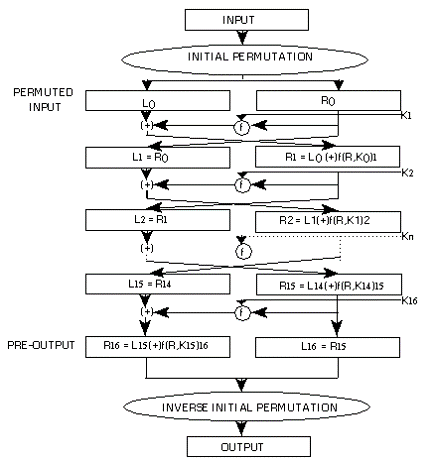
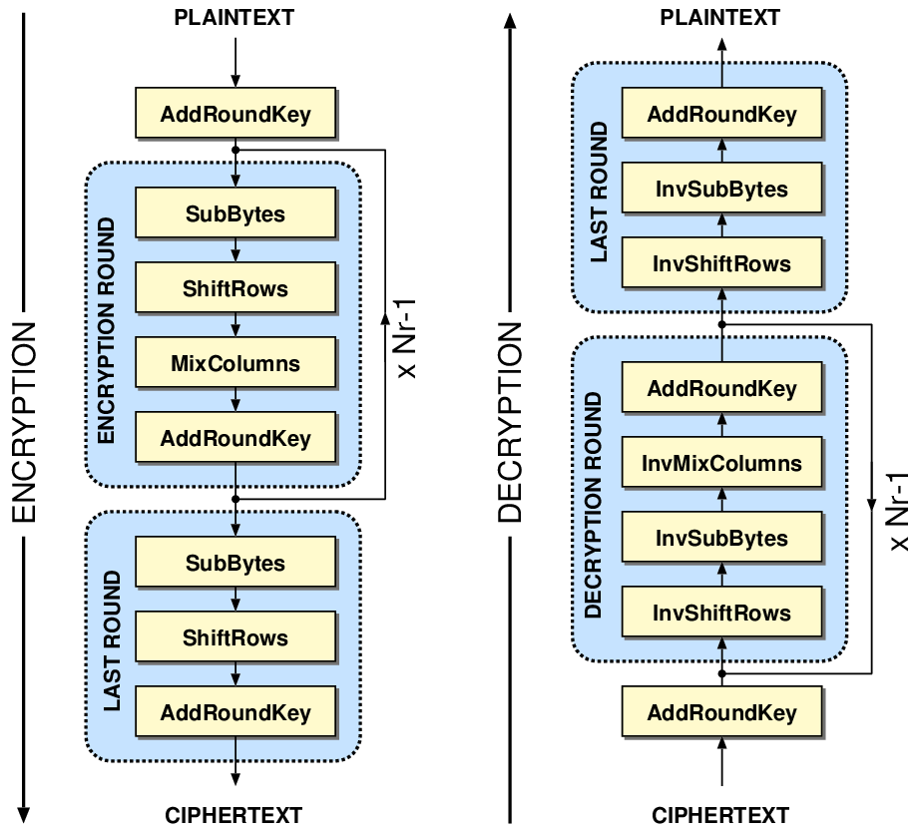
If you are new to my Cryptology Series or are having trouble with any of the terminology, I encourage you to go to my blog and check out parts 1,2,3 and especially part 4. Now let's get started!