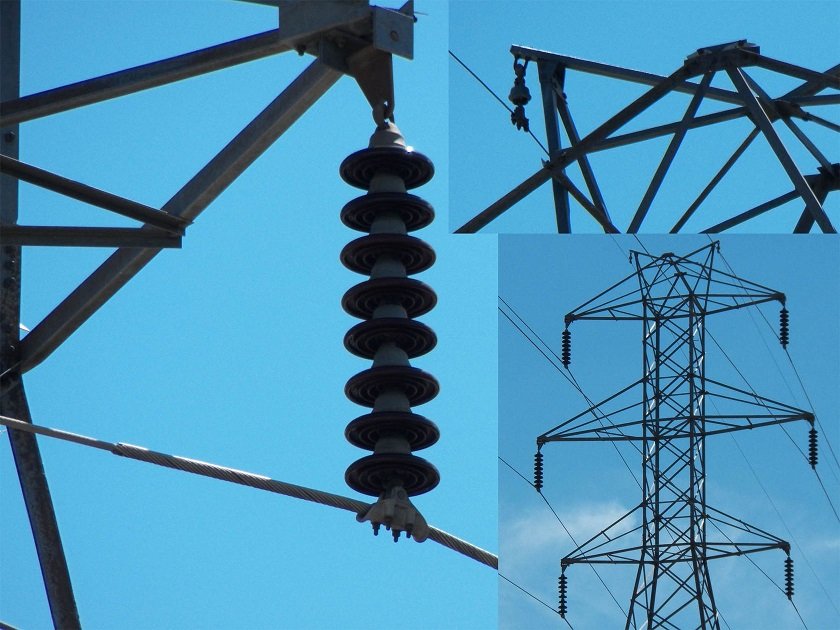

"Ceramic Power Line Insulators and How They're Made"
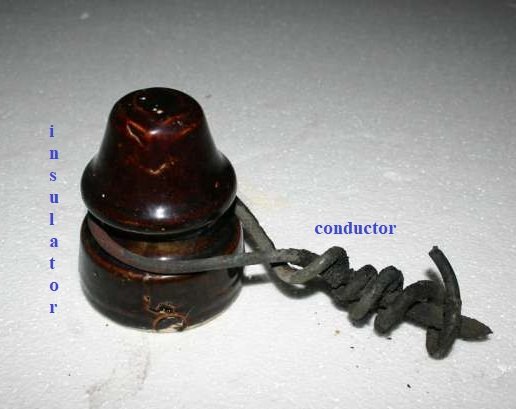

Conductors and insulators are the most significant materials in electronics and electrical industry, and these components are exclusively used for different purposes. Technically, electricity flows spontaneously in materials with high electrical conductivity called conductors. These conductive materials are usually metallic materials. On the other hand, insulators are materials with high resistance to current, which means it prevents electricity to flow freely. In contrast, insulators are generally non-metallic materials. Therefore, in general conductors are just the opposites of insulators.
Insulators are used to isolate conductors from other components to prevent forthcoming and unnecessary damages on devices. Plastic, rubber and leather are the most commonly known insulating materials. These materials are effective insulating materials as they are non-conductive. However, insulators could become conductors when excessive amount of large voltage are applied in it – which is known as the breakdown voltage of insulator. Thus engineers continually developed materials which could durably withstand high voltage in a long run. One of the best insulating materials which are being used today especially in overhead power line are ceramic materials.

Generally, insulators have two main functions; to isolate conductors and to separate conductors from other conductors. Most ceramic materials possessed high dielectric strength. So generally, ceramic materials have very low electrical conductivity due to its ionic-covalent bonding, which makes it good electrical insulators. Additionally, ceramic materials have low thermal conductivity which also supports its insulating capability as electrical conductivity is also influenced by temperature. This is because the movements of the electric charge or charge excitation are primarily caused by thermal energy. And one of the most common ceramic bodies used in overhead power line insulation which possessed these properties are porcelains.
