You don't have a soul. You are a soul. You have a body." C.S. Lewis.
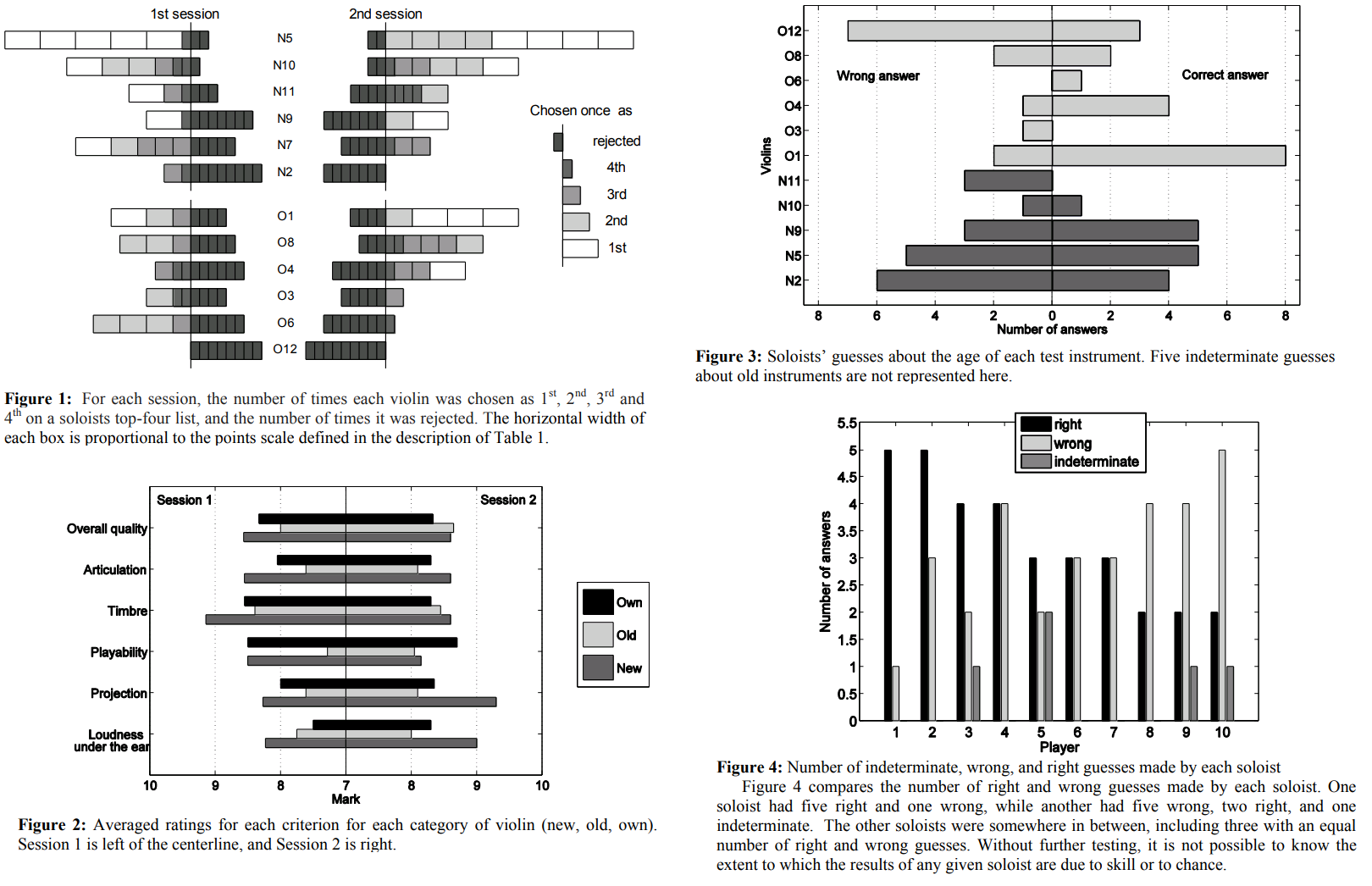
Laurie Niles, John Soloninka, and Ariane Todes each give their impressions and interpretations of what happened that day in Indianapolis, Indiana. During the Eighth International Violin Competition of Indianapolis (IVCI) year 2010, a group of 21 people were selected and assembled for their musical proficiency as judges to choose from a selection of violins in a double blind performance.
6 violins were used: 2 ‘Stradivari’, 1 ‘del Gesu’ (300 years-old instruments); and 3 modern violins.
