A New Study Out This Week Reveals WIkileaks Dominated All Other Media Outlets During The US Election As Well As Played A Major Roll In Clintons Defeat.

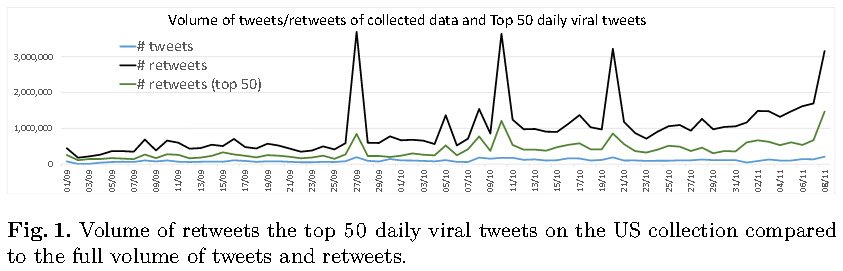
Yesterday Cornell University published an analysis report based on the top Tweets associated with the US elections that went viral between September 1, 2016 and Election Day on November 8, 2016. Every day for 68 days the team tagged the top 50 most retweeted tweets as either 'supporting or attacking either candidate'. Here we shall break it down and look at it in further detail.
Tweets:
Retweeted 26.3 million times
Accounting for over 40% of the total tweet volume
700 Donald Trump Tweets, accounting for 8.7 million retweets
698 Hillary Clinton tweets, accounting for 4.7 million retweets
Classes:
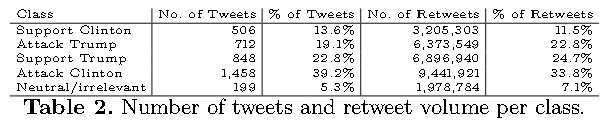
Tweets In Each Class Analyzed For:
Most frequently used hashtags
Terms and locations
Most retweeted accounts and tweets
Most shared news and links
In their report they explain the aim of their analysis is to 'showcase some of the Twitter trends pertaining to the US presidential election'. In particular they try to answer the following research questions:
- Which candidate was more popular in the viral tweets on Twitter? What proportion of viral tweets in terms of number and volume were supporting or attacking either candidate?
- Which election related events, topics, and issues pertaining to each candidate elicited the most user reaction, and what were their effect on each candidate? Which accounts were the most influential?
- How credible were the links and news that were shared in viral tweets?

