Six days ago, the Cassini burned up in the atmosphere of Saturn. It was launched on 15 October 1997 and did not live up to its 20th anniversary only 1 month. During its mission, Cassini has made more than 453 thousand photos, sent to the Earth more than 600 gigabytes of information, by their results already written about 4000 scientific articles.
The spacecraft overcame 7.8 billion kilometers, fulfilled 2.5 million commands. Cassini mission was serviced by more than 5000 people, and its cost exceeded $3.9 billion.
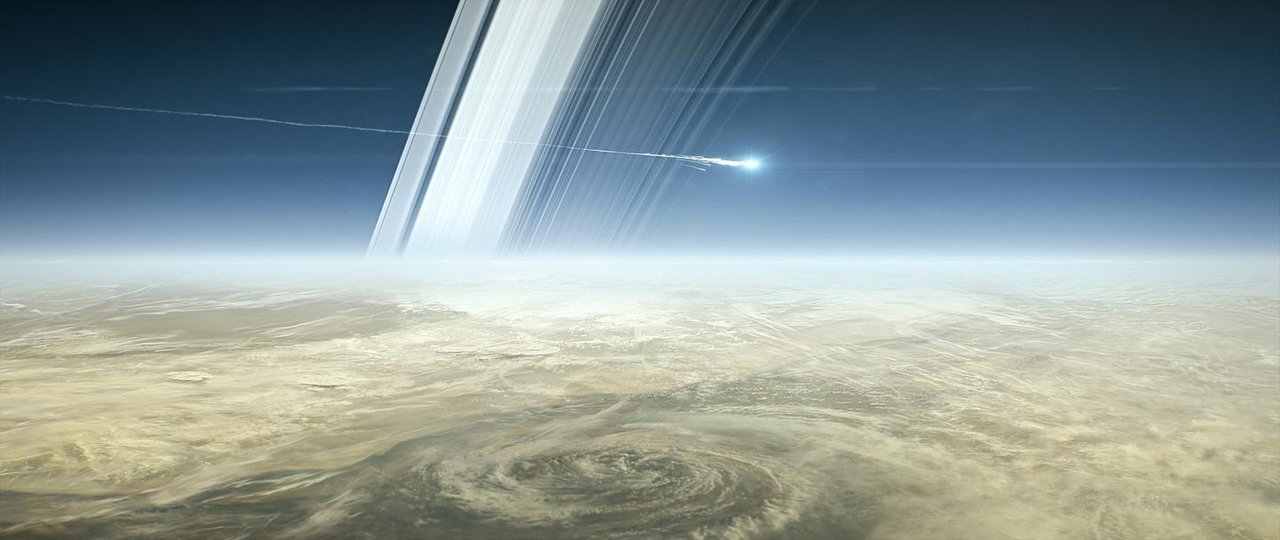

image source
Cassini had no serious failures in the systems, it was designed so that in recent years practically did not use fuel, and could continue to work for many years. Anyway, it was sent to perish in the terrible atmosphere of Saturn…
This is not the first and not the last space traveler, whose life was rudely interrupted in the control center on the Earth. In 2016 Rosetta was destroyed in a collision with a comet. Three years earlier in 2013, the Herschel telescope was left in an unknown orbit around the Sun, millions of years in length.

Touching movie about the mission Rosetta
Most of the devices that are studying the Moon, crashing on its surface at a terrific speed. 2008-2015 Messenger spacecraft was studying the Mercury. The remaining fuel in propulsion engines was used to accelerate the apparatus up to a speed of 3 kms/h. The final destination was the mountain massif of the planet. Collision at this speed did not leave even nano-debris.
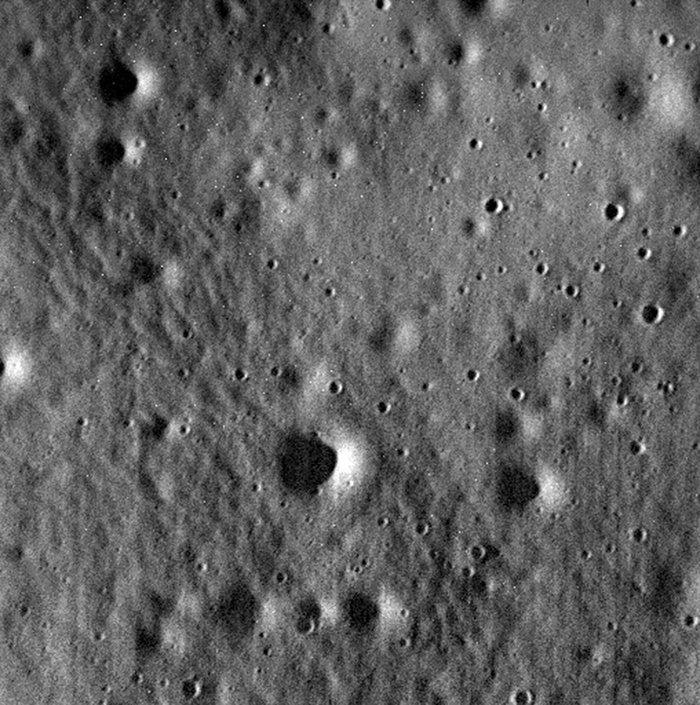