The players' preferences and ability to identify modern vs old-master piece instruments were tested. The conditions for the double-blind study were quite reasonable -Tricking the players to avoid recognition by anything different than sound, the same for performers and researchers- as the analysis of the data.1 The study performed by Claudia Fritz and Joseph Curtin, published in PNAS. Showed that expert performers and listeners could not reliably differentiate masterpiece violins -at least no better than a coin toss- from modern violins made by good luthiers. Also that their preference in sound differed from what they expected.
- The most-preferred violin was new.
- The least-preferred was by Stradivari.
- There was low correlation between instrument age and monetary value, and perceived quality.
- Most players couldn't tell whether the instrument they preferred was new or old.
- 13 of the 21 violinists preferred the new violins. Only eight subjects chose an old violin to take home.
- The violinists could not reliably identify which instruments were old and which were new
- The study revealed that there was no statistical correlation between the age of an instrument and whether participants preferred it in the head-to-head competition.
Of course, there was a lot of criticism about this experiment by musicians which claimed it was unfair and misleading. Some other didn't seem quite surprised about it and some even laughed at the idea3. After all, the ‘Stradivari’ and ‘del Gesu’violins are valued in the tens of millions of dollars each. World class musicians borrow them just to part with them after a few months of practice and some spend lifetime fortunes to keep them.
As a follow up, some violin soloists felt confident in their skills, and contacted the researchers in order to try a more organic test to address some of the criticism. The performance came as a shock to the participants as the data confirmed the previous study and offered even more insights
Video Documentary: Soloists try to challenge the previous study results
The results are consistent with the initial study.4The four figures of the second test can be summarized like this: after a more fair protocol selection tested rated by soloists at each point of the test -that included rehearsals and live performance, - they could define favorites and distinguish their preference among the other violins nonetheless, they could not differentiate an old from a new violin better than chance. The qualities for selection of a violin are fastidious and empiric evidence doesn't support intrinsic qualities to the masterpieces. If anything there were performance advantages to modern players with modern violins
This means that modern performers can acquire an excellent sounding violin for cheaper than millions of dollars, without taking any merit away from the old masterpieces. A question that arises is how cheap.
Most modern master luthiers spend months even years working on a single violin. So even these violins by a good artisan are in the range of the tens of thousands of dollars. Good ol' science loves helping a cheapo. So multiple engineers and scientists started to wonder the underlying principles of the musical alchemy. With physics.
Scientists are not to fond of excuses. So when examining a Violin they want to know how much is essential and what is merely decorative.
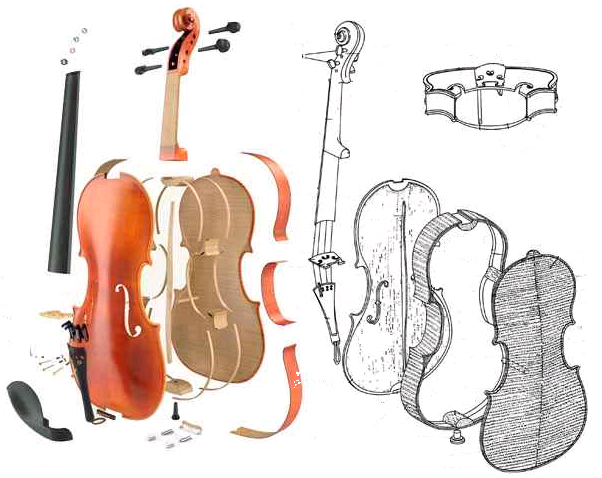
Violin
The production of sound by friction against a stretched string is a known fairly old phenomenon. First, the string was used on a flat surface, that later becomes concave to project the sound and later evolves into a box with an aperture. Is highly reminiscent of the cup-like evolution of the eye.

The viols were originally played in small rooms, so loudness was never a problem. As the instruments advanced and became part of public performance the interest in a louder sound started.
Sound is a longitudinal compression wave. This means it requires the alteration of a medium to propagate in the same sense -opposite or equal direction-. In the case of air, you normally get the desired frequencies and intensity by using an object that vibrates, roughly the same size of the wavelength of the frequencies you want to transmit. Strings are quite small, thus the energy they can transmit to their surrounding medium is small. A lot of energy is not transformed to sound and needs a way to be redirected through something that can create this effect and displace air. It needs energy amplification and efficiency, something like the principle of feathers -light objects attached to a rigid structure to displace more air-.
The interior of the violin is full of asymmetries. This is intentional. Construction of the soundboard -top of the violin- The back and cover of the violin are carved manually out from a solid piece of wood. Adjusting the internal thickness using carefully crafted calipers. The bar bass and the patterns of carving give the cellulose strand nature tone specificity for amplification.