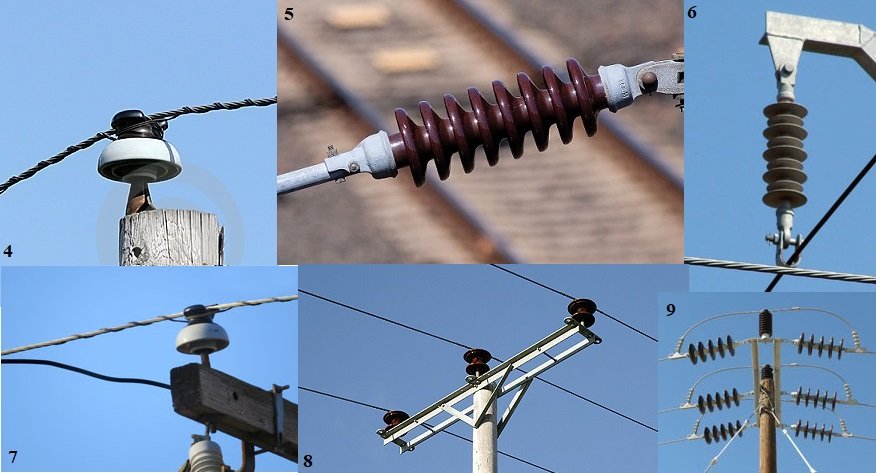
There are mainly two types of overhead power line insulators; pin type insulators which basically support conductors above structures and the suspension type of insulators which support hanging conductors in structures. Materials used as insulators in high-voltage power transmission need to have high dielectric strength such as glass, porcelain and composite polymer materials. Although glass has higher dielectric strength than porcelain, the cold surface of glasses collects dews especially when humid air is in contact with it. Porcelain on the other hand is better insulator with this matter. So how is porcelain insulator made?
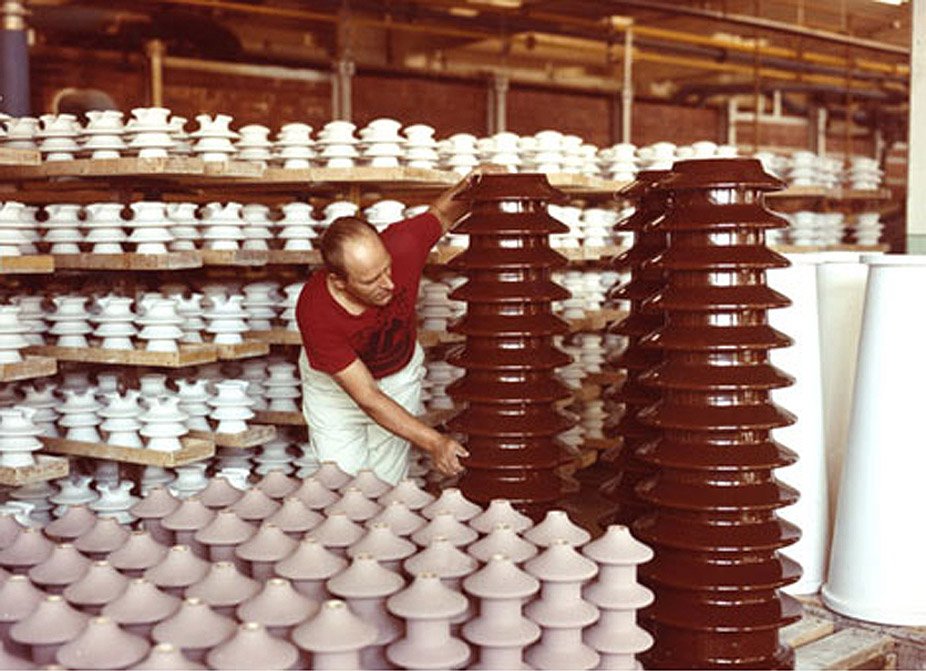

Porcelain insulators are primarily made of clay, kaolin, silica, alumina and feldspar. These raw material components are varied depending on the desired properties of target porcelain insulator to be made. For example, insulators with high mechanical strength have higher amount of alumina ratio in its formulation or raw material components. Smooth vitrified glaze is also applied to porcelain to primarily shed water and remove dirt. The design is also important. Basically, electrical breakdown of insulators occur either puncture breakdown or flashover breakdown and most of the high voltage insulators are designed with lower flashover voltage to avoid damage.