The last photo taken by Messenger
Galileo rotated around the Jupiter at a speed of 51 km / s and was send to its atmosphere, like Cassini. Due to the high density of the atmosphere of Jupiter and high speed, it was literally evaporated.
It looks a bit weird - to destroy expensive space probes, that are still able to function. Why do we kill unique projects with a budget in the billions of dollars, over which thousands of people worked over the years? There are only two reasons.
Money
It sounds sad and materialistic, but any space mission to study the nearest of the planets or distant galaxies is an unprofitable activity from a financial point of view. Once again, remember about Cassini: almost 4 billion dollars and 5,000 people for maintenance.

image source
Hubble has cost at least $ 6 billion. Hundreds of thousands of photos hardly have returned at least 1/1000 of the money spent.
Science for the sake of science, not for commerce. At this stage, humanity does not have the opportunity to apply the obtained data in practice for profit. Undoubtedly, huge volumes of new information are pleasing to scientists and all mankind. But, we should not forget that all the major space agencies are not commercial organizations, and every year they fiercely fight for funding.
Cassini was launched 20 years ago, despite its durability and importance of the mission, for 20 years there was a serious leap in technologies. Therefore, it is much more rational and right to redirect money and manpower on more modern and ambitious projects, which in the future will allow to get more useful and new information.
Among the huge list of victims of the space industry there are two lucky: Opportunity (rover) and Voyager spacecraft, which greatly exceeded their period of operation.
Opportunity became a national hero and a favorite of the public. Therefore, any attempt of the Agency or Ministry to send it in the scrap are taken very negatively.
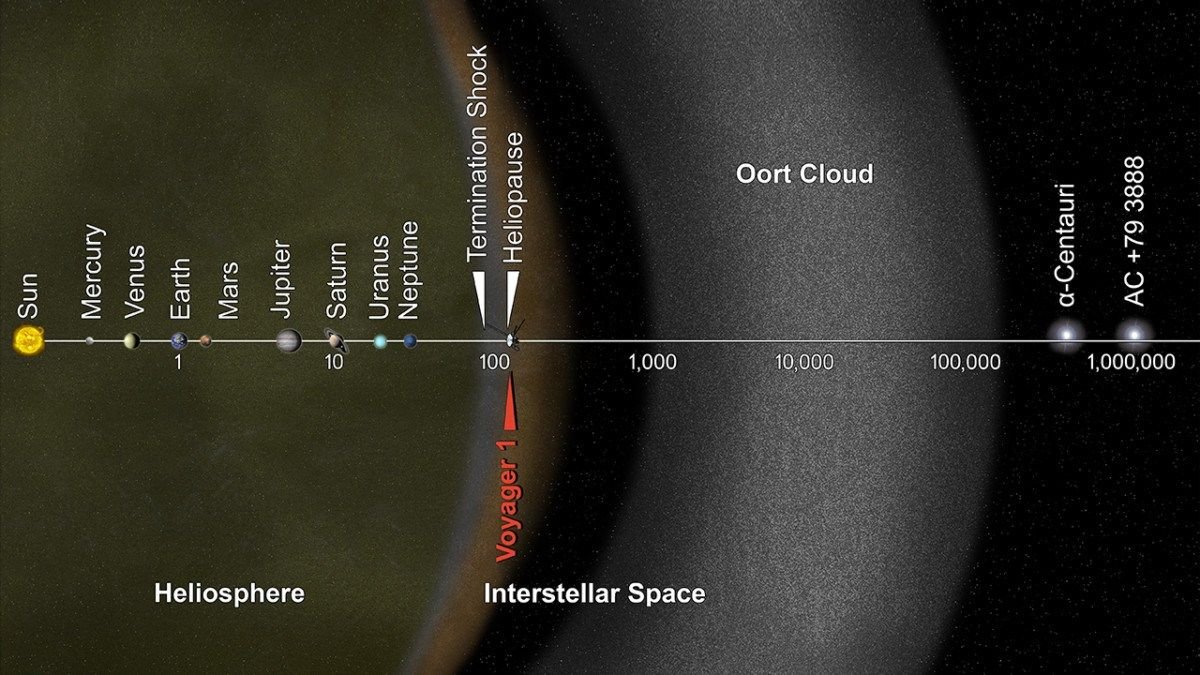
The distance of Voyager from The Earth.image source.
Voyager is the undisputed record holder- 37 years of continuous flight, he overcame the boundaries of influence of the solar wind. Voyager already doesn't send any data, and rather is a symbol of human achievement.
Planetary Protection
The second reason sounds much nobler than the first. We can’t keep our own planet clean, but at least try to care about other objects in our solar system. And it's not about pieces of plastic or fuel waste, the main task - to protect the space from the spread of life.
Many organisms on Earth have unique abilities to survive. Extremophile- creatures that can survive and reproduce under extreme environmental conditions. They are able to live without oxygen, light, withstand enormous pressure and high temperature differences.
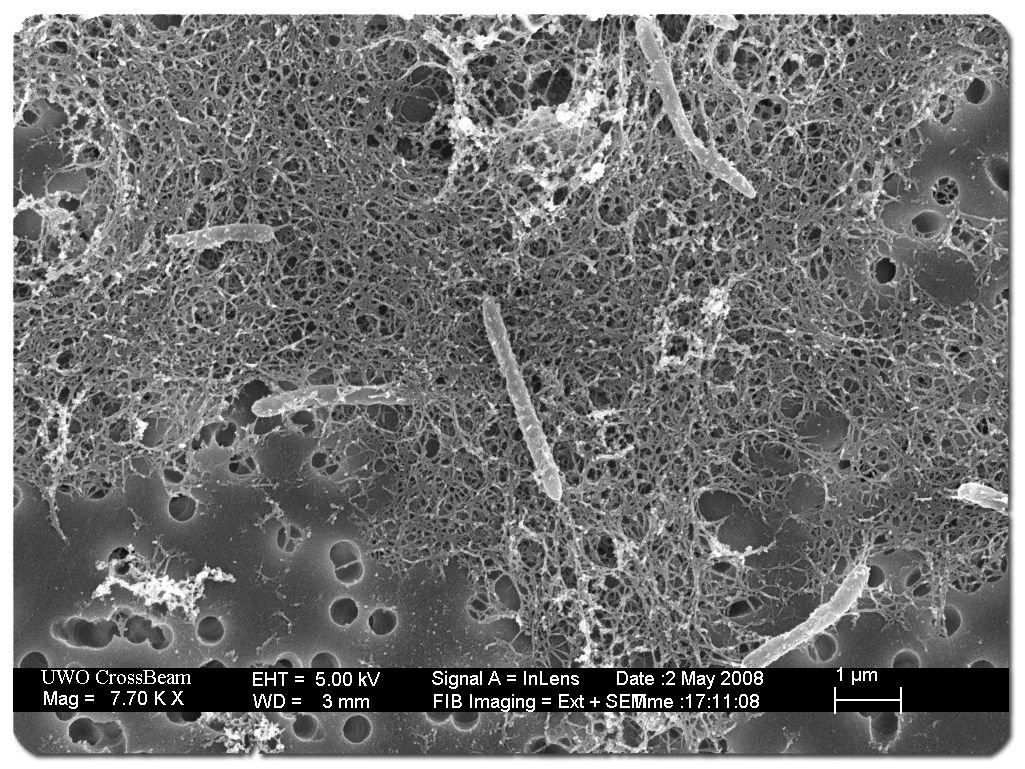

