
Following my four-part essay on decentralization I want here to go more into the notion of a decentralized exchange, what the benefits are, why it is important, and finally how BitShares’ Decentralized exchange solves two important problems in the cryptoeconomy.
The essays are based on blogposts I wrote for my LibertyMotive blog, updated for Steem and the changing times. Throughout I've tried to keep it as simple as possible. I hope you will enjoy it!
Decentralization Benefits

A decentralized exchange is an exchange that has no single point of failure, such as an institution, a person or a server that is in control and running it. With a decentralized exchange there is no need to trust any single authority – it is a trustless service. This also creates a number of benefits beyond this decentralization. I highlight three here:
1. Global, Fast, 24/7, Efficient

A decentralized exchange is global service without borders that is available to any member of the free internet. Servers running at every corner of the globe at all times of the day ensure transactions and settlement within seconds. With no need for a brick and mortar institutions, the cost of transactions can be 10x, 100x or even 1000x less than what they are with the traditional system.
2. Open and Transparent
All transactions occurring on the network and all code that is used for running the network is open source and the live software is open to anyone anywhere to inspect, copy and improve upon.
3. Incorruptibly Secure

The intermediaries in the traditional financial system are centralized institutions that can be corrupted, coerced, hacked or robbed. With such centralized systems, single points of failure can be catastrophic. With a decentralized exchange everyone keeps control of their own keys to their own funds.
Why is it Important?

Decentralized exchanges are important because they are trustless, global, fast, 24/7 and transparent. As the software develops it will become more user friendly and offer innovative services that are hard to imagine at this stage. With both Bitcoin and decentralized exchanges, the “internet of money” is fast becoming a reality that will significantly shape our future.
Beyond these simple benefits, a decentralized exchange is important for deeper reasons as well. I highlight four reasons here:
1. No more identity theft

In the traditional system we give out our identity, credit card information and even our passwords and keys to everyone we do business with. Through the power of cryptography this is no longer necessary, as everyone can keep their information, identity and keys secure while proving that they have the right credentials.
2. No more banking cartels
Everything is now in the open for everyone to see, and there is no need for large institutions to keep things private. The power of this technology allows everything to be out in the open without compromising security. In the traditional system large institutions could use security as an argument to keep all their information, as well as all your information, privately locked up and backed by their authority.
3. Freedom for the unbanked

There is no reason any longer to prevent the poor and unbanked from participating in the global economy. Their corrupt regimes and our capitalist-minded financial services no longer need to play an important part in their freedoms. With decentralized exchanges anyone can store and transfer wealth to anyone, anywhere in the world, at almost no cost.
4. Boundless innovation

With collaborative services like Wikipedia we have seen an explosion of information on topics of all kinds. Wikipedia is many times the size of even the best lexicons. In the new digital age, we need not only to bring money to the internet, but to bring the innovative power of the internet to the services that money can provide: smart contracts, micropayments, and in short “programmable money” will unleash the exponential growth of information-technology into the realm of global, financial services.
BitShares Decentralized Exchange
Before creating BitShares, founder Daniel Larimer was on a quest to create digital money. When he discovered that Satoshi Nakamoto had beat him to it and created Bitcoin, he decided to tackle the next important challenge: Creating a decentralized exchange.
BitShares was the first decentralized cryptocurrency exchange. There have come along other decentralized exchanges such as BitSquare worth looking into, but I will focus on BitShares here as an example of what can be achieved with this sort of system.
Daniel Larimer realized early on that Bitcoin suffered from its reliance on centralized exchanges. The news of Bitcoin that reached mainstream media often focused on the broken services provided by such institutions instead of all the great innovation that was happening on the underlying technological level.
With a decentralized exchange we can avoid the breech of privacy, theft, frozen accounts and confiscations we have seen throughout the Bitcoin industry since its inception. To create a decentralized exchange that goes beyond this paradigm, the BitShares team had first to solve two distinct problems: SmartCoins and KYC. Let us take each in turn.
Smartcoins

BitShares was funded with a vision to implement stable currencies on a decentralized network, so-called Smartcoins. The idea is to have all the great benefits of Bitcoin, but also have the option to save and transfer funds in more stable currencies or assets, like USD, CNY, Gold or Silver. To implement this hybrid of ordinary assets/currencies and cryptoassets/cryptocurrencies required a novel mechanism.
To generate these smartcoins, people can borrow a given smartcoin into existence, like bitUSD, bitCNY, bitGOLD, or bitSilver by putting up put up 100% or more BitShares “shares” in a digital lock, for security (collateral). These Smartcoins can thus at any time be converted back to bitshares at an exchange rate set by a decentralized price feed. This is similar to how a bank does it, only a bank lends money into existence by using for instance your house as security, and usually allows you to borrow with just 10% of the total placed in security.
After a year of discussing the market mechanism and the mechanism for locking up security in the decentralized system, the big question was if the free market would decide to value these assets the same as their real world counterpart. The current status of this economic experiment is that Smartcoins like bitUSD, bitGOLD and other are trading on par with their real world counterpart, although liquidity is still quite poor.
Know Your Customer (KYC) Compliance

