Cryptology Series Part 1: Getting the Basics
Hello,I am digicrypt and thank you for checking out part one of my “Cryptology Series”! If you haven’t done so already, go to my #introduceyourself post here. The post will give you a bit of my background and help explain what I plan to do with this blog.
One more thing before we start, this is part one of my series and thus my first attempt. The purpose of this series is to educate and entertain, I will try and balance this blog between the technical and easily understood but your feedback is crucial, if you like something or think I can do something better comment and let me know!
Thanks now let’s get started!

Cryptology Series Part 1: Getting the Basics will focus on establishing some basic vocabulary and fundamentals nothing too earth shattering. Future posts will get more complex and I will actually teach you several cryptography methods later on that you can use with friends.
What Is Cryptology?
Cryptology- comes from the Greek words kryptos, "hidden," and logos, "word”. Cytptology is the scientific study of cryptography and cryptanalysis.
Cryptography and Cryptanalysis
Cryptanalysis- is the science of studying and breaking the secrecy of encryption processes, compromising authentication schemes, and reverse-engineering algorithms and keys.
Cryptography- is a method of storing and transmitting data in a form that only those it is intended for can read and process. It is considered a science of protecting information by encoding it into an unreadable format.
- The goal of cryptography is to hide information from unauthorized individuals.
- With enough time, money and resources hackers can break most algorithms, a more realistic goal for cryptography is to make obtaining the information much to work-intensive and time consuming for the attacker.
- The roots of cryptography can be traced back to roughly 2,000 B.C when Egyptians used hieroglyphics to decorate tombs. Part 2 of my series “The History of Cryptography” will give a lot more detail and provide some really interesting examples and stories.
Encryption-is the process of encoding messages or information in such a way that only authorized parties can access it.
- Three main methods of encryption (All of these will be explained in detail later on)
- Substitution
- Transposition (Permutation)
- Product Cipher
Other important Definitions and Concepts to know before we start Cryptography.
These concepts are crucial building blocks so pay extra attention here!
Plaintext- readable text
Ciphertext- unreadable/ encrypted text
Cryptosystem- a system or product that provides encryption and decryption.
Algorithm- the set of rules also known as the cipher, dictates how enciphering and deciphering take place
Key (cryptovariable)- Sequence of bits that are used as instructions that govern the act of cryptographic functions within an algorithm.
Keyspace- a range of values that can be used to construct a possible key.
We can see in the diagram below the relationship between Plaintext, Ciphertext and the key.
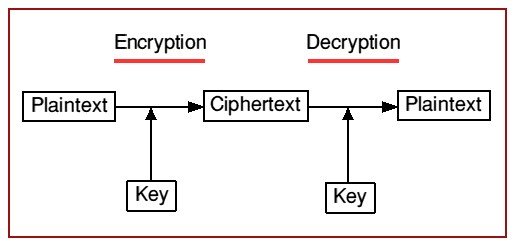
Plaintext is put through an algorithm governed by the key becoming encrypted cipher text. To decrypt we reverse the process with the key to read the hidden message.
This information comes from my own experience and knowledge as well as The CIISP Exam Guide Sixth Edition ISBN:978-0-07-178174-9
This information is really the building blocks for cryptology. Some of the info is a bit dry and basic but it lays the foundation before we can go any further I hope you learned something new and I hope you will stick with me for Part 2 “The History of Cryptography” which will be really fun and interesting!
In the meantime, stay tuned for a few challenges!
Your feedback is really important to me, please comment and let me know if you liked this post or have questions.
Please upvote and resteem if you found this post interesting!
Follow my blog @digicrypt if you want to learn more!
Digicrypt,
Signing Off
