲내부광전자방출 원리를 보여주는 모식도. (a) 광자 들뜸 (b) 표면으로 전자 전송 (c) 전자 에너지 장벽 극복 (d) 기판 전류로 기여. 내부광전자방출 측정법은 서로 다른 물질 간 접합면의 전자 에너지 장벽을 정밀하게 측정하는 방법 중 하나입니다. 금속/반도체 접합의 경우, 금속에 단색광을 쪼였을 때 광자들을 흡수한 금속 내 전자의 에너지가 높아져 계면의 전자 에너지 장벽을 넘고 반도체 쪽으로 흘러가게 되는데요. 따라서 쪼여준 단색광의 에너지에 따른 반도체 쪽의 전류를 측정하게 되면 전자 에너지 장벽의 높이를 정확히 알 수 있죠!
A schematic diagram showing the principle of internal photoemission (a) Optical excitation (b) Transport of electron to the surface (c) Surmount potential barrier (d) Collected as substrate current. Internal photoemission is one of the methods to precisely measure the electron energy barrier of the junctions between different materials. In the case of metal/semiconductor junctions, when monochromatic light is applied to a metal, the energy of the electrons in the metal absorbing the photons increases to flow over the electron energy barrier at the interface and toward the semiconductor. Therefore, if the current of the semiconductor is measured according to the energy of the monochromatic light, the height of the electron energy barrier can be accurately determined.
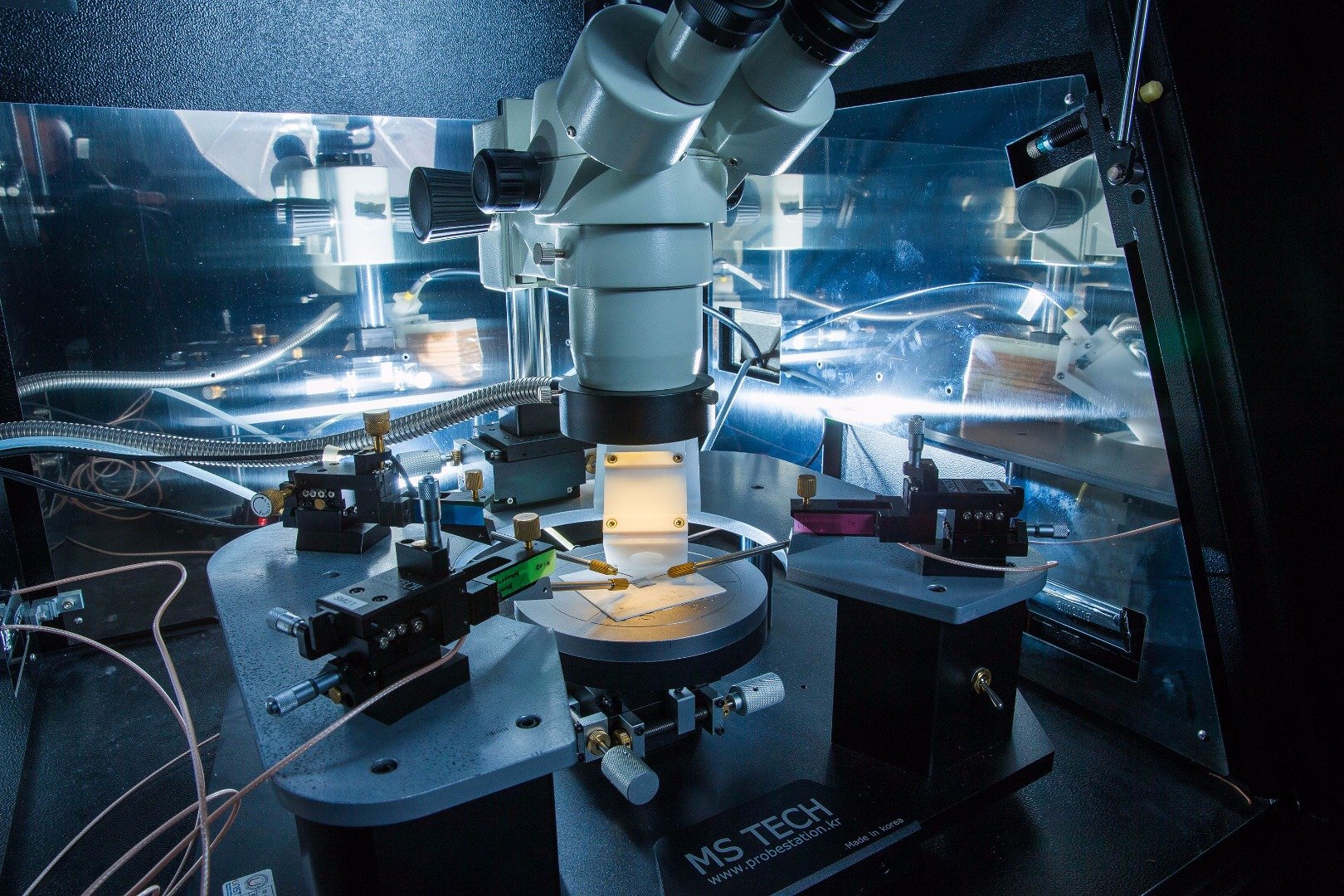

▲내부광전자방출 측정 시스템의 모습입니다. 제가 직접 모든 장비를 구매, 조립하고 랩뷰 프로그래밍을 통해 제작하였기에 애정이 많이 가는 장치입니다. 학부 1학년이었던 2010년부터 매달려 2012년 경에 들어서야 기본적인 측정을 시작할 수 있었죠. 지금까지 꾸준히 연구에 활용 중이며 앞으로도 더 발전시켜나갈 계획입니다.
