
The consumption of drugs produces a large number of deaths throughout the year throughout the world. The UN carried out a global report on its consumption in 2017. It found that only the previous year increased the number of deaths derived from consumption by 11.4%.
The pleasurable effects they produce in the brain, somehow abducting the reward system, lead the person to become addicted. A prolonged consumption can generate neuronal impairments that affect motivation, emotions, cognition and executive control. All of this, on occasion, can be translated into the appearance of a mental disorder.
But what is meant by mental disorder? Guided by the clinical definition performed by the DSM-5, it is understood as a syndrome characterized by a clinically significant alteration of the cognitive state, emotional regulation or behavior of an individual, which reflects a dysfunction of the psychological, biological or developmental processes that underlie their mental function.
Drugs and their relationship with dopamine
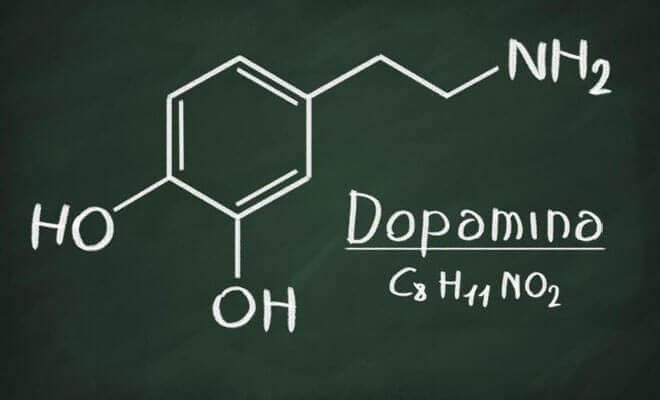
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter released by the brain. Among all its functions, the one that matters most to us at this time is the pleasure reward. That is, when we do something that we like, dopamine is released, creating a pleasant sensation. In this way, our body tends to seek again those activities "generating good sensations" to re-experience that feeling of fullness.
Both food and sex are actions that release dopamine. But also the drug. All of them will release high amounts of dopamine in very specific areas, such as, for example, the nucleus of accumbens. The latter will have a great participation in the brain reward system and in the integration of motivation and action. This zone maintains high connections with the limbic system and the hippocampus.
How do drugs work in the brain?
Neurons are the cells responsible for the nervous system responsible for the reception, transformation, management and storage of information. Between one neuron and another there is a space called synaptic space. This space is very important because in it if they release the neurotransmitters that enable chemical communication between neurons. Dopamine is going to be released and found in that synaptic space.
This implies that when any substance susceptible to addiction is consumed, dopamine levels in the synaptic space will increase. In this sense, drugs can increase the release of dopamine to this space, but they can also partially block the reuptake, so that the result is the same. This increase in dopamine levels in the synaptic space will generate pleasant and euphoric effects.
In the end, drugs physiologically cause the same effect as any natural reinforcer, as an accomplice talk with a great friend. The problem is that the intensity of its effect is much greater, so that the rest of natural reinforcers we end up "knowing a little" after trying the sensations that a drug produces. Hence its great attraction.
Some theories about dopamine and drugs
Some hypotheses that have emerged -even without many studies that support them- speak of a deficit in dopamine levels - either naturally or due to a lack of reinforcers, sources that produce pleasure or a sense of wellbeing - would predispose us to consumption of drugs.
In this way, by not getting enough dopamine release, the person could get to abuse those dopamine-releasing activities to achieve the same pleasant effects. However, we can not forget that, despite being starting to generate a good volume of research, this is a theory that still needs a lot of empirical support to consolidate it.
Mental disorders
As we had already announced at the beginning of the article, the use of drugs can be the trigger of a mental disorder. Be it transitory or permanent.
The DSM-V picks up substance intoxication itself and abstinence as a disorder in itself. However, there are other types of mental disorders induced by this type of substance. There are some that have a higher incidence than others, or that appear at specific times. The most characteristic are: psychotic, bipolar, depressive and anxiety disorders. All of them occur not only at the time of intoxication (the immediate effects of drugs), but also during abstinence. Even on occasion, some drugs can produce spectra of schizophrenia.
In this sense, psychotic disorders are characterized by an alteration in the cognitive functions of the brain, which can lead to a loss of intellectual abilities. These anomalies in the cognitive components are going to be of different types.

Alteration in perception
They are alterations that will affect the senses.
* Hallucinations: you see an object that does not really exist (eg spacecraft).
* Illusions: the object exists in reality, but is deformed (eg it is believed that a determined person, real, is the devil in disguise).
* Formications: also referred to as Eckbom syndrome. Imagination of animals running, like ants, through the body. The anguish that this causes leads the person to drastic decisions, such as taking them out in any way (eg, using knives, scissors, etc.).
Alteration in thought
We can divide them into two types
* In the course: loss of attention and associative capacity. The person who presents this dysfunction as a symptom is characterized by an inability to delimit the stimuli it receives. That is, when we are talking to a person, we are capturing various stimuli: other voices, a passing car, the lights of shops ... People without this condition are able to stick only to the information we want to transmit, however, a The person with this alteration will not only transmit what he / she wants to say, but will introduce in his speech the lights of the shops, the passing car and the voices of other passers-by.
* In the content: delirious ideas. They think things that are not real, giving them precisely the nature of reality. This thinking is within a framework of possible reality (that is, what is thought may actually happen, that is, the person may be convinced that his or her couple deceives him and it is true that this person has a partner, and that his partner has friends, but he does not cheat him in reality), but there is a disorganization of the content. It is totally illogical. (Eg people chase me, jealousy, etc.).
The drugs produce harmful effects in different levels or levels of the person, hence their effects are so devastating. Not only do they seriously damage the physical state of the body, but also, as we have seen, can cause serious mental disorders or limitations.
The treatment for these people must be individualized, according to the specific pathology they suffer and attending to the social, environmental and psychobiological circumstances that have led them and maintain their consumption.
I invite you to see these articles
* the-best-revenge-is-not-revenge *
* a-break-is-not-a-failure *
* friendship-the-family-that-one-chooses *
* Prayers, rituals and prohibitions on Valentine's Day *
* How stress affects negotiations *
* Why do Orientals see pressure as an enemy *
* The pressure of the 30: can we talk about crisis? *
* What to do when love is over? *
* Life lessons by joelgonz1982 *
All the images were taken from the public domain
Thanks for taking 5 minutes of your time to read this post
I'm waiting for your visit for the next time

