
Repository
https://github.com/flutter/flutter
What Will I Learn?
- You will learn the difference between Plugins and Packages in Flutter
- You will learn how to push data to the Android and iOS platforms
- You will learn how to have Android and iOS push data to Flutter
- You will learn about the MethodChannel and Platform Messages
- You will learn about Flutter's general API
Requirements
System Requirements:
- IDEA intellij, Visual Studio Code with the Dart/Flutter Plugins, Android Studio or Xcode
- The Flutter SDK on the latest Master Build
- An Android or iOS Emulator or device for testing
OS Support for Flutter:
- Windows 7 SP1 or later (64-bit)
- macOS (64-bit)
- Linux (64-bit)
Required Knowledge
- A little understanding of libraries and plugin systems.
- A fair understanding of Mobile development and Imperative or Object Oriented Programming
- Some understanding of APIs
Resources for Flutter and this Project:
- Flutter Website: https://flutter.io/
- Flutter Official Documentation: https://flutter.io/docs/
- Flutter Installation Information: https://flutter.io/get-started/install/
- Flutter GitHub repository: https://github.com/flutter/flutter
- Flutter Dart 2 Preview Information: https://github.com/flutter/flutter/wiki/Trying-the-preview-of-Dart-2-in-Flutter
- Flutter Technical Overview: https://flutter.io/technical-overview/
- Dart Website: https://www.dartlang.org/
- Flutter Awesome GitHub Repository: https://github.com/Solido/awesome-flutter
Sources:
Flutter Logo (Google): https://flutter.io/
Flutter Chart: https://flutter.io/
Difficulty
- Intermediate
Description
Outline and Overview
In this tutorial example we take a look at how we can interface with the host platforms by creating a simple plugin. We take a look at the boilerplate plugin that is generated when you run the basic command and we expand upon it by building out another getter. We also build out a small little timer feature that allows the android host platform to send messages to the Flutter View layer and increment an integer when the user pushes a button.
Outline for this Tutorial
Should I make a Plugin or a Package?
Packages are a good way of cutting down code reuse and you can use them to generalize abstractions and other concepts. Plugins on the other hand are what allows Flutter to be so flexible as a framework. The ability to interface with and access any of the native APIs that are built into iOS and/or Android is very powerful.
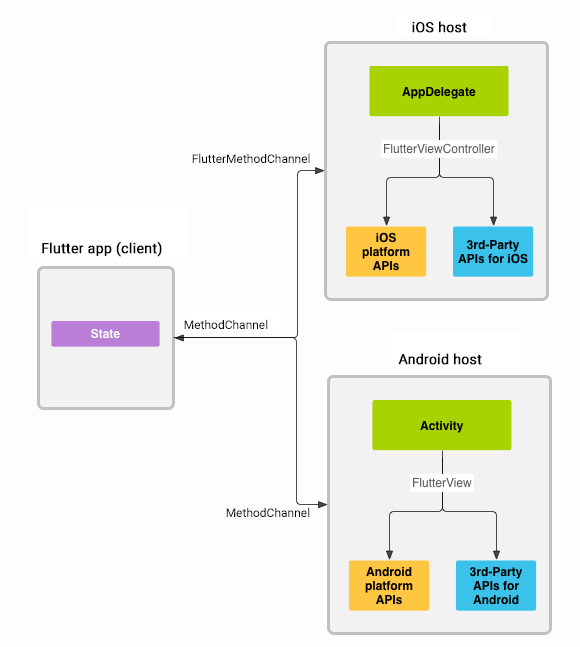
The chart above details the basic layout and pattern of a flutter plugin. By using flutter Method Channels and Platform Messages, not only can flutter gain access to native APIs; it can also access 3rd party APIs as well. This makes flutter a very robust framework which is easy to build in and still full of features.
Pushing and Pulling Data
Flutter is a fully featured layer that is built on top of other platforms. As such it need to have methods of pushing and pulling data to and from those platforms to optimize its abilities to leverage those platforms. Flutter accomplishes this by using MethodChannels and PlatformMessages. Flutter plugins register their method channels on both the Flutter layer and the host layer which allows for the passing of platform messages.