The strings are attached with different degrees of tension at the extremes of the violin. Once the string vibrates, the energy is transmited 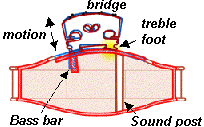 from the strings laterally to the bridge. Through the treble feet energy is distributed and relayed mainly by the sound post. How fast this energy is transmited depends on the force(F) required to create that displacement(Y), know as impedance (F/y)5.
from the strings laterally to the bridge. Through the treble feet energy is distributed and relayed mainly by the sound post. How fast this energy is transmited depends on the force(F) required to create that displacement(Y), know as impedance (F/y)5.
The strings have an impedance, so does the bridge and the body. If the impedance of two objects is different it flows across the joint slowly, if it's equal it ignores the energy flows ignoring the joint. As the impedance of the strings is low, the strings require heavy strings and a light body to get the impedance close to matching. You want a matched matched low impedance amplifier .
| String | G | D | A | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 196 Hz | 294 Hz | 440 Hz | 660 Hz |
| Tension6 | ≈4kg | ≈4kg | ≈5kg | ≈8kg |
The down beaming that occurs in the bridge at an angle of ≈25°means the bridge -a small and light piece of wood of about 3mm thickness- requires to support close to 10kg of force. Thus one of the main reasons for the curve like structure of the violin is to give strength. Even the curved shape of the sound holes aids in this task.7
New look at materials: Carbon Fiber and ... Balsa?
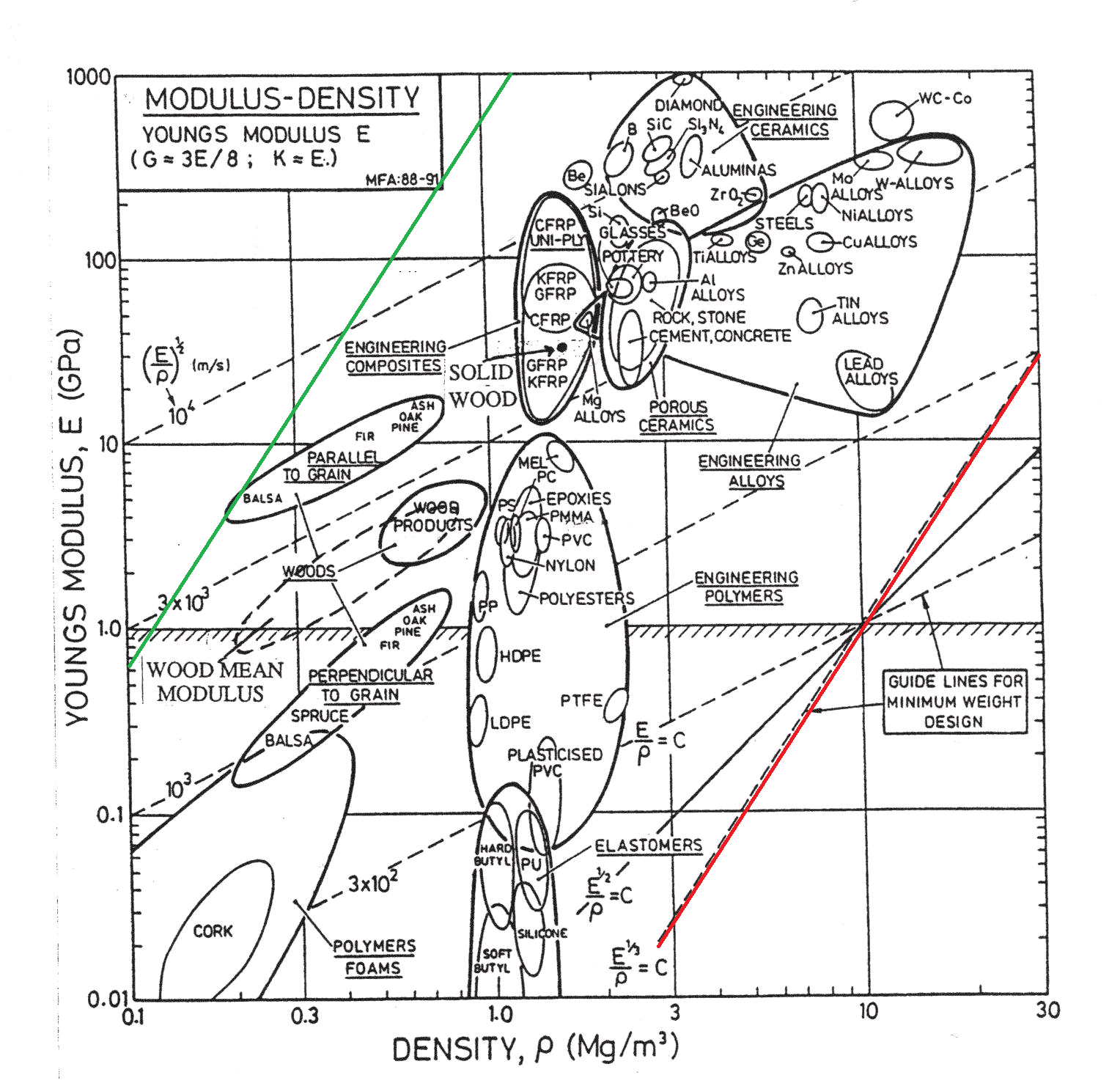
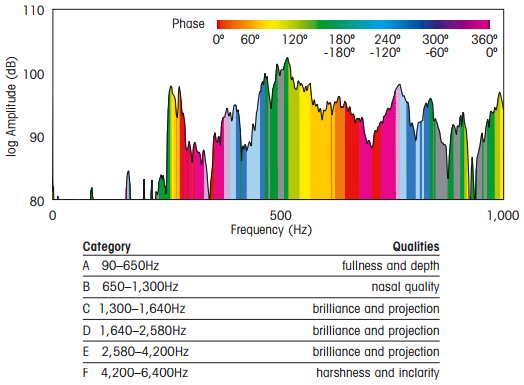
The above diagram shows the logarithmic distribution of two properties in most existing materials. Density (ρ) that measures volume and the youngs modulus (E), that gives you a measure of how stiff -and thus the energy required to make it bend- is a material. Inside the curved sets are the families of materials. For instance, at the extreme top, you can see diamonds is the stiffest material and foams and cork as the other extreme.8 The diagonal lines (slopes) in the logarithmic scale show the equivalent ratio of properties from one material to another. I've highlighted with red the ideal ratio for a loud violin with minimum weight 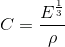 any violin constructed of materials in that line would be equally loud and the more to the left it is, the louder it will be.9
any violin constructed of materials in that line would be equally loud and the more to the left it is, the louder it will be.9
Wood is a marvelous cheap, versatile, advanced biopolymer nanomaterial that happens to grow on trees. The reason it appears twice in the graphic depending on the orientation of its cellulose fibers. Modern soundboards are made out of spruce.10 One of the reasons one would suspect balsa, that outperforms spruce in emission and radiance was not used to make violins by old master luthiers is because it was not available. Is a wood of the new world and didn't arrive in Europe till the 18th century and by then the art was set -after all, people till this day try to imitate the Cremona 18th century luthiers-.
A good amplifier should emit a sound with flat frequency response. The problem is that people enjoy degrees of noise and are used by statistical experience to enjoy some sound profiles above others. Some of them are psychoacoustic in nature as I described in my post on Gastrophysics and some of them are secondary to individual variation.11
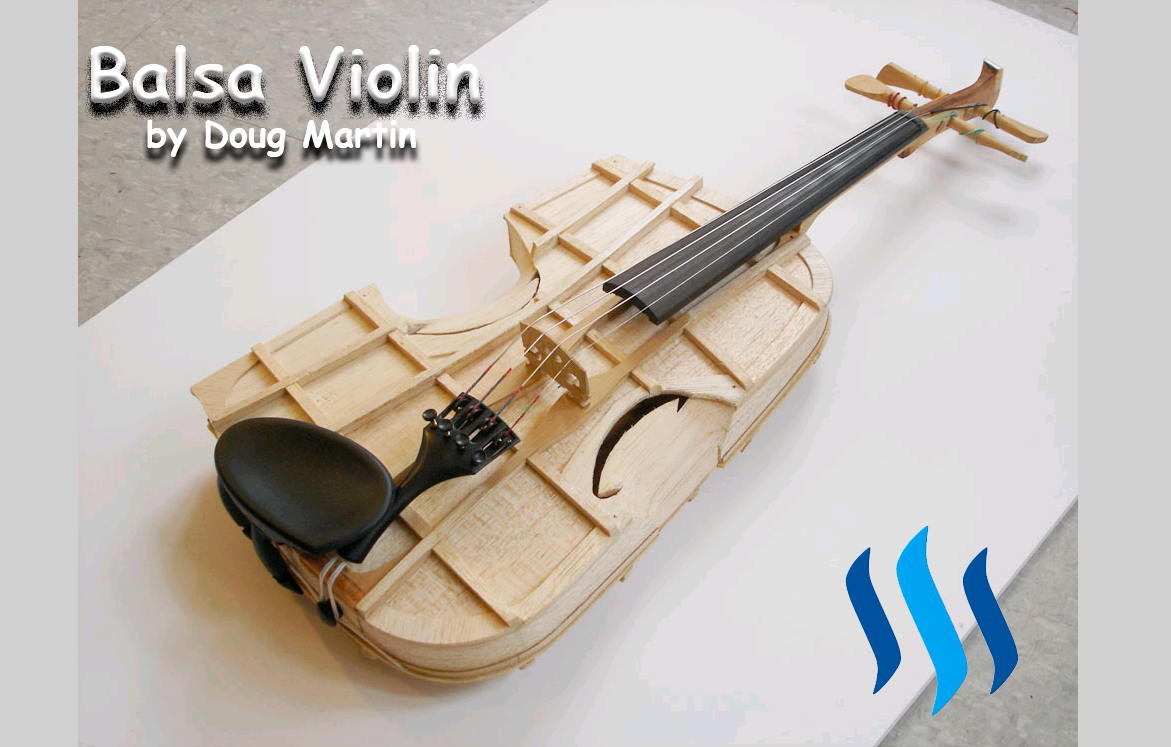
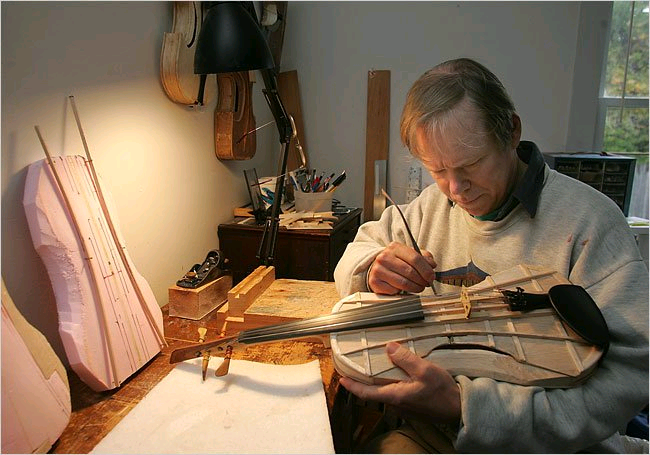
The green line in the modulus-density log chart, shows that out of existent materials, balsa should be the loudest. Balsa is said to be too fragile, despite it being structurally strong enough according to physics. Some people have started to experiment with the material like Dough Martin portrayed in the picture with great results. Although the musical luthier's community is not happy with the sound and material. Despite -Here it comes- some of them liking the sound during double-blind test performance.