BitShares had to give the decentralized exchange the option to comply with KYC regulations to bridge the gap between traditional finance and the cryptoeconomy. KYC regulations say that as an exchange you have to “know your customer” which means that you have to know their personal information, how their are spending their money, and finally you have to be able to control their funds in the event that authorities tell you to confiscate or freeze their funds.
BitShares enables KYC compliance at the “edges” of their platform, while keeping the core of the platform decentralized. It does this by making it possible to issue assets on the decentralized BitShares network that are controlled by the people issuing them. In this way people can issue their own IOUs for their local fiat currencies, and retain back-up control of these IOU assets while keeping track of the identity of their users.
KYC and bitAssets: Gateways
With BitShares having solved both of these problems we are now finally free to combine them in the free market to form gateways - bridges to between the traditional economy and the cryptoeconomy. Let us first consider how a normal exchange works, before we get to how BitShares solves the problem:
A normal exchange like BitStamp who receives USD from the bank of a customer, covers the USD into a token on the BitStamp exchange that represents one USD. When we trade with these BitStampUSD tokens on the centralized exchange we are really shuffling around numbers in BitStamp’s internal accounting system: If something goes wrong, if there is a theft, if my account is frozen, my BitStampUSD token can be lost in a heartbeat.
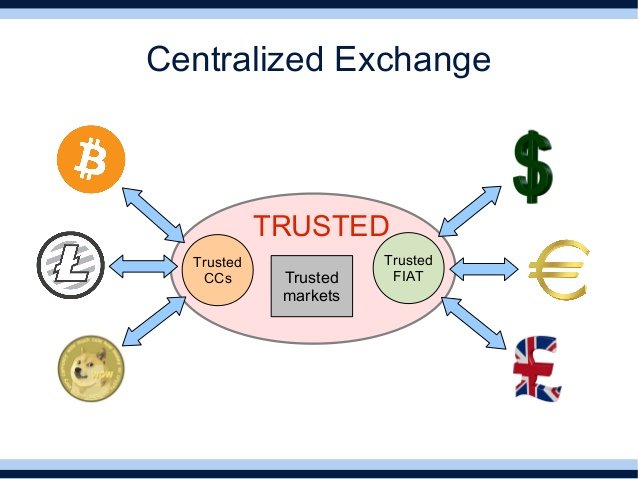
BitShares now solves this problem by allowing BitStamp to have a public accounting in the BitShares network, because as we saw above BitShares lets exchanges comply with KYC regulations. Now that there is a BitStampUSD (Trusted USD) on the BitShares network, the user who is holding these tokens can do something interesting – they can trade these BitStamp IOU tokens for bitUSD!
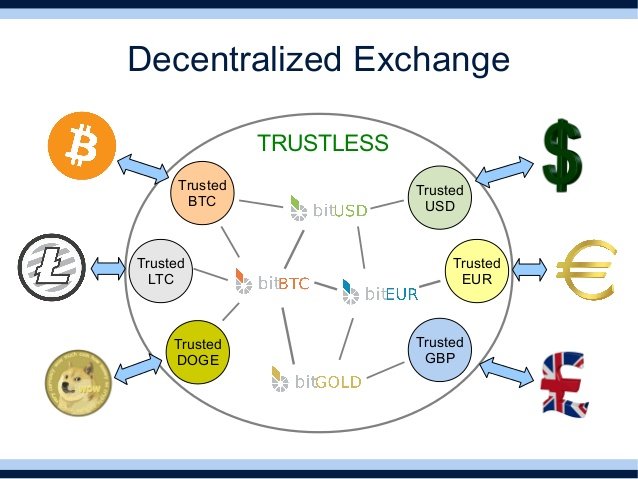
This means that they are now suddenly holding a kind of USD that is not subject to theft, confiscation or someone spying on how you use your money. With this step the users has suddenly transitioned into a completely free, open and decentralized exchange, where you are the sole authority of your own funds.
Conclusion
Decentralized exchanges are the key to global, frictionless value-transfers. Without decentralized exchanges, there will always be intermediaries having control over the flow of value, causing inefficiencies and worse. BitShares’ decentralized exchange solves two key problems, that of creating a cryptocurrency-backed derivative and that of enabling the cryptoeconomy to interact legally with the traditional economy without sacrificing its essential power to decentralize the global economy.
To Learn More:
https://bitshares.org/technology/decentralized-asset-exchange/
https://bitshares.org/technology/price-stable-cryptocurrencies/
https://bitshares.org/technology/user-issued-assets/
My Related Content
@psylains/what-is-bitshares
@clains/the-what-why-and-how-of-centralization-and-decentralization
@clains/bitcoin-banks-the-final-disintermediation
@clains/what-is-bitcoin
@clains/capitalism-communism-and-decentralization
