
Repository
https://github.com/flutter/flutter
What Will I Learn?
- You will learn how to use Cloud Firestore on Flutter
- You will learn how to implement Create, Read, Update and Delete commands with Firestore
- You will learn how Streambuilders can reactively change the UI of stateless widgets
- You will learn how to properly implement firestore and firebase transactions
- You will learn how to avoid race conditions with Firestore
Requirements
System Requirements:
- IDEA intellij, Visual Studio Code with the Dart/Flutter Plugins, Android Studio or Xcode
- The Flutter SDK on the latest Master Build
- An Android or iOS Emulator or device for testing
OS Support for Flutter:
- Windows 7 SP1 or later (64-bit)
- macOS (64-bit)
- Linux (64-bit)
Required Knowledge
- A little understanding of key/value stores
- A fair understanding of Mobile development and Imperative or Object Oriented Programming
- Some understanding of realtime databases
Resources for Flutter and this Project:
- Flutter Website: https://flutter.io/
- Flutter Official Documentation: https://flutter.io/docs/
- Flutter Installation Information: https://flutter.io/get-started/install/
- Flutter GitHub repository: https://github.com/flutter/flutter
- Flutter Dart 2 Preview Information: https://github.com/flutter/flutter/wiki/Trying-the-preview-of-Dart-2-in-Flutter
- Flutter Technical Overview: https://flutter.io/technical-overview/
- Dart Website: https://www.dartlang.org/
- Flutter Awesome GitHub Repository: https://github.com/Solido/awesome-flutter
Sources:
Flutter Logo (Google): https://flutter.io/
Difficulty
- Intermediate
Description
Outline and Overview
In this Flutter Tutorial Video, we build out a simple application using Cloud Firestore. The application allows the user to use Create, Read, Update and Delete (CRUD) on the pieces of data that we created. The data has a string title and an integer score. It also has a boolean value attached to it to signify when the user is editing a piece of data. The user can tap a list tile to open up a text editing field which allows them to write a new title into the field. They can also tap on various buttons to increment and decrement the score. There is a button at the top of the screen which is used to create new documents and a trash can button on the far right which deletes specific documents.
Outline for this Tutorial
Item 1: Setting Up and Using Cloud Firestore
Setting up Cloud Firestore for Flutter is almost identical to setting up Firebase. You go to the firebase console, create a new application, setup a Android and iOS project and then add the appropriate files to your Android and iOS folders. To properly setup Firestore from here, you go to the database tab and click on the firestore beta button which gives you a firestore database rather then a firebase database.
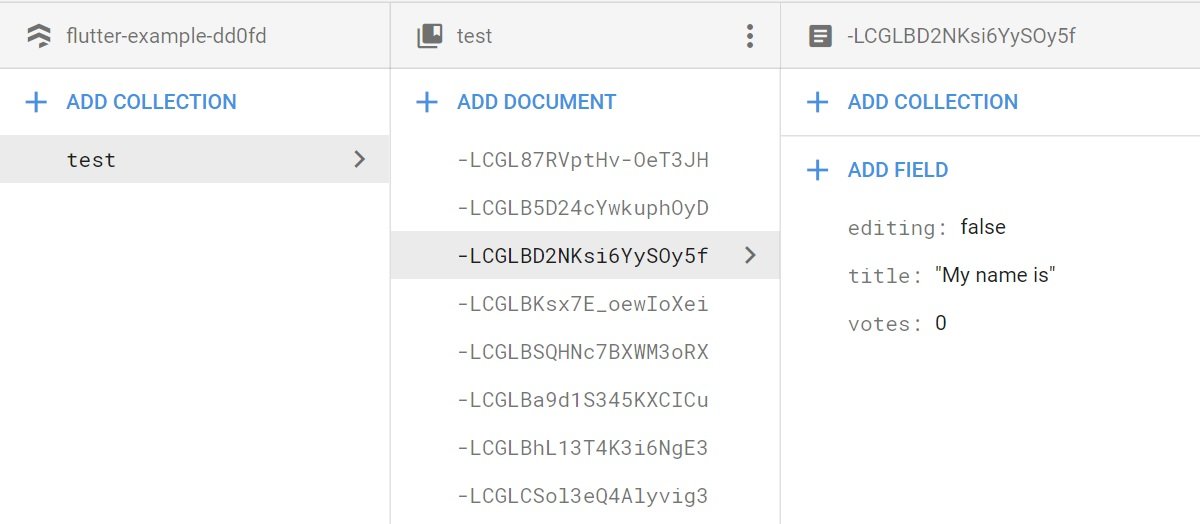
In this image you can see an example of the firestore database layout. On the top layer you have a database which contains a set of collections. Each collection contains a set of documents. These documents contain the data in key-value pairs that are similar to JSON. This type of layout has its advantages when compared to the Firebase JSON data layout. With firestore we have better querying and searching for data. Also, the database is much more suited for scaling. Most importantly, firestore is more secure then Firebase.