Desulforudis audaxviator lives at depths of 2-3 km in strongly alkaline solution at a temperature of about 60 degrees and completely without oxygen. image source
Сosmic radiation is the main sterilizer, but it is not a 100% guarantee. Some organisms are able to survive under radiation influence in the presence of metal protection with a thickness only of 1mm.
That is why on 10 October 1967 was signed Outer Space Treaty. In two words: States-parties should undertake the study of space objects with minimal chance of its contamination.
Imagine: Cassini simply disconnected and stay on the orbit of Saturn. Collision with an asteroid knocks it out from this orbit and routes to the Titan or Enceladus. These satellites have a theoretically habitable atmosphere and chemical elements for live on the surface. The spacecraft even with 1 microorganism on board can become the missing element, which will create another life.
In the framework of planetary protection for each mission used The Coleman-Sagan equation. This equation allows to calculate the approximate probability that microorganisms from the Earth will survive all the phases of the space mission.
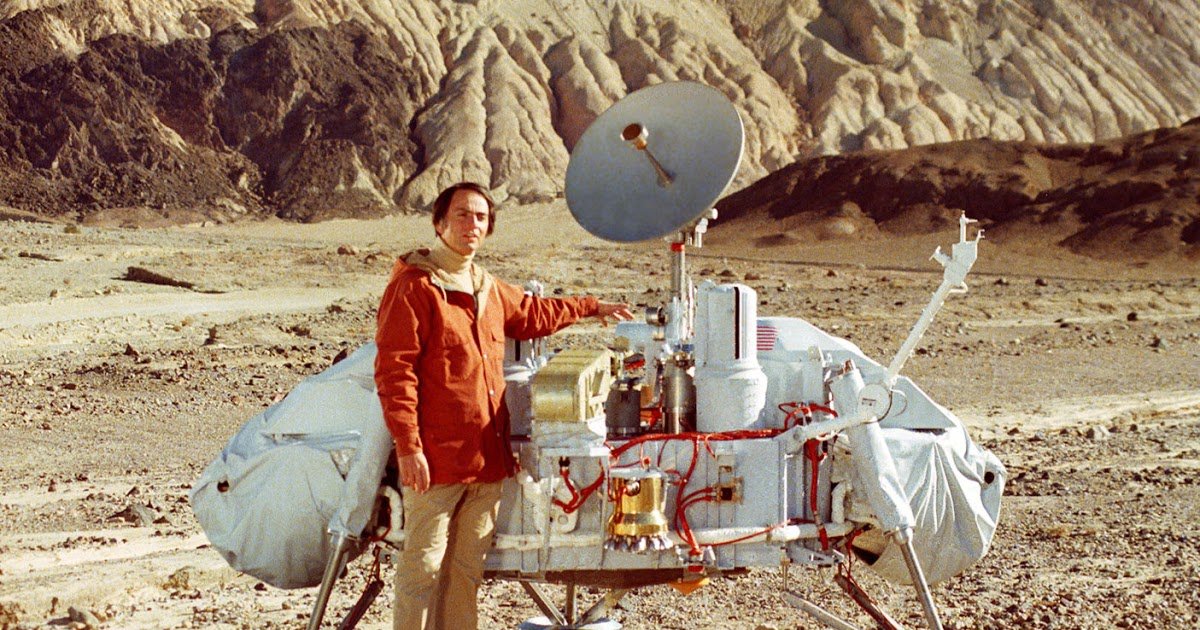

Carl Sagan and prototype of the Viking. image source
That is why you must be sure that the spacecraft will not be in the vicinity of objects, on which theoretically there are conditions suitable for life.
The main last task of any space mission- to destroy or isolate the spacecraft with the maximum probability of the death of any living organism.
***
Cassini legacy will live long. Photos of Saturn and his satellites will stay with us forever. Money and personnel, freed after the completion of the mission, will be directed to other projects. A similar fate awaits the Hubble telescope in 2018, after almost 30 years of service, it will be replaced by the new telescope James Webb. And that's fine, we have a lot of new projects that will further expand our understanding of the Universe. The end of one mission only means the beginning of a new one...

sources: The death of Cassini, Nasa attaks the Moon, Recycling spacecrafts, Planetary Protection, Cassini's end, and others in the article. Images from Google Search.
If you liked this article, you can also check other interesting materials about he space industry:
- Space Food: Welcome To The ISS Kitchen
- What Space Objects We Can Reach With Our Speed
- Space Debris: A Problem Without a Solution?
- Asteroid Mining: The Near Future or False Hope?