Even if one were to consider the durability of balsa as a problem, is an engineering problem that composite materials and ingenuity can overcome also a problem that some Cello makers don't have, as their experimentation with balsa and the room for more weight distribution attests.12
Dough Martin playing the balsa Violin
Great appearent projection, microphone specs for recording unknown
A little to the right of the log chart we have materials like carbon fiber (CFRP) that have far more durability and less prone to changes in sound due to environment conditions. Of course most luthiers and musicians hate it, despite some of them winning single-blind tests like the Deutschen Musikinstrumentenpreis (German Music Instrument Awards)13
Systems of review face an almost paradoxical two-faced problem: How do you judge the quality of something, and at the same time how do you innovate?
Normally you use peer review systems.
Zombie Ideas
As technology advances, some previous judging systems and judges become obsolete. This creates a system where incentives to remain relevant breed biased selection and cheating. A problem with incentives in a zero-sum game is that people are gonna try to game the system. Always.
Professional expert investigation -particularly in science- is usually funded by grants. This means there's a pool of money that must be divided among everyone to fund research that will advance humanity. Problem is everyone thinks their research is important and will advance humanity.
My next post will deal with this. "Forensic approach to cheaters" see you next time.

References
2 Supporting Information Fritz et al. 10.1073/pnas.1114999109
5 Music Science at UNSW. Violin acoustics: an introduction.
6 D'Addario. Orchestral string manufacturers. Violin strings tension chart
10 Ulrike G. K. Wegst. Wood for sound. Am. J. Bot. October 2006 vol. 93 no. 10 1439-1448
11a. Can You Hear Me? : Violin Acoustics, Part 1 By J. Curtin & M. Schleske, The Strad, October 2003
11b.A World Apart? : Violin Acoustics, Part 2 By J. Curtin & M. Schleske, The Strad, January 2004
12 Balsa Cello construction project
13 Carbon fibre violin wins German Musical Instrument Award. 23 March 2015. The Strad magazine
Images referenced, sourced or modified from google images, labeled for reuse