Item 2: CRUD in Firestore
The FlutterFire GitHub repositories have evolved quite a bit since we looked at Firebase. Now instead of having to instantiate a new firebase or firestore application using the firebase core library, we can directly reference the firestore or firebase object inside of our application and use it to preform transactions. We do not however, want to do this directly with firestore however, because it can potentially cause race conditions. If two users try to access a piece of data at the same time, then the data can get mangled and it can cause errors if we are accessing the database directly. This is why we use references and transactions to preform the various CRUD operations on our data.
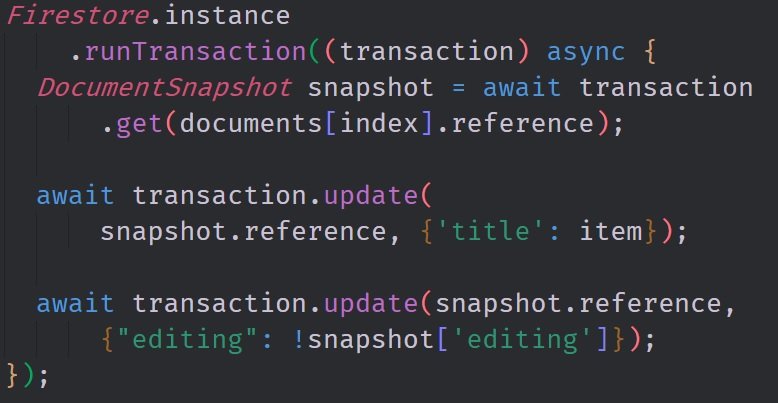
Here you can see one of the transactions that we preform in this application. This transaction is what allows us to change the title's value and also close the editing window once the value has changed. You can see that we use a method called runTranscation which allows us to use a asynchronous callback. This asynchronous callback is crucial for avoiding race conditions. Inside of it we create a Datasnapshot of the database object that we want. We are then able to reference this object to make editing the fields of the database much easier.
Item 3: Using Builders to Update the Interface in Stateless Widgets
In this application we have no StatefulWdigets nor do we call the setState method. We can get away with this because we are using builder functions to create most of the widget tree. More specifically, we make use of the StreamBuilder and the ListView Builders to generate and update the User Interface of this application as the data changes in our database. Firestore lets use access the data in a stream format and we can use this abstraction to our advantage to make our application reactive.
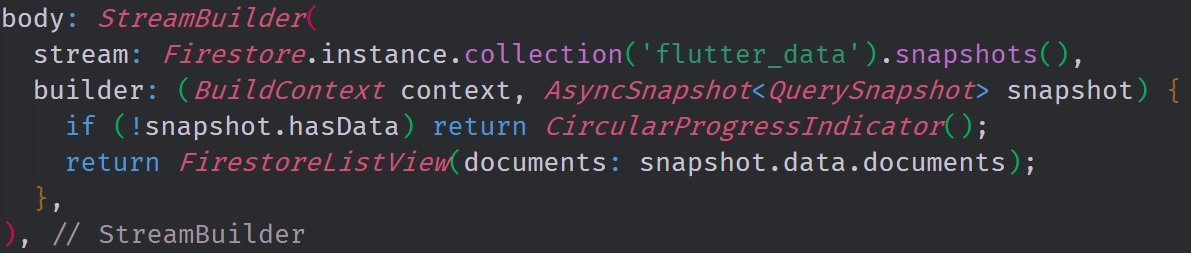
In this image you can see the StreamBuilder Widget which is the heart of the application. The stream that we are inserting into it is the Firestore.instance.collection('flutter_data').snapshots() stream which grabs the event cycle of our firestore database's flutter_data collection and lets us generate asynchronous snapshots from it. Every time a piece of data is sent into our stream builder the widget tree below it is rebuilt according to the builder callback function.
