The world's climate is changing, and the changes will have an enormous impact on our planet's people, ecosystems, cities, and energy use. Average global air temperatures are already 1.4 degrees higher than they were at the start of the 20th century and have risen about 1.1 degrees F over just the last 30 years.
According to the latest report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), average global temperatures are likely to rise by another 2 to 11.5 degrees F by 2100 [1]. If we take aggressive action to reduce emissions, the temperature change could be modest. If we continue on our present course, however, the amount of change will be substantial. These are probably because these changes are anthropogenic, meaning to say it is caused by us humans. The burning of fossil fuels is one of the examples of human emissions of greenhouse gases. The chief greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide and CO2 levels are at their highest in 650,000 years.
Oftentimes people expect the weather to change just like that but struggle to come to an agreement about how exactly the climate is changing. This is due to the fact that climate change itself manifests differently depending on the trend and people always tend to remember extreme events like droughts, hurricanes, very cold or very hot.
How is the climate changing?

Basically, how is the climate changing? There have been long-term and short-term climate cycles for hundreds of millions of years, as far back as these changes can be measured. Many of those climate changes were dramatic and rapid, some the result of impacts from comets or asteroids.
During 2006 and 2007, several major reports from the IPCC, founded on a wide scientific agreement, catalyzed broad acceptance that Earth's climate is changing rapidly and that human activities are the primary factors causing this change. Many of the factors that caused earlier changes continue to influence today's climate, but human activities have now become the predominant force causing our climate to change very rapidly. There is now strong consensus throughout the scientific community on this point.
What is global warming?

Now, what is global warming? Humans are creating climate change by burning large amounts of fossil fuels, coal, oil, natural gas. Also, another factor is deforestation. Deforestation happens when wide areas of trees are cut down or burned, and these trees can no longer store carbon, therefore, releasing the carbon into the atmosphere. This process will result in global warming. These gases, like carbon dioxide, act like a blanket that restricts the ability of the Earth’s surface to radiate heat back into space. Today, current levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere are higher than at any time during the last 650,000 years.
Since 1992, each year has been one of the 20 warmest years on record. 2010 was the hottest year on record, worldwide. Exactly how much warmer the atmosphere gets will depend on how quickly and effectively people can substantially reduce the activities that are causing rising temperatures. In relation to this greenhouse effect takes place.
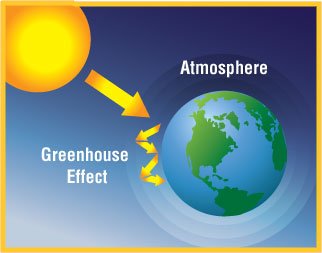
What is greenhouse effect?
By definition, the greenhouse effect is the warming of Earth’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) that is caused by the presence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapor has the largest effect [2]. Surprisingly, the atmosphere's most abundant gases which are the nitrogen, oxygen, and argon do not influence climate. Instead, it's the molecules of trace gases, especially carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrous oxide (N2O), methane (CH4), water vapor (H2O) and ozone (O3) that strongly absorb infra-red radiation contained in sunlight, or emitted by land and water as they cool [3]. Just as greenhouses keep the air inside them warm, so water vapor and trace gases keep Earth about 54º F warmer than it would be without them. This retention of heat is called the greenhouse effect and the gases that cause it are known as greenhouse gases.In Conclusion
There is no single solution to global warming and climate change that's why we students are trying to understand and study the cause and effect of these natural phenomena. So that at some point we can aid and help in the future generations through helping at least in reducing the causes and avoiding in contributing to worsening what has already been damaged.
References:
- http://www.rema.gov.rw/climateportal/spip.php?rubrique14
- https://www.britannica.com/science/greenhouse-effect
- http://www.sakshieducation.com/CA/GStory.aspx?cid=1&sid=4&nid=140747
- http://www.ipcc.ch