ANALYSIS
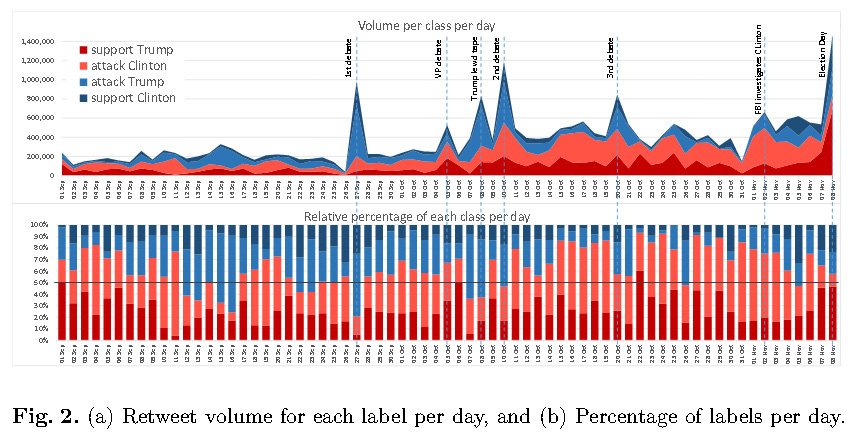
The retweet volume of tweets attacking Clinton outnumbered the retweet volume of tweets supporting her by nearly a 3 to 1, while Tweets supporting and attacking Trump were almost evenly matched. This is prbably down to David Brocks multimillion dollar properganda machine Media Matters.
Hashtags
The most frequently used hashtags used for the different labels reveal some interesting differences between the two candidates.
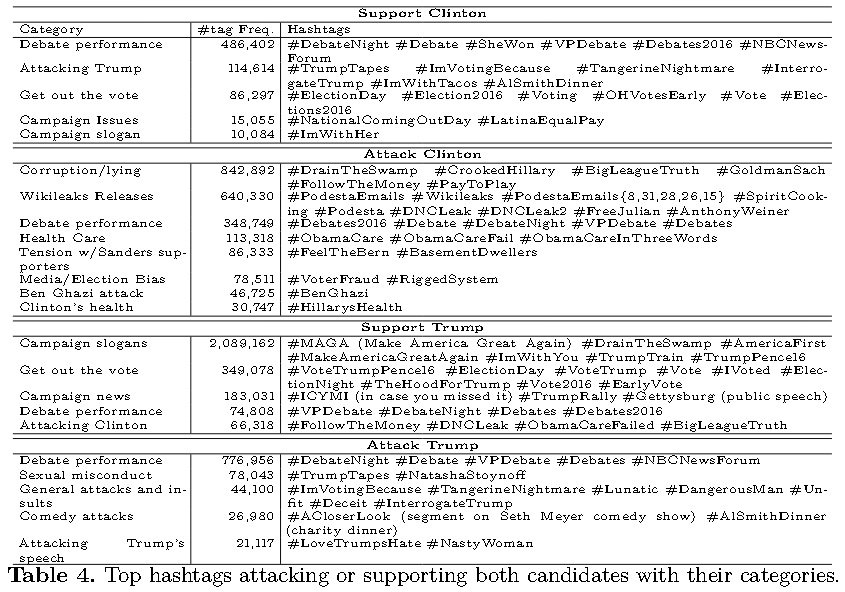
- The top most frequently appearing hashtags favoring Clinton were those praising her debate performances and attacking Trump.
- The most frequently appearing hashtags on the Trump side were those iterating his campaign slogans, encouraging people to vote, and spreading campaign news.
- Trump’s campaign slogans hashtags appeared nearly 200 times more than Clinton’s campaign slogan (IAmWithHer).
- Hashtags indicating “Get out of the vote” were 4 times more voluminous for Trump than Clinton.
- Trump campaign more effective in promoting their activities.
- The support to attack hashtag volume ratio was roughly 3 to 2 for Clinton and 1 to 9 for Trump.
- Debates were the number one category for the “support Clinton” and the “attack Trump” classes.
- Attacks against Trump were dominated by his debate performance.
- Policy issues such as health care were eclipsed by issues pertaining to the personalities of the candidates and insults.
Attacks against Clinton focus on her character and on the WikiLeaks leaks, which cover Clinton’s relationship with Wall Street, alleged impropriety in the Clinton Foundation, mishandling of the Ben Ghazi attack in Libya, Democratic Party primary race against senator Sanders, the FBI investigation of Clinton, and accusation of witchcraft.

Creditable News Sources
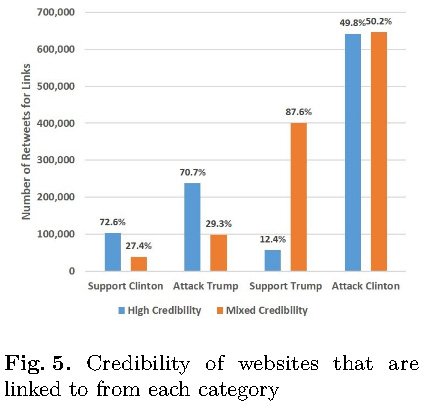
An important debate that surfaced after the US elections was whether fake news affected the election results or not. So the university research team decided to analyze the credibility of the websites that were most linked to in the tweets for each group.

