As I compare to any other whitepapers, IOTA takes the more technical and mathematical approach in trying to explain the "Tangle" using a variety of high level mathematical equations that will surely make my nose bleed, or atleast if you are a mathematician, take up a bit of your time into retracing these equations. Therefore I have decided to be able to create for you an easily understandable article to starting out with IOTA. IOTA_Whitepaper
IOTA: Internet of Things plus the Blockchain
IOTA is simply a new blockchain technology which will support the now growing concept of Internet of Things. IoT as in its name, is basically connecting any physical device to the internet and to other devices as well. This concept will definitely change the way we live and work today once fully executed. Whereas Blockchain is a distributed ledger or a growing list of transactions secured with the use of cryptography.
With the use Blockchain technology, a huge scope of problems that IoT has could be solved. IoT will need the ledger for machine to machine transactions, security of devices which includes identity and automated processing of data.
I once asked why is there a need for IOTA when there is Bitcoin. Well, a lot of us know that the biggest problem Bitcoin is facing today is its scalability and high transaction fees. If a cryptocurrency could hardly scale, then it would not be perfect for IoT. Such projects will serve a wider audience therefore it should be able to cater transactions equally or more for faster execution and lower fees.
The Tangle
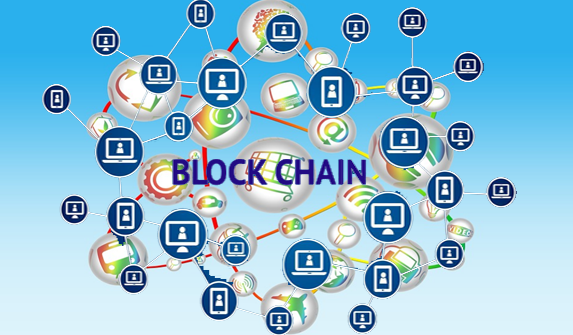
To achieve more of the challenging demands of IoT, the team created the Tangle. Tangle is IOTA's major innovation. It is a different and new type of distributed ledger which is based in Directed Acrylic Graph (DAG) architecture. They refer to it as “A Blockchain without the blocks and the chain”.
In my own understanding, Tangle can be totally separated from Blockchain as a new type of technology. Even though it has similar rules such as a peer-to-peer network, a distributed ledger and executing on validation and consensus mechanism, it is not structured as the blockchain.
Tangle has no blocks but only single transactions referenced to two or more transactions. Maybe that is why it is called Tangle because it is not a straight chain of transactions but rather some kind of a maze. Final transactions are considered one if there is a great probability that it has paths leading to a new and unconfirmed transaction, which is a sort of attestation evidence that a certain transaction is true or valid.
Each transaction directly proves that two previous transactions are valid and indirectly proves a subsection of the Tangle the same. This means that there is no need for miners to confirm or validate transactions as active participants are straightly involve in the confirmation process.
The transaction process
IOTA transactions are processed in simple 3 steps. If I am going to send IOTA, the first step that I will do is to sign my transaction inputs with my private keys. Then the system will randomly choose two tips or unconfirmed transactions which will be made reference by my own transaction. Lastly, I need to complete some Proof of Work for my transaction to be accepted by the network.
After the process, my transaction will then be broadcast to the network and a new transaction will choose mine as part of its two tips selection. That is the time my transaction is confirmed. This referencing process serves as an attestation or showing of evidence that something is true or valid.
Three Levels of IOTA transactions
To explain further, there are three Levels where IOTA transactions will have to undergo. We will call Level 1 as the unconfirmed transactions, Level 2 as the uncertain transactions and Level 3 as the final and secured transactions.
Once an unconfirmed transaction is referenced by a new and unconfirmed one, then it will reach Level 2. For it to reach level 3, it needs to reach consensus where the receiver or merchant needs to accept such transaction.
If I would be the merchant, it would depend on me at what percent of probability I will start accepting transactions. The probability I am talking about is the number of times that a transaction land to an unconfirmed one over the number of times a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm is executed. MCMC algorithm is used for sampling from a probability of distribution.
So let us say 60% probability is already good for me to accept transactions. For a 100 times of MCMC execution, I will accept the transaction when there is already 60 times that a transaction lands to an unconfirmed transaction.
ZERO TRANSACTION FEES
IOTA was able to attain consensus in making transactions valid without the help of miners and so they don't have transaction fees. Also, IOTA is the first to allow micropayment and nanopayment transcations without transaction fees for the sender or the receiver. I am personally amazed as transaction fees are always a bother for me and IOTA has set an unbeatable standard for future sub-cent transactions use cases.
SCALABLE
The process at which consensus is achieved in IOTA is parallelized and that what makes it to dynamically grow and scale. Unlike blockchain wherein consensus are done in sequence of blocks. As transactions grow in the Tangle, the more it gets secure and more efficient. That is the promise of IOTA technology.