Internal photoemission measurement system. All by myself, I bought all the equipments, assembled it and automatically operated it through LabVIEW programming. Starting from 2010, when I was a university freshman, I was able to start basic measurements around 2012. I have been steadily using it for research so far and plan to further develop it.
물리학적 의미
Physical meaning
특히, “실리콘 반도체의 경우 금속의 종류에 관계없이 접합의 전기적 특성이 거의 변하지 않는다.”는 이론적 예측이 타당하다는 것도 그래핀 확산 방지막을 사용해 실험적으로 정량적이고 재현성 있게 검증했습니다. 이는 실리콘이 반도체 소자 제작에 널리 쓰이기 시작한 이래 반세기를 훌쩍 넘긴 시간 동안 제대로 확인하지 못했던 부분이었답니다.
In particular, the validity of the theoretical prediction that "the electrical properties of the junction do not change in the case of silicon semiconductors, regardless of the type of metal," are quantitatively and reproducibly verified using a graphene diffusion barrier. This was something we had not been able to confirm for well over half a century since silicon began to be widely used in semiconductor device fabrication.
응용
Application
본 연구에서 선보인 그래핀의 우수한 확산 방지 기능은 기존 실리콘 반도체 공정에 직접 적용이 가능합니다. 반도체 소자의 크기가 나노미터(㎚) 정도까지 작아질 경우 접합면에서 발생하는 물질 간 원자 확산 문제는 소자의 기능 및 신뢰성에 더욱 심각한 영향을 미치는데요. 따라서 그래핀 확산 방지막은 이러한 문제의 근본적인 해결책이 될 수 있을 것으로 예상됩니다.
The excellent diffusion prevention function of graphene introduced in this study can be directly applied to existing silicon semiconductor process. When the size of a semiconductor device is reduced to the order of nanometers(nm), the problem of atom diffusion between materials occurring at the joint surface has a more serious effect on the function and reliability of the device. Therefore, the graphene diffusion barrier is expected to be a fundamental solution to this problem.
앞으로의 기대
Future expectations
그래핀을 이루는 탄소 원자들 사이 공간에는 양자역학적 전자 밀도가 높아 어떤 원자도 투과할 수 없지만 충분히 얇기 때문에 무시할 정도로 작은 전기 저항을 갖습니다. 원자 확산은 방지하면서 동시에 전기는 잘 통하는 그래핀만의 특성은 금속/반도체 접합뿐만 아니라 반도체 고주파 통신 소자, 반도체 전력 소자, 초전도 소자 등 여러 다양한 전자소자들의 물질 간 경계면 특성을 향상시키는 데에도 광범위하게 사용될 수 있을 것으로 기대해봅니다.
The space between the carbon atoms that consisting graphene has a high quantum mechanical electron density so that any atoms cannot penetrate through it. However, it is thin enough to have negligible electrical resistance. I hope that Graphene's unique characteristics that give a high electrical conductivity and prevent atomic diffusion at the same time, are widely used to improve interfacial properties of various electronic devices such as high-frequency communication devices, semiconductor power devices, and superconducting devices.
▲ 저와 제 지도교수님, 이번 연구에 참여한 동료 연구원들을 소개합니다.
introduce my team. I (mid), my advisor (Professfor Kibog Park; left 1st), fellow researchers (Sungchul Jung; right 1st , Gahyun Choi; left 2nd, Junhyung Kim; right 2nd) who participated in this study.
More information: Hoon Hahn Yoon et al, Strong Fermi-Level Pinning at Metal/n-Si(001) Interface Ensured by Forming an Intact Schottky Contact with a Graphene Insertion Layer, Nano Letters (2017).
Link: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b03137
Acknowledgments: The corresponding author is my advisor, Professor Kibog Park of UNIST Natural Science. And this study has been jointly conducted by Professor Hu Young Jeong of the UNIST Central Research Facilities (UCRF), Professor Kwanpyo Kim of UNIST Natural Science, Professor Soon-Yong Kwon of UNIST Materials Science and Engineering, and Professor Yong Soo Kim of Ulsan University. It has been also supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, Nuclear Research Basis Expansion Project, as well as the Global Ph.D Fellowship (GPF).
# YHH