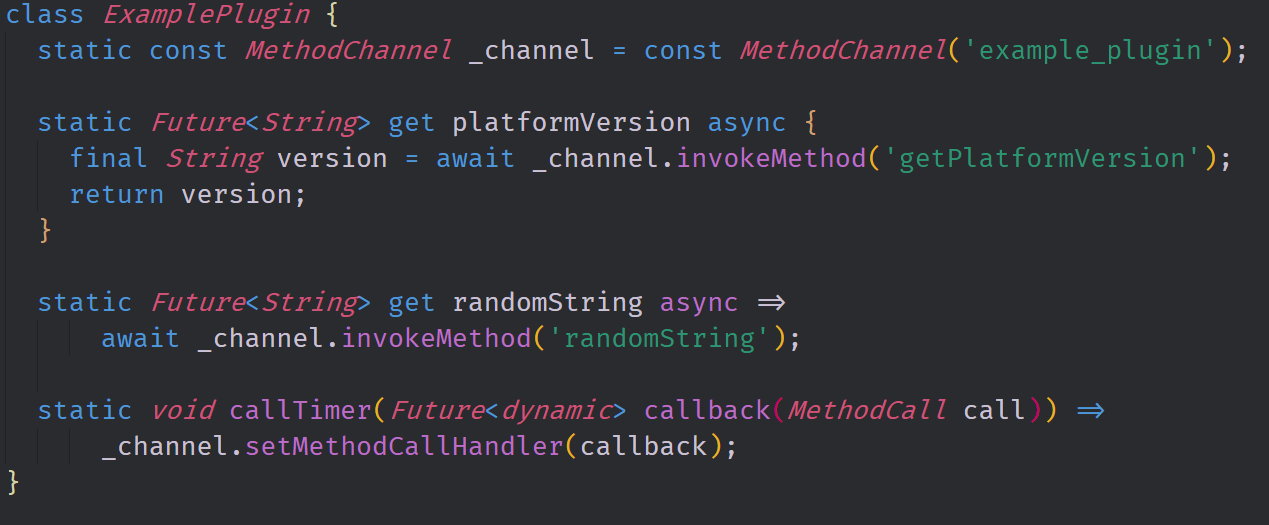
In the flutter side of our plugin, we have two getter methods and one "setter" method. The getter methods return a Future with the data type that we want to get from the host platform. In this case, both of our getter methods return a String type. Our "setter" method allows us to execute a callback function which creates a method call. This method call is then executed on the platform which returns a message to the flutter layer. In this case, the message it returns contains an argument that is an integer type.
Building an API on the Platform
Each platform has a very platform neutral way of communicating with Flutter. This is achievable because of the way that Flutter is structured. A string representation of the Method that we want to call is pass along the MethodChannel down to the platform. Once the platform receives this string message; it executes the appropriate method and then returns a new string with the resulting data. In some cases, the data is empty and in others it can be fairly large.
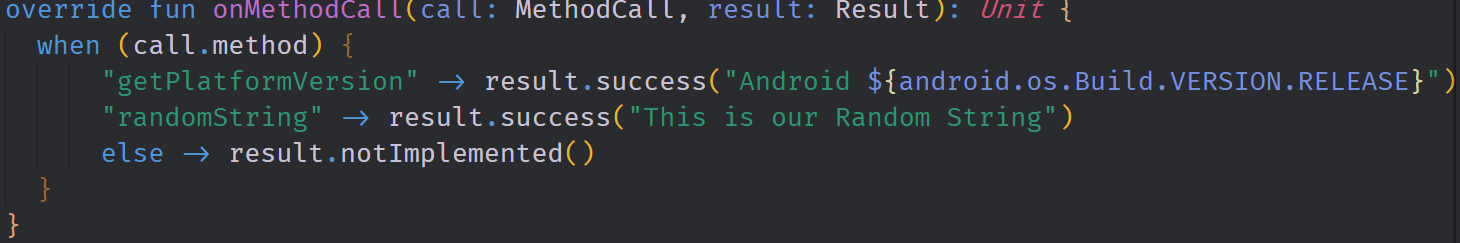
The Kotlin code used to communicate with Android is simple and makes use of the when operator to pattern match on the string method that is being sent through the MessageChannel. This makes the logic of the API between the Flutter view layer and the platform fairly easy to read and deal with. We are able to create fairly complex methods and attach them to these strings. Also, most of the types included in the platforms are able to be passed back to the Flutter Layer through a conversion.