The source code for this project can be found here
Video Tutorial
Projects and Series
Stand Alone Projects:
- Dart Flutter Cross Platform Chat Application Tutorial
- Building a Temperature Conversion Application using Dart's Flutter Framework
- Managing State with Flutter Flux and Building a Crypto Tracker Application with Dart's Flutter Framework
Building a Calculator
- Building a Calculator Layout using Dart's Flutter Framework
- Finishing our Calculator Application with Dart's Flutter Framework
Movie Searcher Application
- Building a Movie Searcher with RxDart and SQLite in Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 1)
- Building a Movie Searcher with RxDart and SQLite in Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 2)
- Building a Movie Searcher with RxDart and SQLite in Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 3, Final)
Minesweeper Game
- Building a Mine Sweeper Game using Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 1)
- Building a Mine Sweeper Game using Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 2)
- Building a Mine Sweeper Game using Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 3)
- Building a Mine Sweeper Game using Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 4, Final)
Weather Application
- Building a Weather Application with Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 1, Handling Complex JSON with Built Code Generation)
- Building a Weather Application with Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 2, Creating a Repository and Model)
- Building a Weather Application with Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 3, RxCommand (RxDart) and Adding an Inherited Widget)
- Building a Weather Application with Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 4, Using RxWidget to Build a Reactive User Interface)
- Localize and Internationalize Applications with Intl and the Flutter SDK in Dart's Flutter Framework
Curriculum
- Building a Multi-Page Application with Dart's Flutter Mobile Framework
- Making Http requests and Using Json in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building Dynamic Lists with Streams in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Using GridView, Tabs, and Steppers in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Using Global Keys to get State and Validate Input in Dart's Flutter Framework
- The Basics of Animation with Dart's Flutter Framework
- Advanced Physics Based Animations in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building a Drag and Drop Application with Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building a Hero Animation and an Application Drawer in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Using Inherited Widgets and Gesture Detectors in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Using Gradients, Fractional Offsets, Page Views and Other Widgets in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Making use of Shared Preferences, Flex Widgets and Dismissibles with Dart's Flutter framework
- Using the Different Style Widgets and Properties in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Composing Animations and Chaining Animations in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building a Countdown Timer with a Custom Painter and Animations in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Reading and Writing Data and Files with Path Provider using Dart's Flutter Framework
- Exploring Webviews and the Url Launcher Plugin in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Adding a Real-time Database to a Flutter application with Firebase
- Building a List in Redux with Dart's Flutter Framework
- Managing State with the Scoped Model Pattern in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Authenticating Guest Users for Firebase using Dart's Flutter Framework
- How to Monetize Your Flutter Applications Using Admob
- Using Geolocator to Communicate with the GPS and Build a Map in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Managing the App Life Cycle and the Screen Orientation in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Making use of General Utility Libraries for Dart's Flutter Framework
- Interfacing with Websockets and Streams in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Playing Local, Network and YouTube Videos with the Video Player Plugin in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building Custom Scroll Physics and Simulations with Dart's Flutter Framework
- Making Dynamic Layouts with Slivers in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building a Sketch Application by using Custom Painters in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Using Dart Isolates, Dependency Injection and Future Builders in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Looking at the Main Features of the Beta Three Release of Dart's Flutter Framework
- Working with Material Theme and Custom Fonts in Dart's Flutter Framework