The candidates official websites received the most links interestingly though there's a large difference in focus in strategies and trends between them both. Clinton’s website attacked Trump more than it supported Clinton, while Trump’s website supported Trump more than it attacked Clinton.
- The aggregate number of links for “High” and “Mixed” credibility websites was 1.4 million and 1.18 million respectively.
- A significantly higher proportion of highly credible websites were linked to for the “support Clinton” and “attack Trump” categories compared to mixed credibility sites.
- The opposite was true for the “support Trump” category, where the majority of links used to support Trump was from mixed credibility websites.
- Trump supporters more susceptible to sharing less credible sources compared to Clinton supporters.
- High and mixed credibility sites were evenly matched for the “attack Clinton” category.
WikiLeaks was the foremost shared site for attacking Clinton, which has high credibility. This again highlights the role of WikiLeaks in steering public opinion against Clinton. It worth mentioning that “The Podesta Emails” was the most popular link. Thus, though lower credibility links were used to attack Clinton, high credibility links featured prominently.
Retweets
Retweeted Tweets
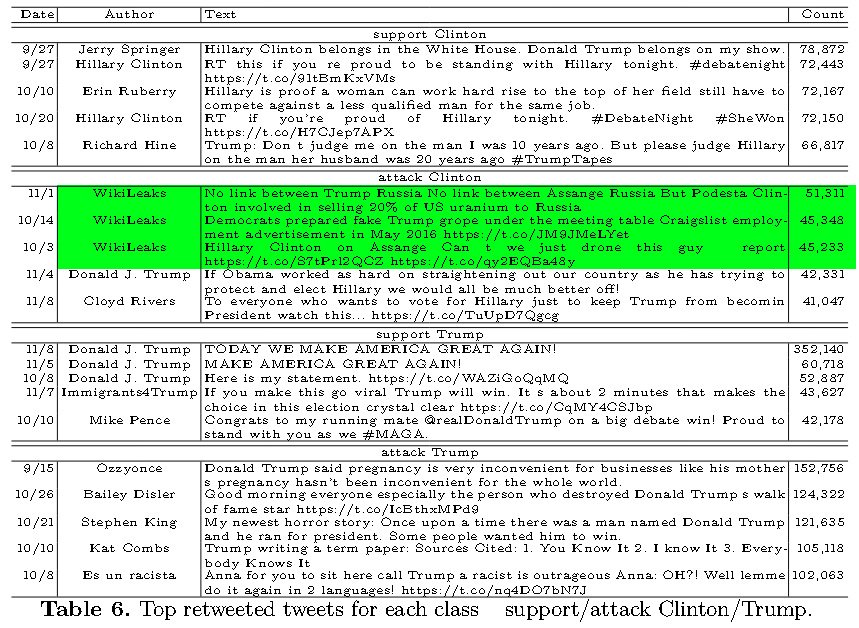
- Follows same trends to those exhibited in previous analysis, namely: “support Clinton” tweets are led by talk about debates and attacks against Trump.
- The most retweeted “attack Clinton” tweets are from WikiLeaks.
- Trump campaign slogans appear atop of “support Trump” tweets
- Most retweeted "attack Trump” tweets cover demeaning statements against women and minorities and mockery of Trump.
Retweeted Accounts

- Most retweeted accounts for “support” and “attack” classes were those of the candidates themselves and their rivals respectively.
- Clinton authored 10% more “attack Trump” tweets (with 35% more volume) than “support Clinton”.
- Trump authored 81% more “support Trump” tweets (with 38% more volume) than “attack Clinton” tweets.
This suggests that Clinton expended more energy attacking her opponent than promoting herself, while Trump did the exact opposite.
- Clinton authored 48% more tweets attacking her rival than tweets Trump authored attacking her.
- Trumps attack tweets led to 34% more retweet volume which suggests that his attacks were more effective than hers.
- Trump tweets were more retweeted on average than Clinton’s tweets with an average of 11,195 and 6,120 retweets per tweet for both respectively.
Highlighting WikiLeaks’ role in the election, WikiLeaks was the second most retweeted account attacking Clinton and had four times as much retweet volume than the next account.
Summary
- Trump received more negative coverage than Clinton in the mainstream media.
- Trump benefited from many more tweets that were either supporting him or attacking Clinton.
- 63% of the volume of viral content on US election were in his favor compared to only 37% in favor of Clinton.
- Of the days in the last two months preceding the election, Trump had more tweets favoring him than Clinton.
This observation shows the gap between the trends of social media and traditional news media.
The volume of tweets attacking and supporting Trump were evenly matched, while the volume of tweets attacking Clinton outnumbered tweets praising her by a 3 to 1 margin.
Trump campaign accounts featured more prominently in the top retweeted accounts supporting their candidate.
The analysis report finally signs off with:
Our analysis highlights some of the differences between the social media strategies of both candidates, the effectiveness of both in pushing their messages, and the potential effect of attacks on both. We show that compared to the Clinton campaign, the Trump campaign seems more effective in: promoting Trump’s messages and slogans, attacking and framing Clinton, and promoting campaign activities in “swing” states.