The source code for this project can be found here
Information on the platform specific types can be found here
Video Tutorial
Projects and Series
Stand Alone Projects:
- Dart Flutter Cross Platform Chat Application Tutorial
- Building a Temperature Conversion Application using Dart's Flutter Framework
- Managing State with Flutter Flux and Building a Crypto Tracker Application with Dart's Flutter Framework
Building a Calculator
- Building a Calculator Layout using Dart's Flutter Framework
- Finishing our Calculator Application with Dart's Flutter Framework
Movie Searcher Application
- Building a Movie Searcher with RxDart and SQLite in Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 1)
- Building a Movie Searcher with RxDart and SQLite in Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 2)
- Building a Movie Searcher with RxDart and SQLite in Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 3, Final)
Minesweeper Game
- Building a Mine Sweeper Game using Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 1)
- Building a Mine Sweeper Game using Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 2)
- Building a Mine Sweeper Game using Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 3)
- Building a Mine Sweeper Game using Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 4, Final)
Weather Application
- Building a Weather Application with Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 1, Handling Complex JSON with Built Code Generation)
- Building a Weather Application with Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 2, Creating a Repository and Model)
- Building a Weather Application with Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 3, RxCommand (RxDart) and Adding an Inherited Widget)
- Building a Weather Application with Dart's Flutter Framework (Part 4, Using RxWidget to Build a Reactive User Interface)
- Localize and Internationalize Applications with Intl and the Flutter SDK in Dart's Flutter Framework
Curriculum
- Building a Multi-Page Application with Dart's Flutter Mobile Framework
- Making Http requests and Using Json in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building Dynamic Lists with Streams in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Using GridView, Tabs, and Steppers in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Using Global Keys to get State and Validate Input in Dart's Flutter Framework
- The Basics of Animation with Dart's Flutter Framework
- Advanced Physics Based Animations in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building a Drag and Drop Application with Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building a Hero Animation and an Application Drawer in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Using Inherited Widgets and Gesture Detectors in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Using Gradients, Fractional Offsets, Page Views and Other Widgets in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Making use of Shared Preferences, Flex Widgets and Dismissibles with Dart's Flutter framework
- Using the Different Style Widgets and Properties in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Composing Animations and Chaining Animations in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building a Countdown Timer with a Custom Painter and Animations in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Reading and Writing Data and Files with Path Provider using Dart's Flutter Framework
- Exploring Webviews and the Url Launcher Plugin in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Adding a Real-time Database to a Flutter application with Firebase
- Building a List in Redux with Dart's Flutter Framework
- Managing State with the Scoped Model Pattern in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Authenticating Guest Users for Firebase using Dart's Flutter Framework
- How to Monetize Your Flutter Applications Using Admob
- Using Geolocator to Communicate with the GPS and Build a Map in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Managing the App Life Cycle and the Screen Orientation in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Making use of General Utility Libraries for Dart's Flutter Framework
- Interfacing with Websockets and Streams in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Playing Local, Network and YouTube Videos with the Video Player Plugin in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building Custom Scroll Physics and Simulations with Dart's Flutter Framework
- Making Dynamic Layouts with Slivers in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building a Sketch Application by using Custom Painters in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Using Dart Isolates, Dependency Injection and Future Builders in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Looking at the Main Features of the Beta Three Release of Dart's Flutter Framework
- Working with Material Theme and Custom Fonts in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Using Cloud Firestore as a Realtime Datastore for CRUD with Dart's Flutter Framework
- Authenticating Users with Google Sign In and Firebase\Firestore inside of Dart's Flutter Framework
- Using the Elm Architecture or the MVU pattern with Dartea inside of Dart's Flutter Framework
- Using the BloC Pattern to Build Reactive Applications with Streams in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building Immutable Models with Built Value and Built Collection in Dart's Flutter Framework
- Building Pure Dart Libraries and Packages for Dart's Flutter Framework