The Forming Process
There are different methods in making porcelain insulator but there are appropriate methods for every type of porcelain insulators. Insulators with simple shape can be formed and produced by pressing. Most common method in making porcelain insulator is called jiggering method.
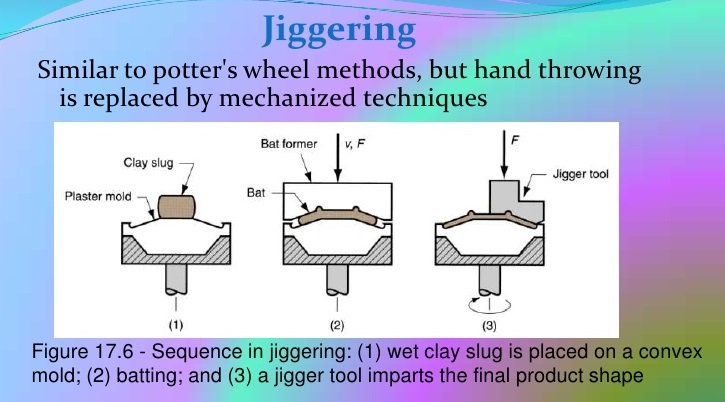
Raw materials are prepared by mixing with water to prepare plastic mass or wet clay slug. Jiggering method is somewhat similar to throwing method but does not involved hand throwing; instead the potter’s wheel is replaced with jiggering machine which take care of the whole jiggering process. Right after the insulator is formed, air drying or oven drying followed. Glaze application through dipping is done after initial oven drying process then firing procedure follows. However, this process is only limited to symmetrical and not complicatedly shaped insulators. For porcelain insulators with difficult and complex shapes, slip casting method is used, where the raw material components involved are prepared in the form of slurry or slip.
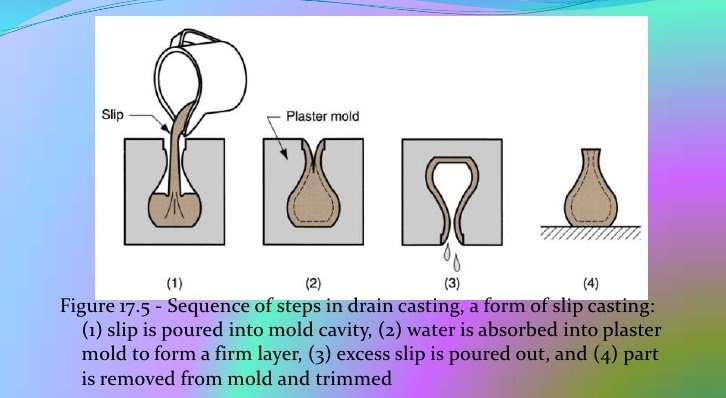
Slurry is a mixture suspended ceramic raw materials in water. This method also involved the use of plaster mold or gypsum mold. The slip is slowly poured unto the gypsum mold cavity and is permitted to settle down for minutes depending on the target thickness of the product. The plaster mold gradually absorbed the water of the slurry to form a firm layer. The excess slurry is poured out of the mold and the formed layer inside the mold is allowed to partially dry to obtain initial strength. The initially formed insulator is then removed out of the mold. Preheating follows then glazing via dipping or other glazing method. It is then fired at high temperature usually around 1100-1300 depending on the raw materials components used.
The Manufacturing Process of Ceramic Floor Tiles & Wall Tiles
Traditional Ceramic Methods in Making Earthenware, Stoneware and Porcelain
Lightweight Ceramics and its Advanced Application in Modern Military Armors
Ceramic Materials and its Advance Application to Aerospace Industry
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Overhead_power_line
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulator_(electricity)
http://kitbook.com/skin/frontend/base/default/files/ECK%20te%20chapter%204.pdf
http://www.substech.com/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=electrical_properties_of_ceramics#insulating_properties
https://www.slideshare.net/aliraza62742/ceramic-materials-their-processing-shared-using-visualbee

